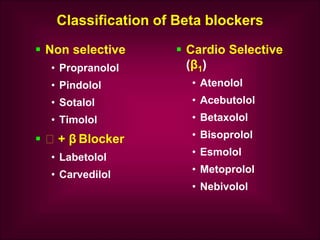
Beta blockers interact with adrenergic receptors to modify tissue activity, classified into non-selective, selective, with intrinsic sympathomimetic action, and those with membrane stabilizing properties. They are indicated for various cardiac and non-cardiac conditions, exerting effects such as reducing heart rate and blood pressure while potentially causing side effects like bradycardia and metabolic changes. Each beta blocker has distinct pharmacokinetics and profiles, influencing their therapeutic applications and adverse effects.