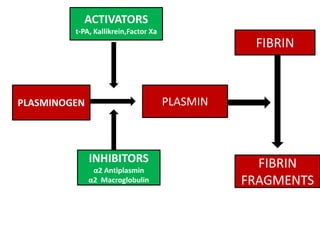
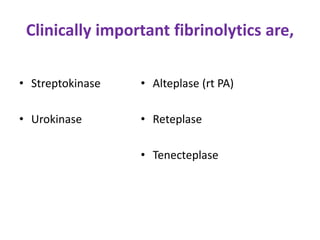
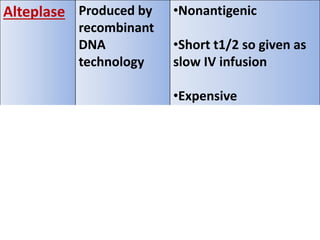
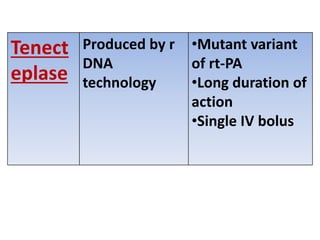
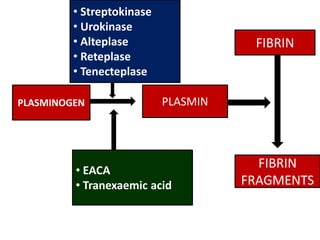
Fibrinolytics such as streptokinase, urokinase, alteplase, reteplase, and tenecteplase activate the natural fibrinolytic system and lyse thrombi to recanalize occluded blood vessels. They are used to treat myocardial infarction, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and peripheral arterial occlusion. Antifibrinolytics like epsilon amino-caproic acid and tranexamic acid inhibit plasminogen activation and clot dissolution to prevent or control bleeding caused by fibrinolytics or surgical procedures. The timing of fibrinolytic administration is critical for heart attack treatment, with better outcomes seen within 1-3 hours of symptom onset.