Embed presentation
Downloaded 210 times




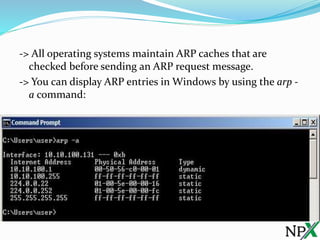

ARP is a protocol that maps IP addresses to MAC addresses. It works by broadcasting an ARP request packet to all devices on the local network segment. The device with the matching IP address responds with its MAC address, allowing the requesting device to send packets directly to the destination MAC address on the local network.




