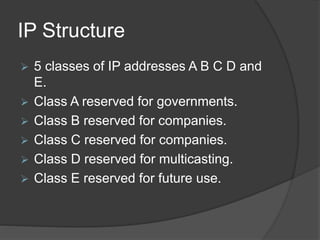
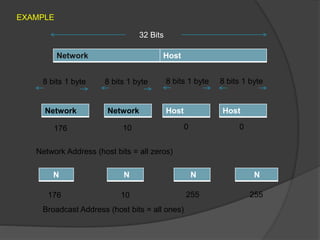
An IP address is a unique 32-bit number that identifies each device on a network. It allows devices to communicate by sending and receiving data packets. IP addresses are made up of a network portion and host portion, with four sections that each range from 0-255. There are five classes of IP addresses - A, B, C, D and E - that determine the number of networks and hosts. IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses written in dotted decimal notation, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses written in hex. IP addresses can be static or dynamically assigned by a DHCP server.