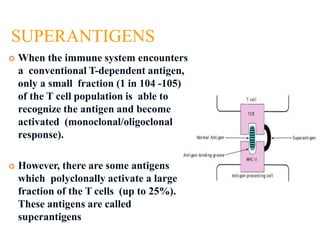
This document discusses antigens and their properties. It defines an antigen as a substance that generates an immune response through antibodies or T cells. Antigens have epitopes that bind to immune cells. Examples of antigens include autoantigens from one's own body, alloantigens from the same species, and heterophile antigens found across species. The document also examines the chemical nature of antigens as mostly proteins and polysaccharides, and properties such as size, degradability, and dose that influence antigenicity. Superantigens are described as antigens that can polyclonally activate a large fraction of T cells. Finally, some common tests for detecting antigens are listed.