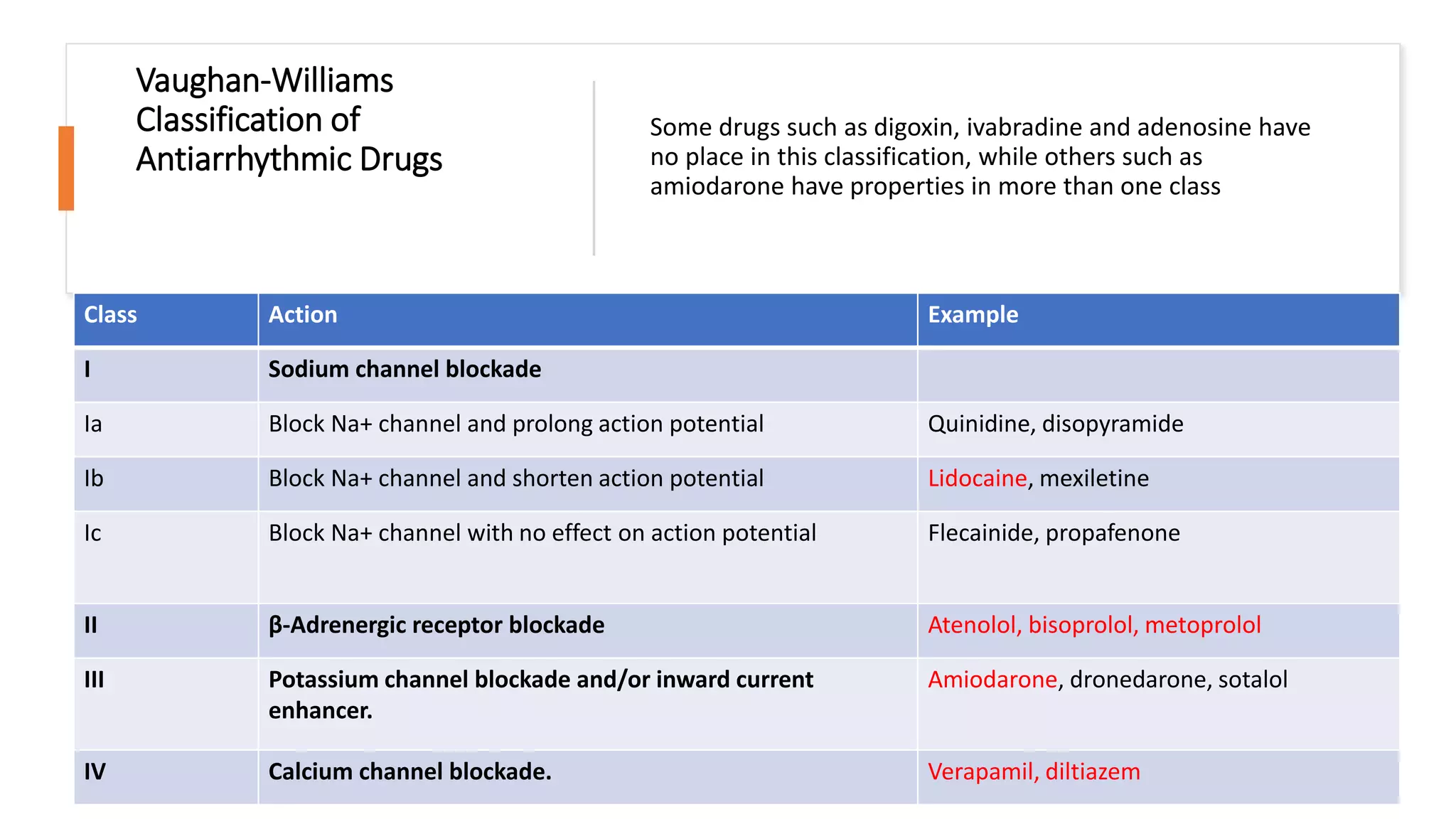
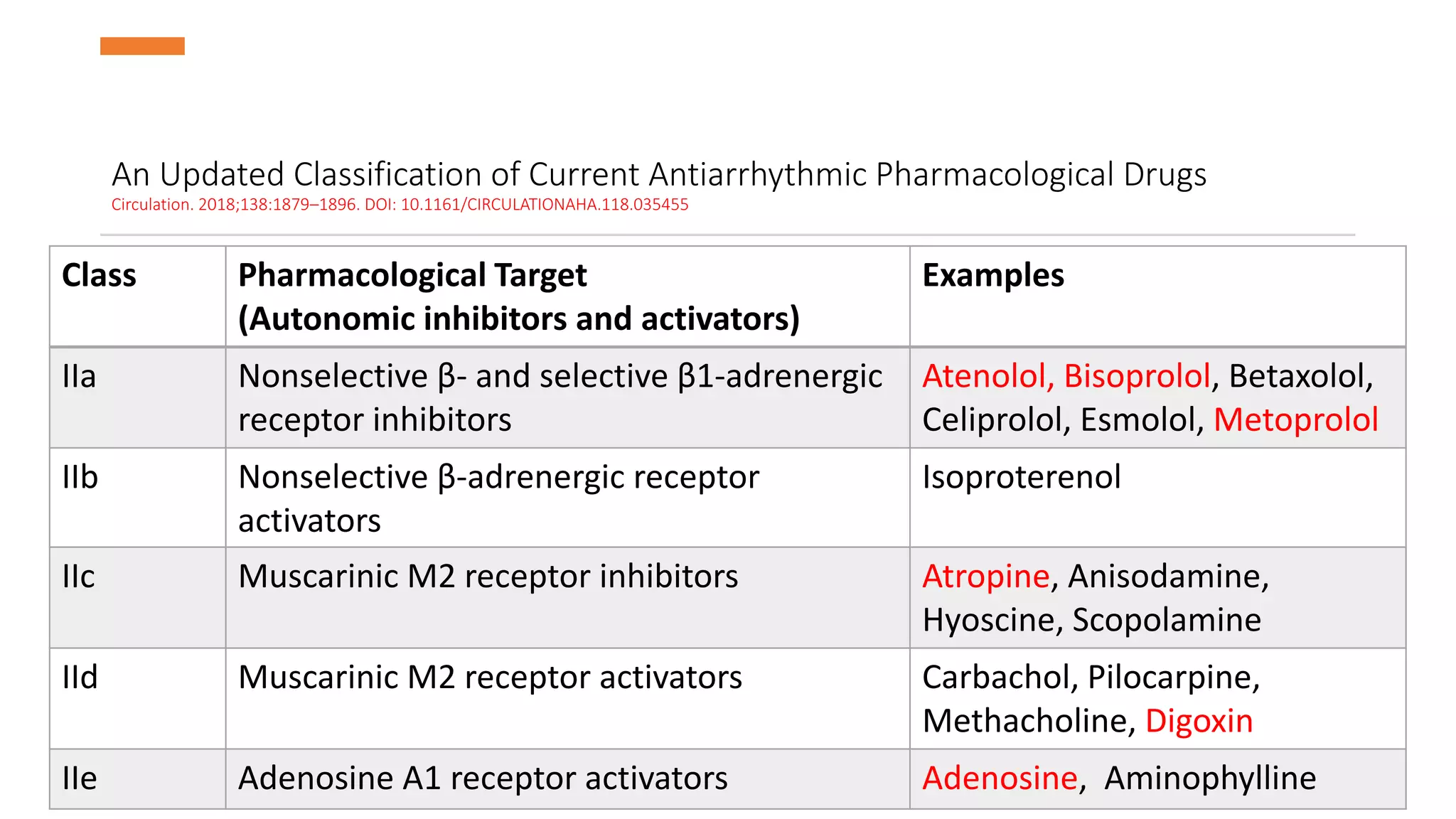
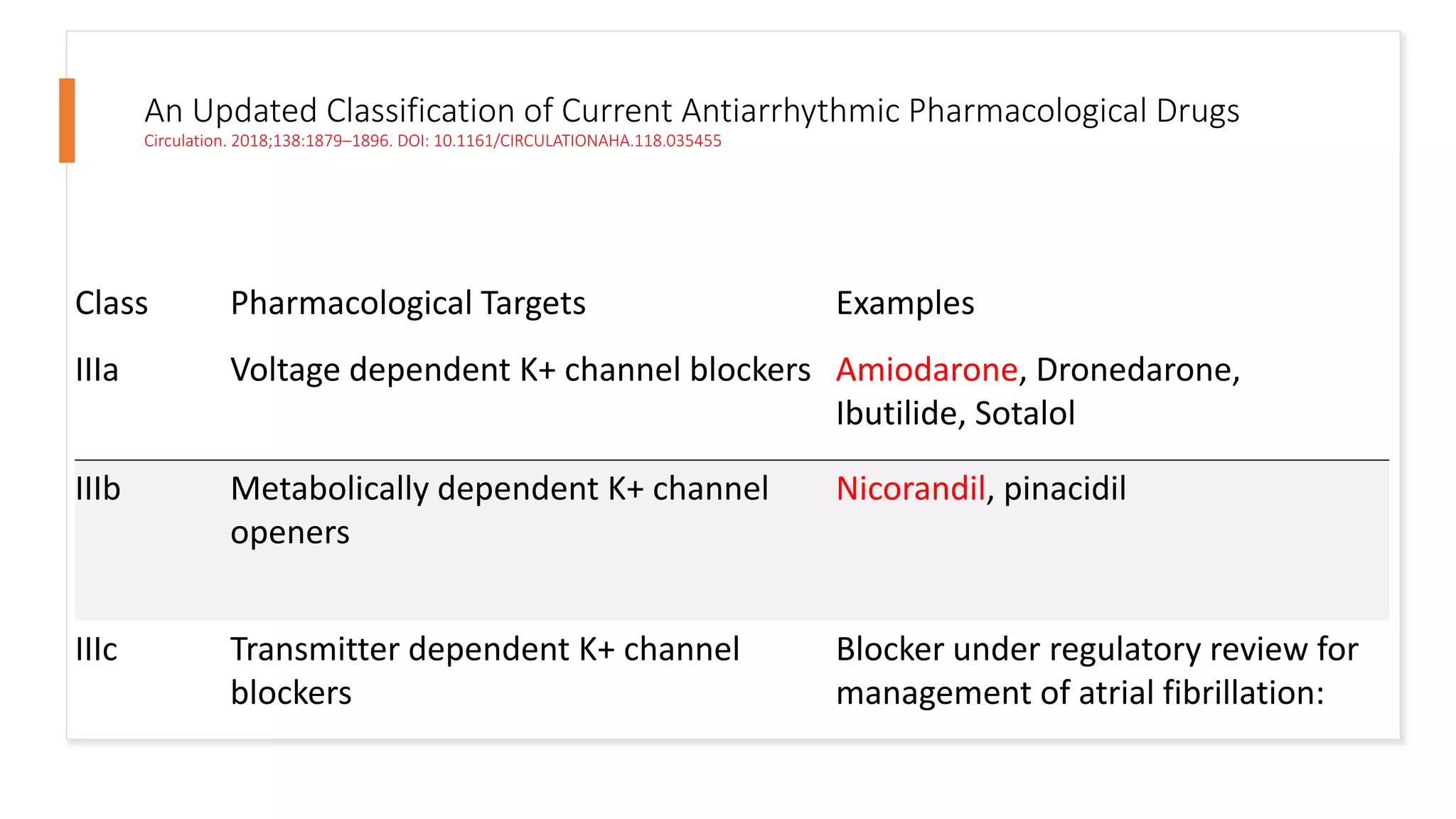
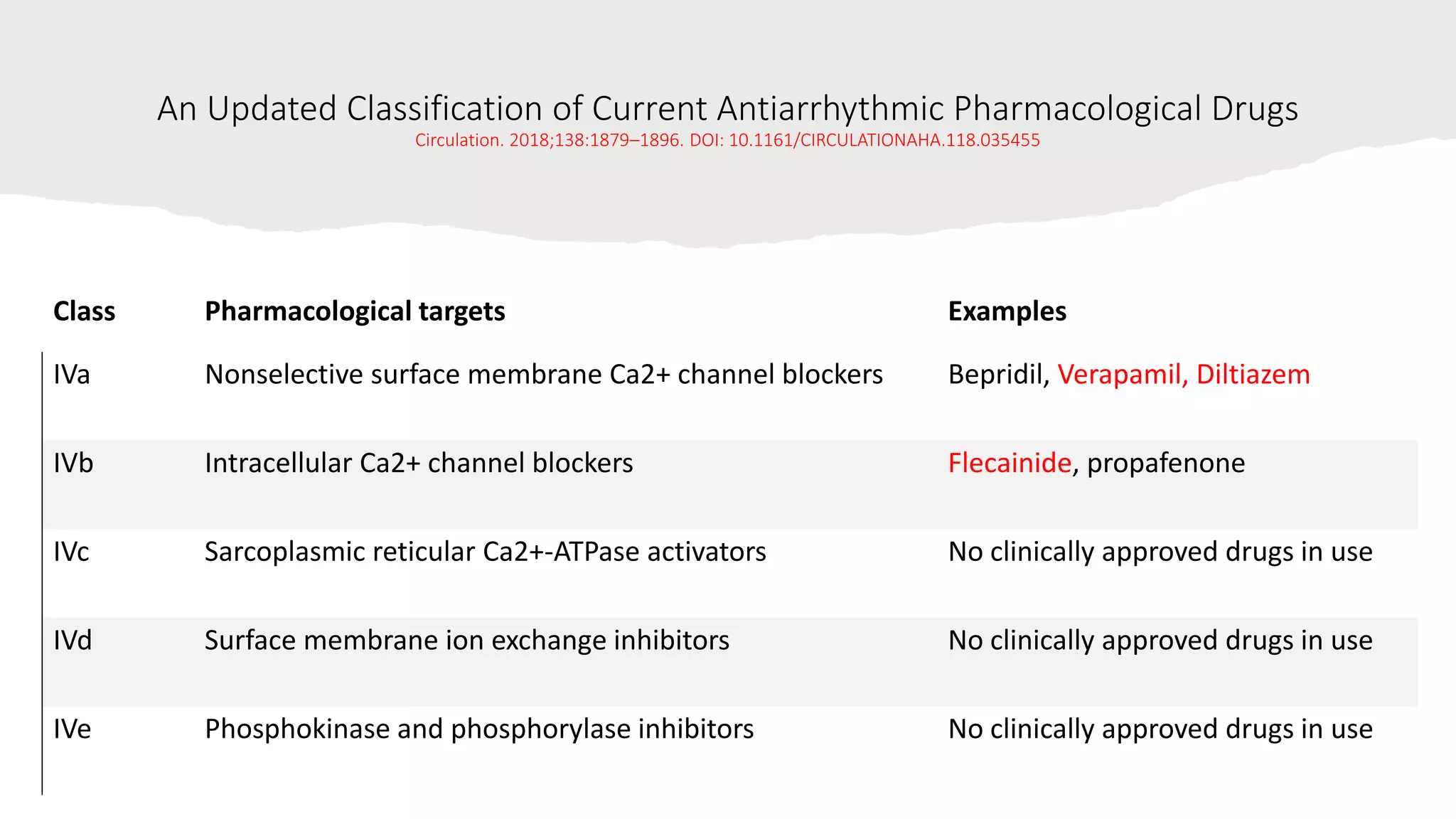
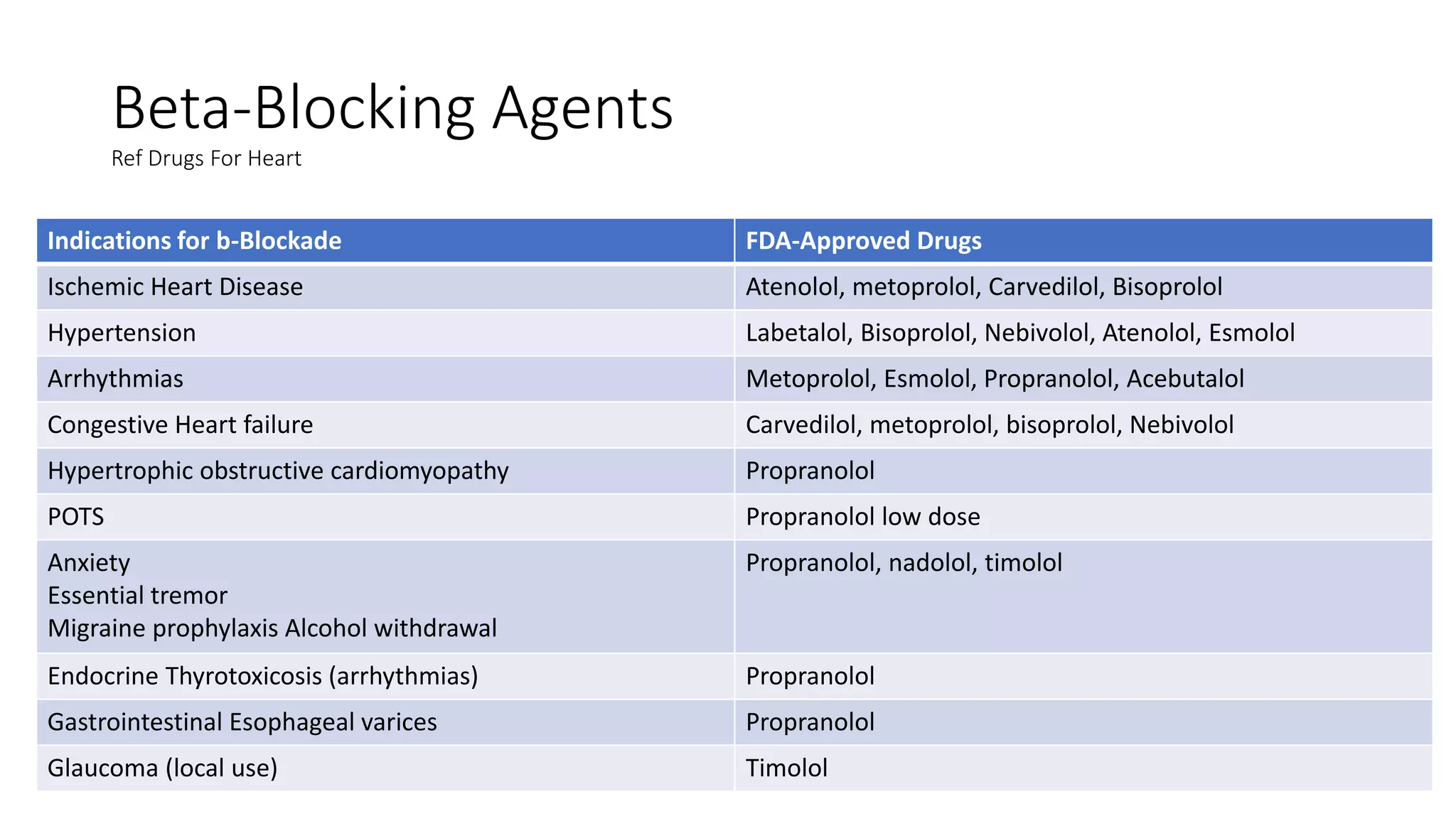
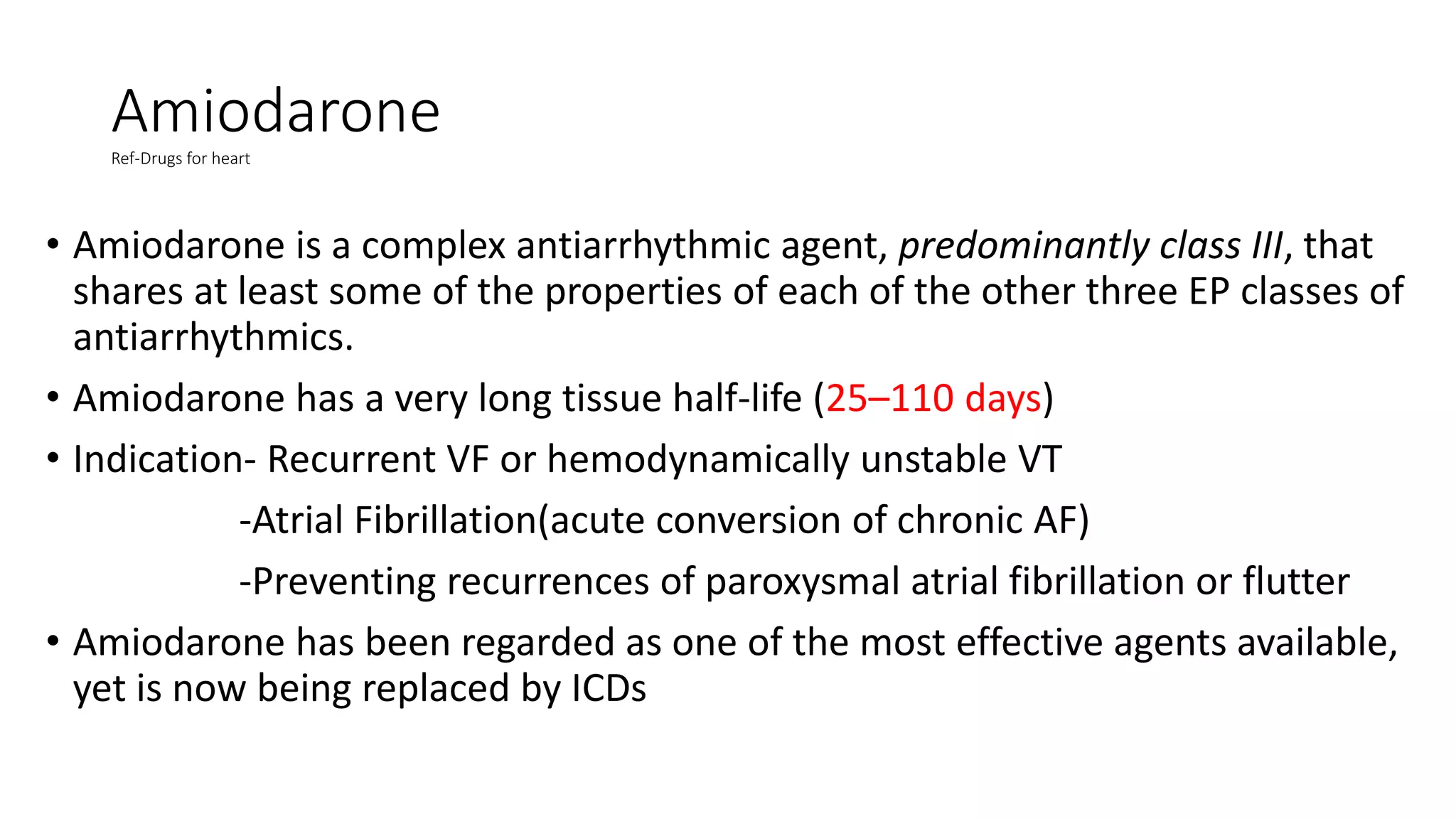
This document discusses antiarrhythmic drugs. It begins by defining arrhythmias as abnormal heartbeats that can be too slow, fast, irregular or early. It then discusses the sites in the heart where arrhythmias can originate, such as the sinus node or ventricles. The mechanisms of arrhythmia are described as automaticity, reentry, after depolarization or enhanced pacemaker activity. The document reviews the Vaughan-Williams classification system for antiarrhythmic drugs and provides examples of drugs from each class. It also discusses specific antiarrhythmic drugs like amiodarone, beta blockers, lidocaine, calcium channel blockers and more.