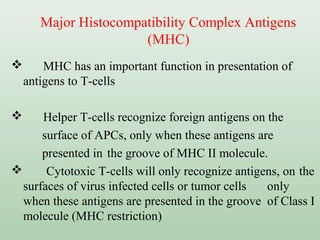
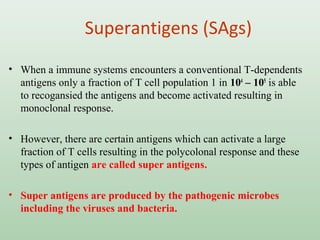
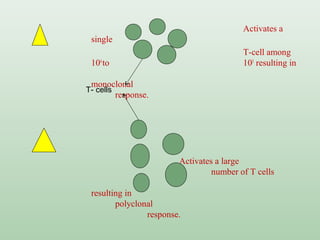
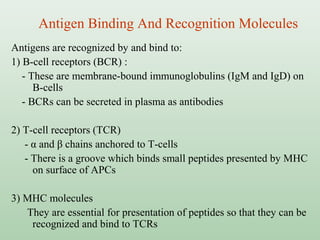
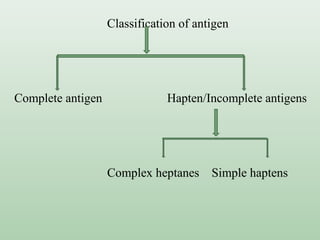
Immunogens or antigens are foreign substances that elicit an immune response when introduced to the body. They are recognized by antibodies or T-lymphocytes. Immunogens can induce antibody formation themselves, while haptens require a carrier molecule to produce an immune response. Antigens are presented on antigen-presenting cells and recognized by B and T cells, initiating humoral or cell-mediated immunity. Exogenous antigens from bacteria, viruses, and other external sources are phagocytosed and processed, while endogenous antigens from infection or autoimmunity are presented via MHC I molecules.






![ALONE CANNOT PRODUCE AN
IMMUNE RESPONSE
HaptensHaptens Carrier
molecule
s
HaptensHaptens Carrier
molecules
HAPTENS CARRIER MOLECULE
IS FORMED [LARGE MOLECULES]
RESULTING IN PRODUCTION OF
RESPONSE
Haptens](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antigen-180530082033/85/Antigen-8-320.jpg)