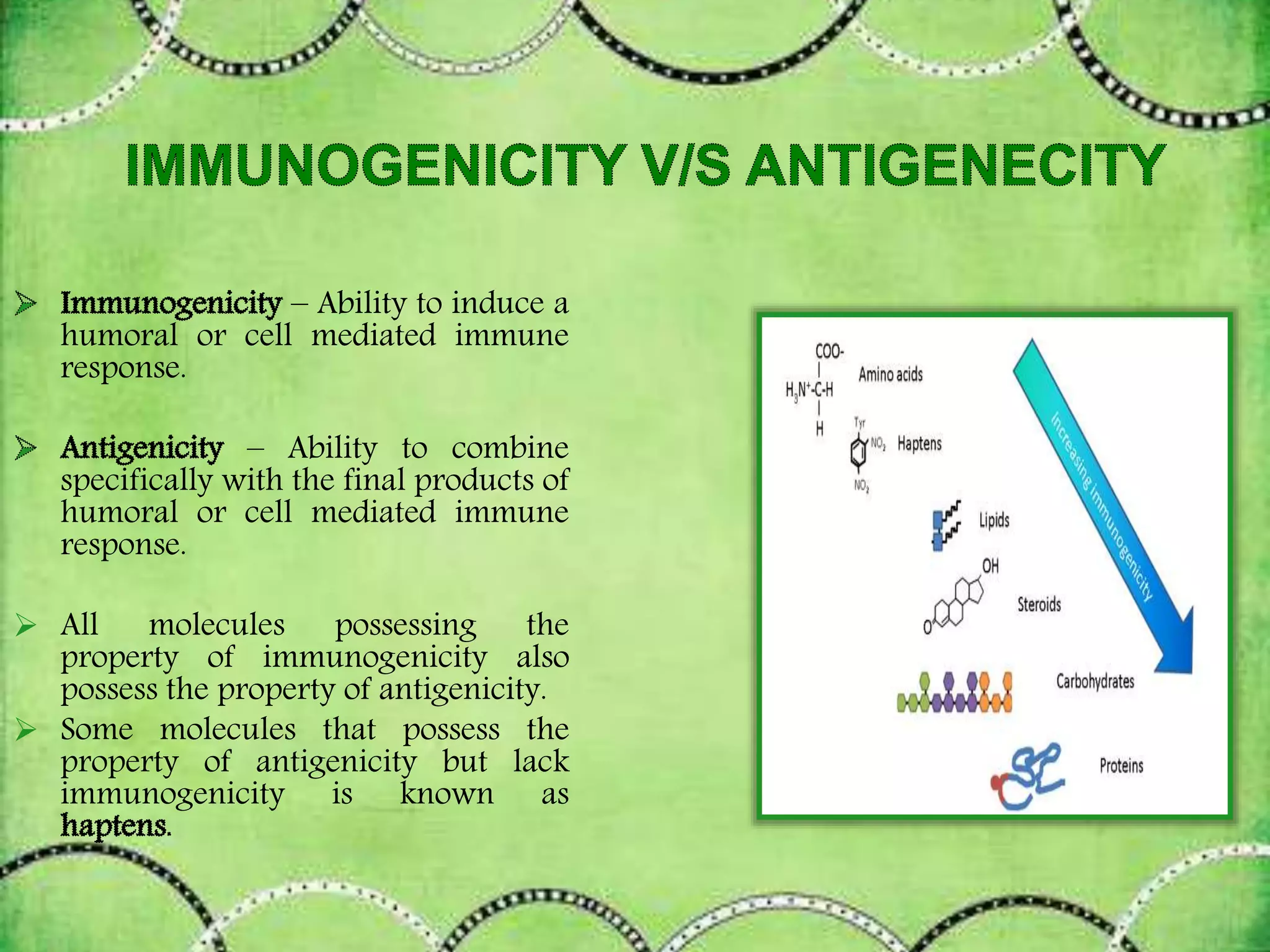
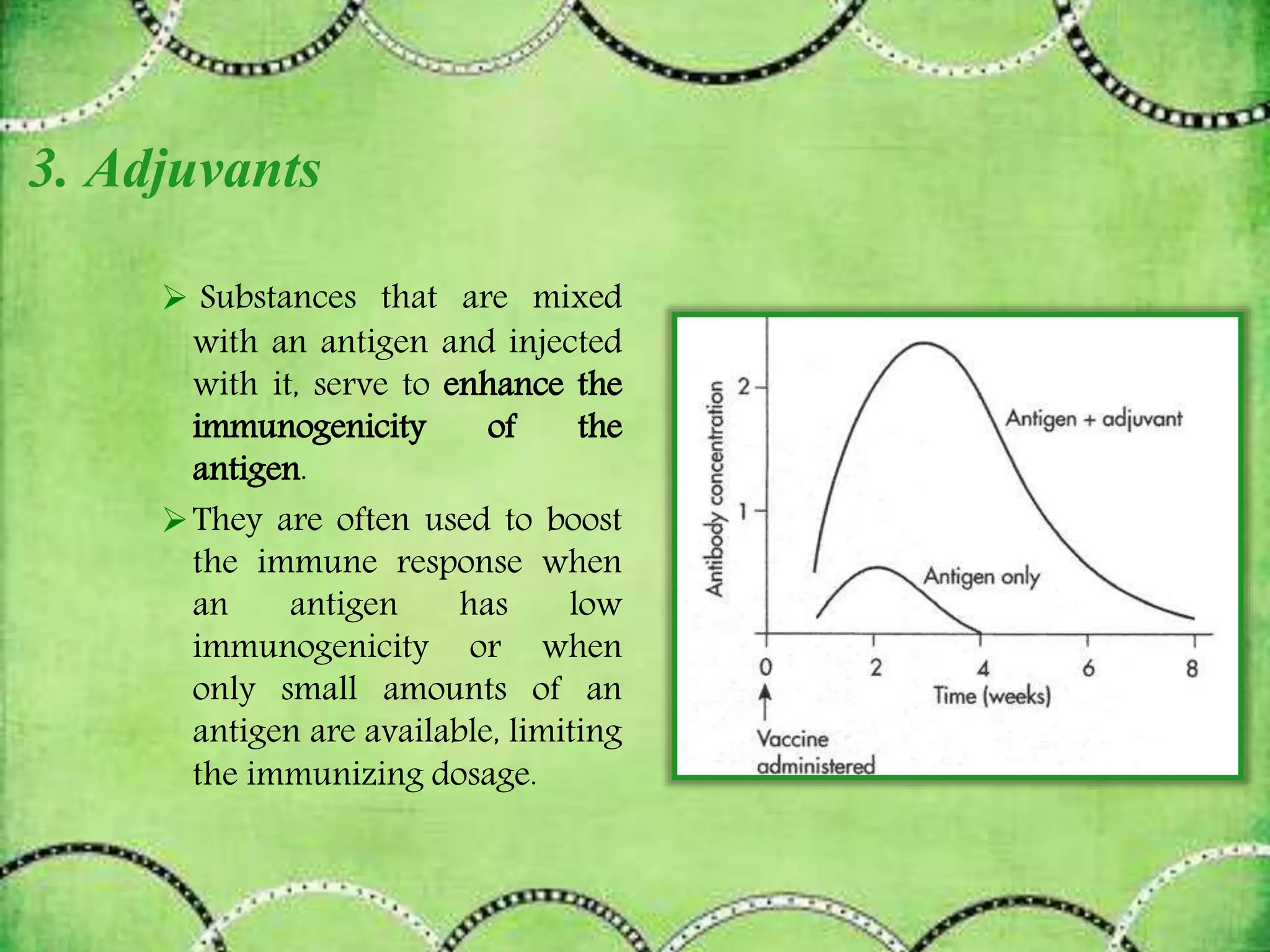
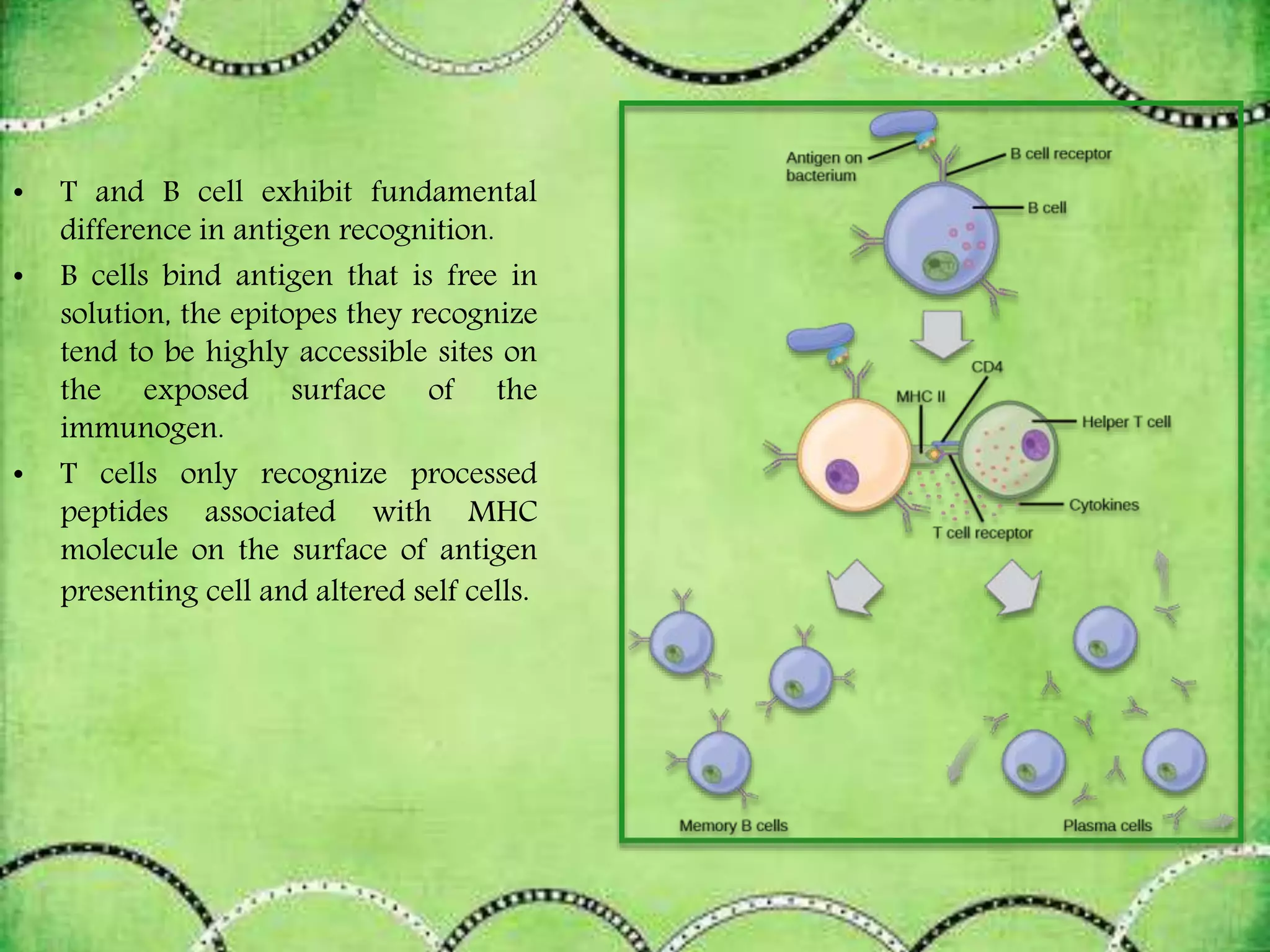
This document discusses antigens and their classification. It defines antigens as substances that can induce an immune response. Antigens are classified as either exogenous (external) or endogenous (internal) antigens. Exogenous antigens enter the body from the external environment, while endogenous antigens are further divided into xeno-genic, allogenic, and autologous antigens based on their origin. The document also discusses the properties of immunogens and antigens, as well as factors that contribute to immunogenicity.