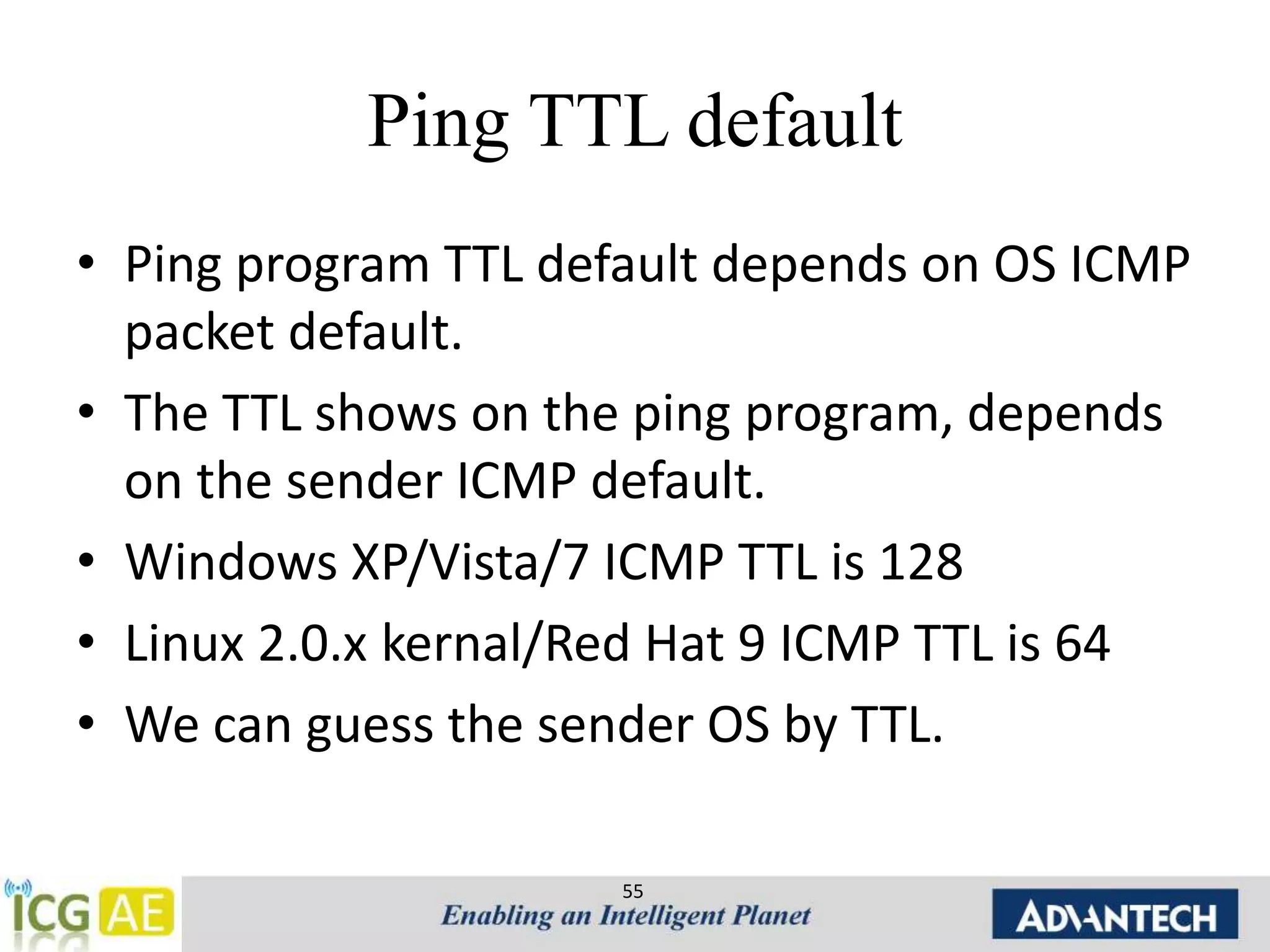
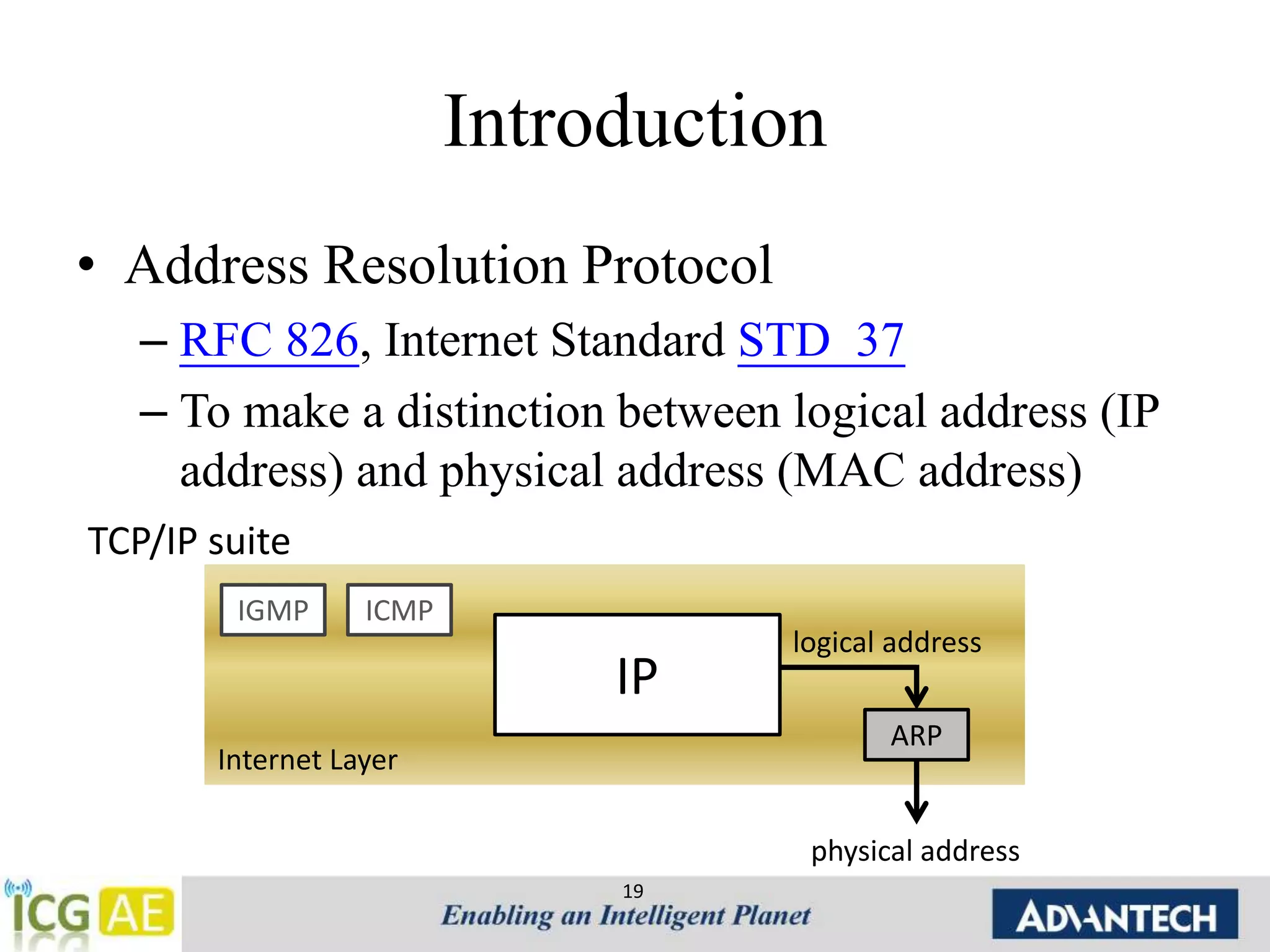
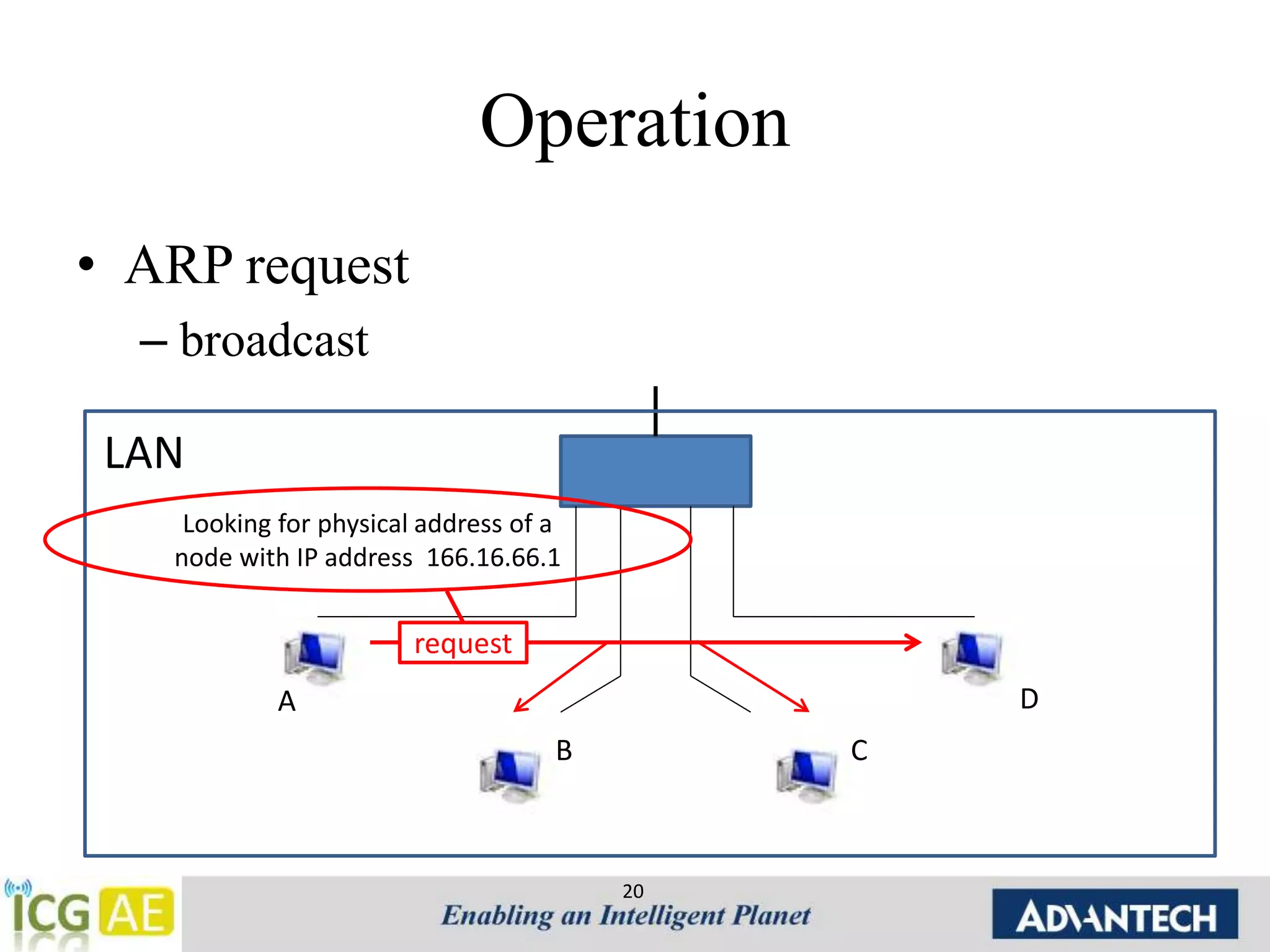
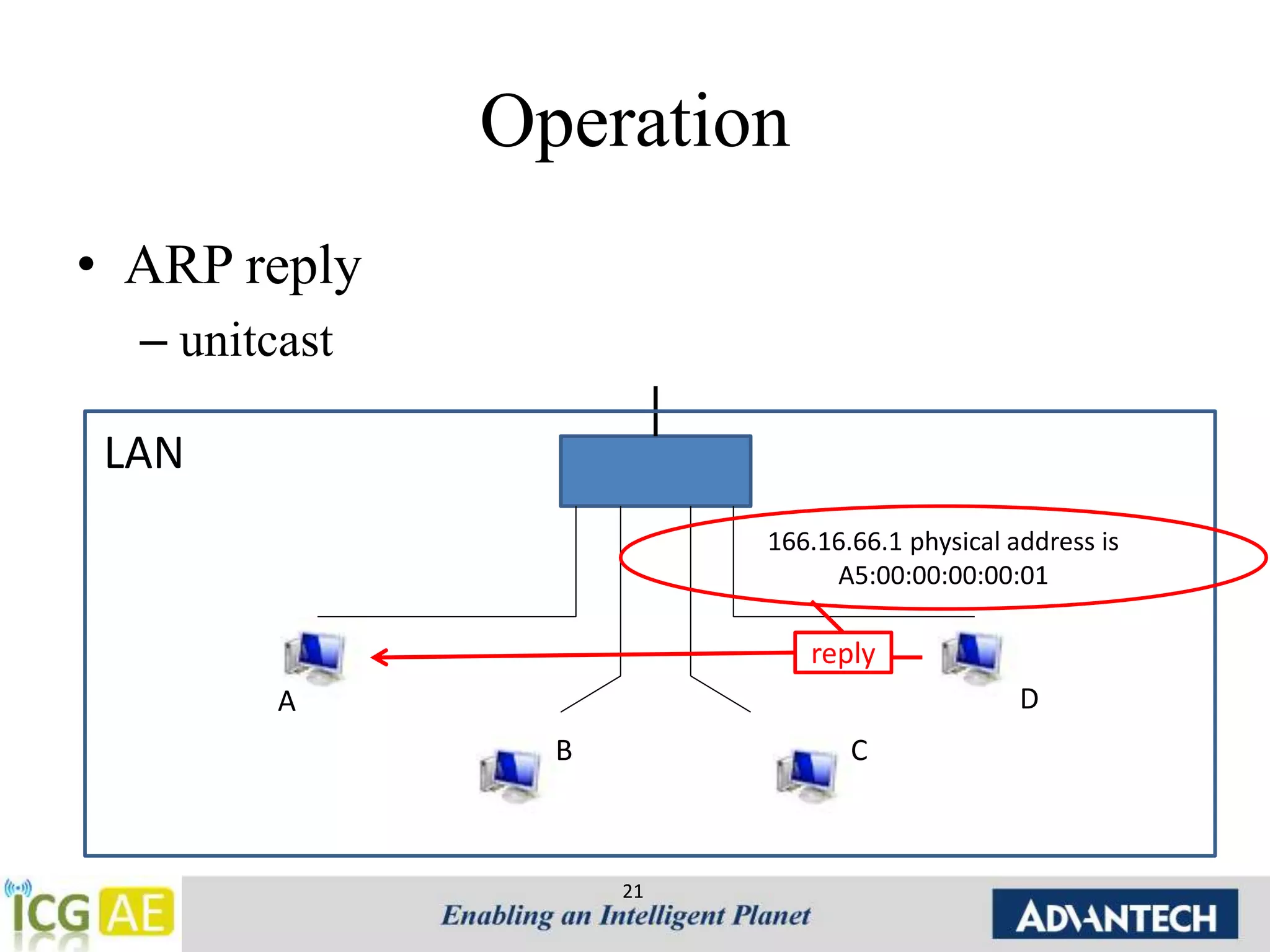
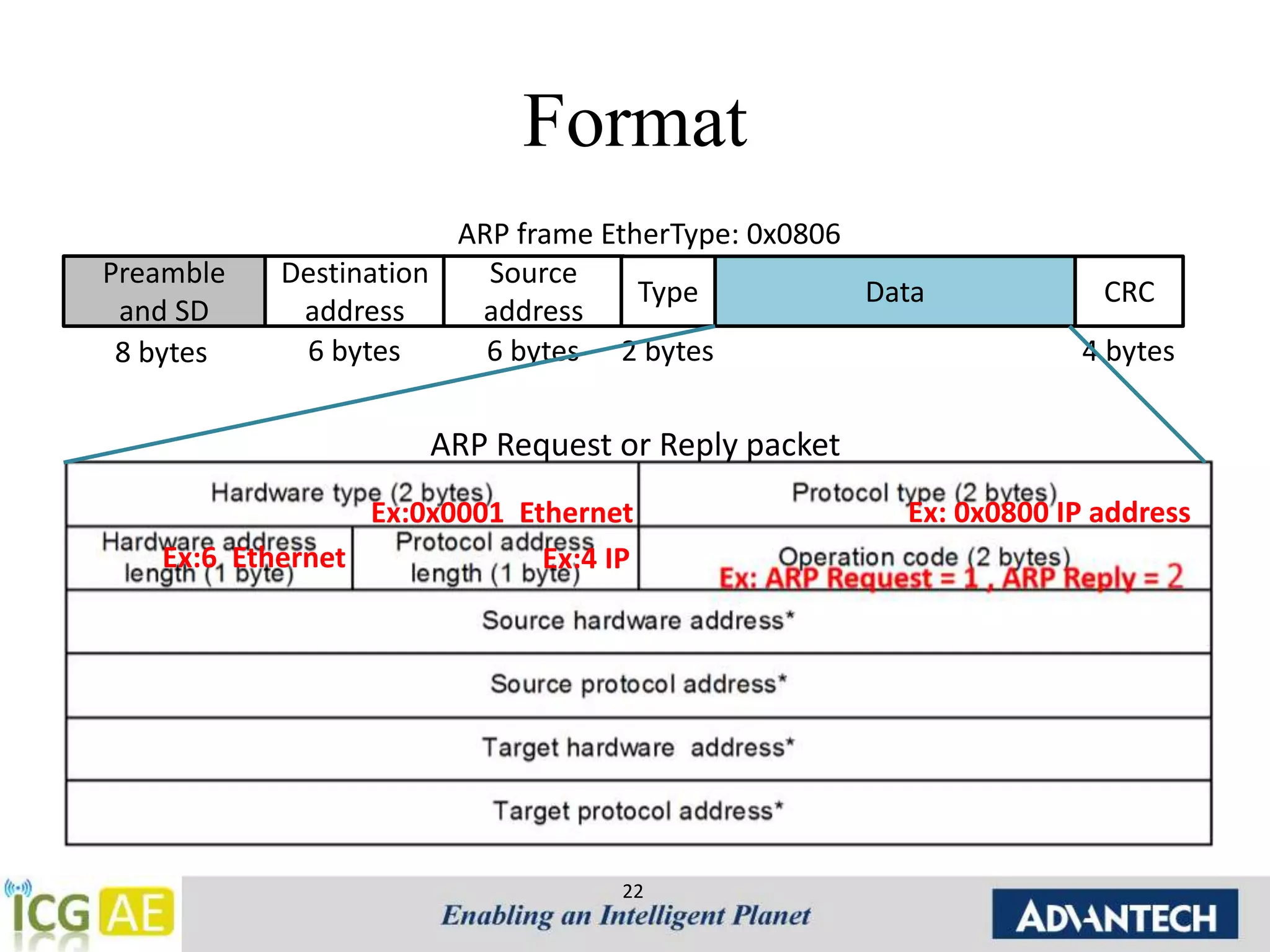
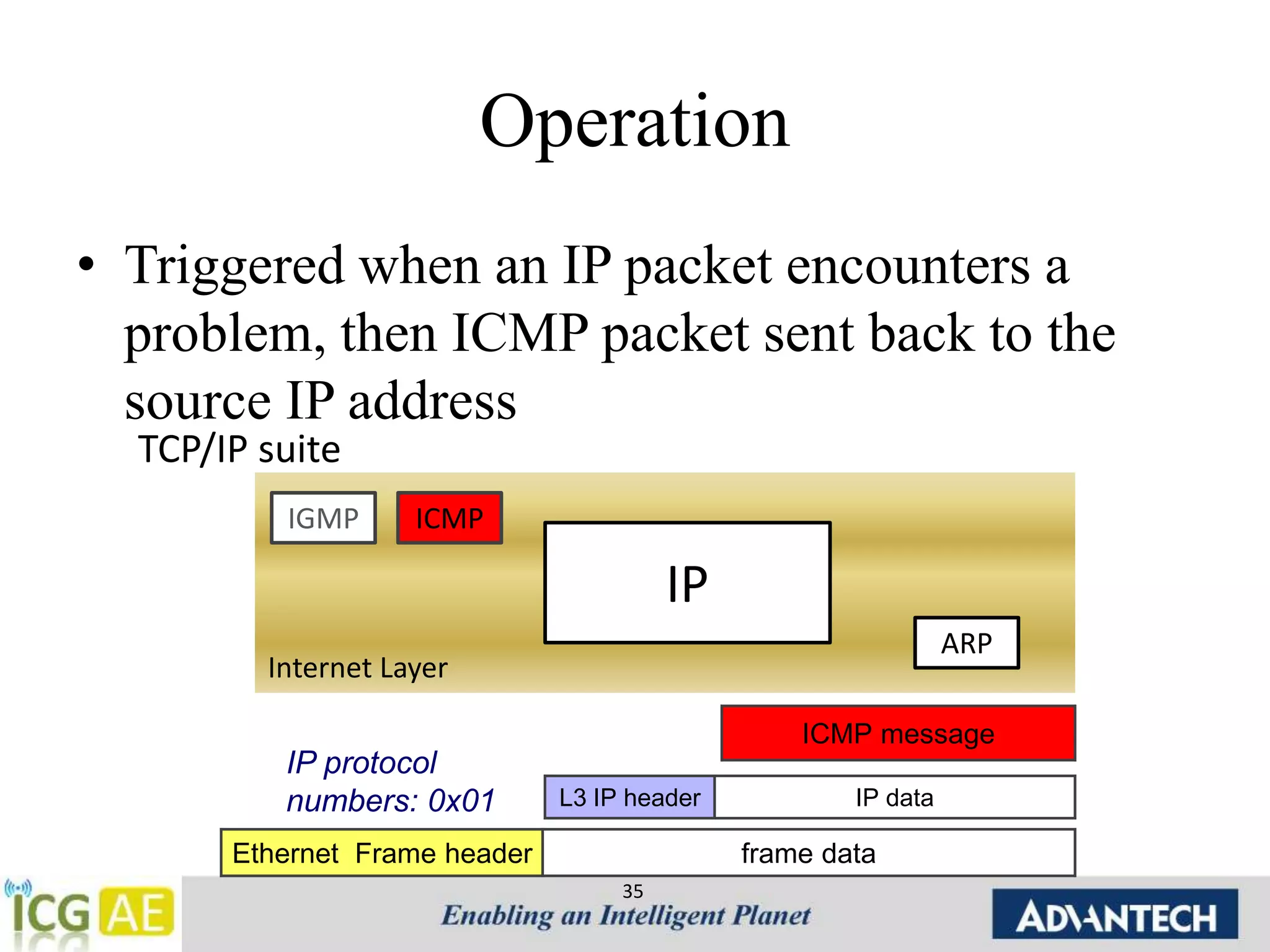
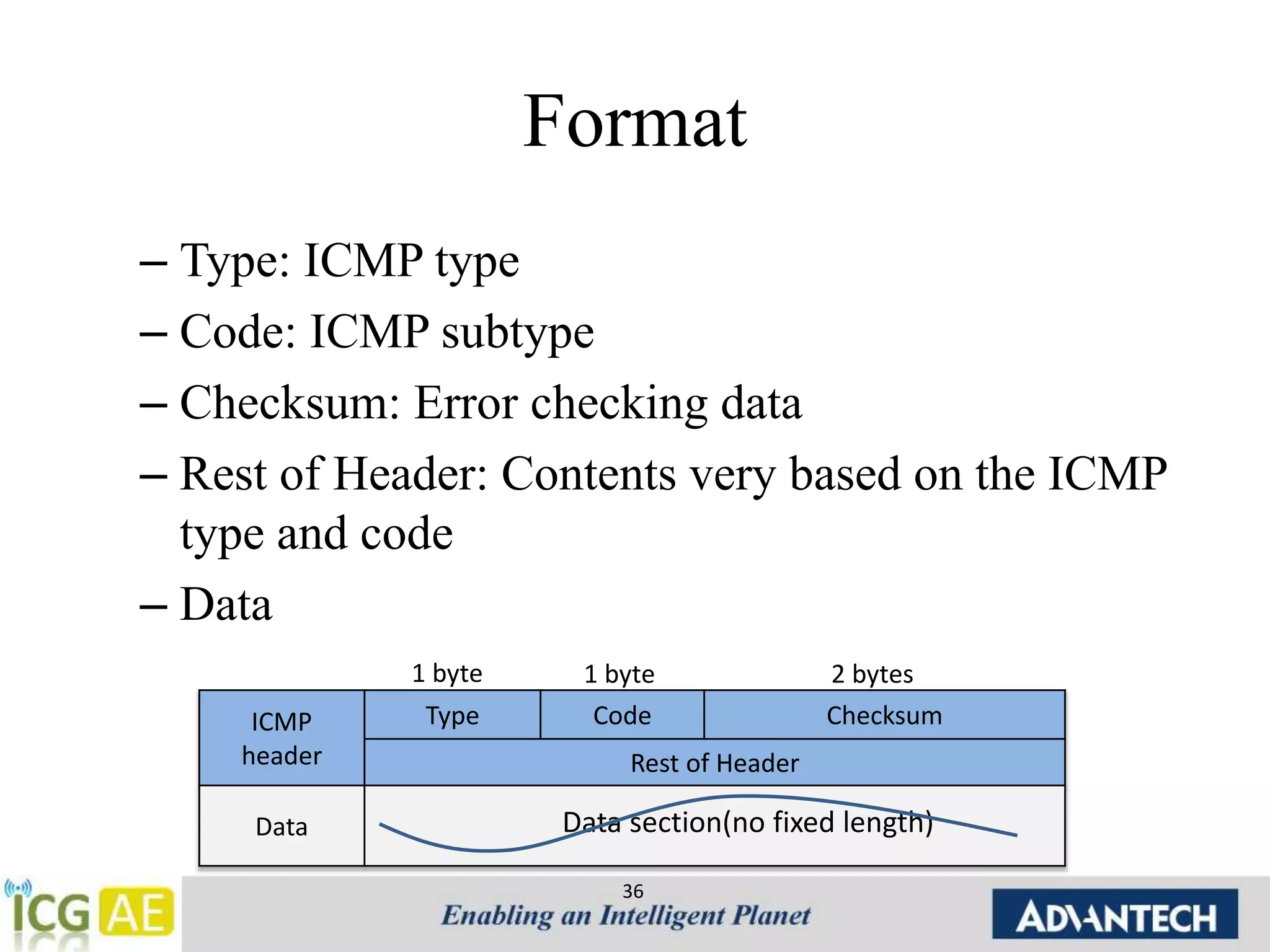
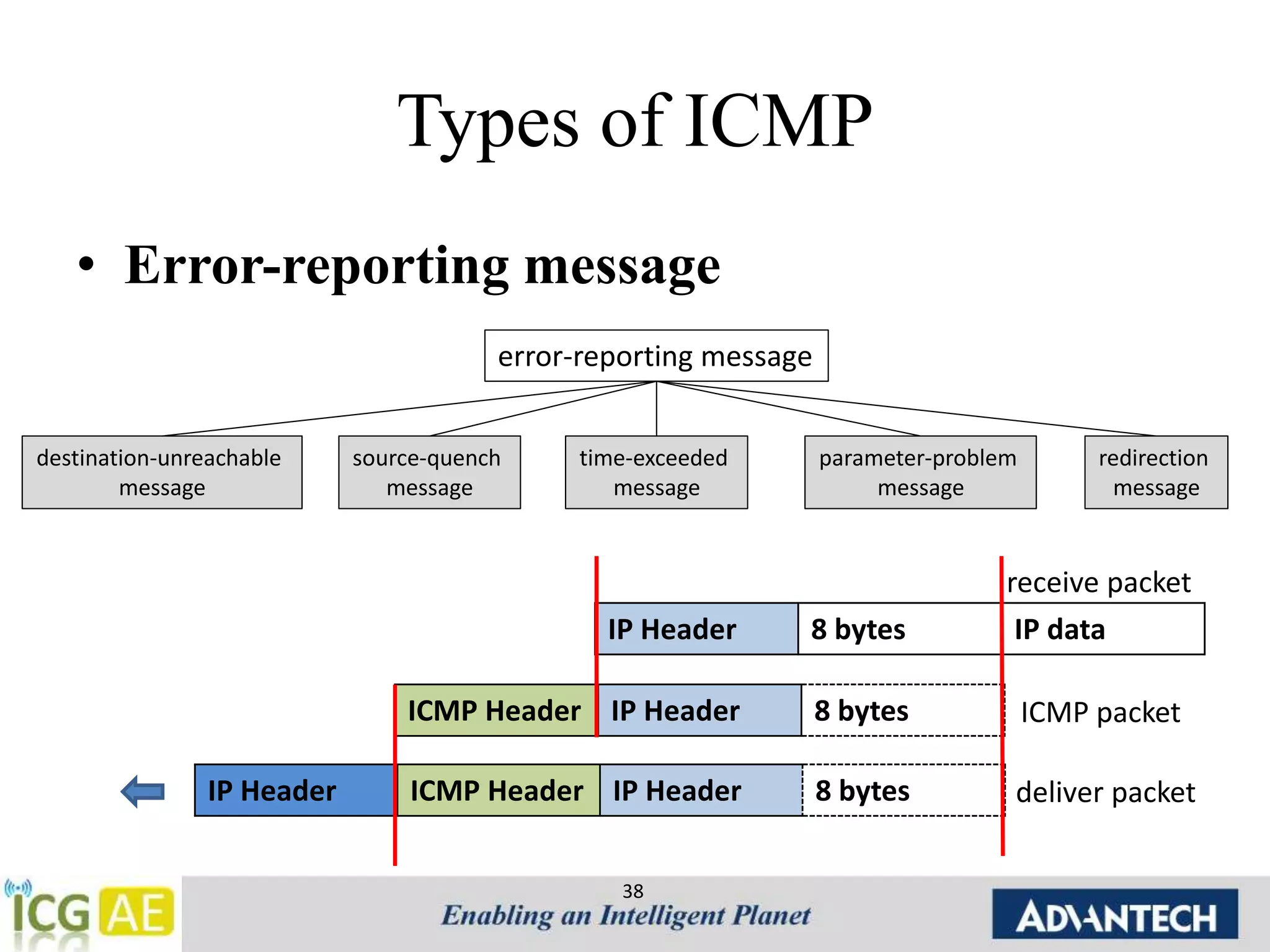
This document provides an overview of IPv4, ARP, and ICMP. It describes IPv4 addressing including classful addressing using classes A-E, classless addressing using CIDR notation, and special addresses. It also covers ARP including its operation, format, cache, and applications like proxy ARP and ARP spoofing. ICMP is introduced including its operation, format, types of messages for error reporting and querying, and tools. Hands-on examples of ARP requests, replies, probes and gratuitous ARP are also provided.







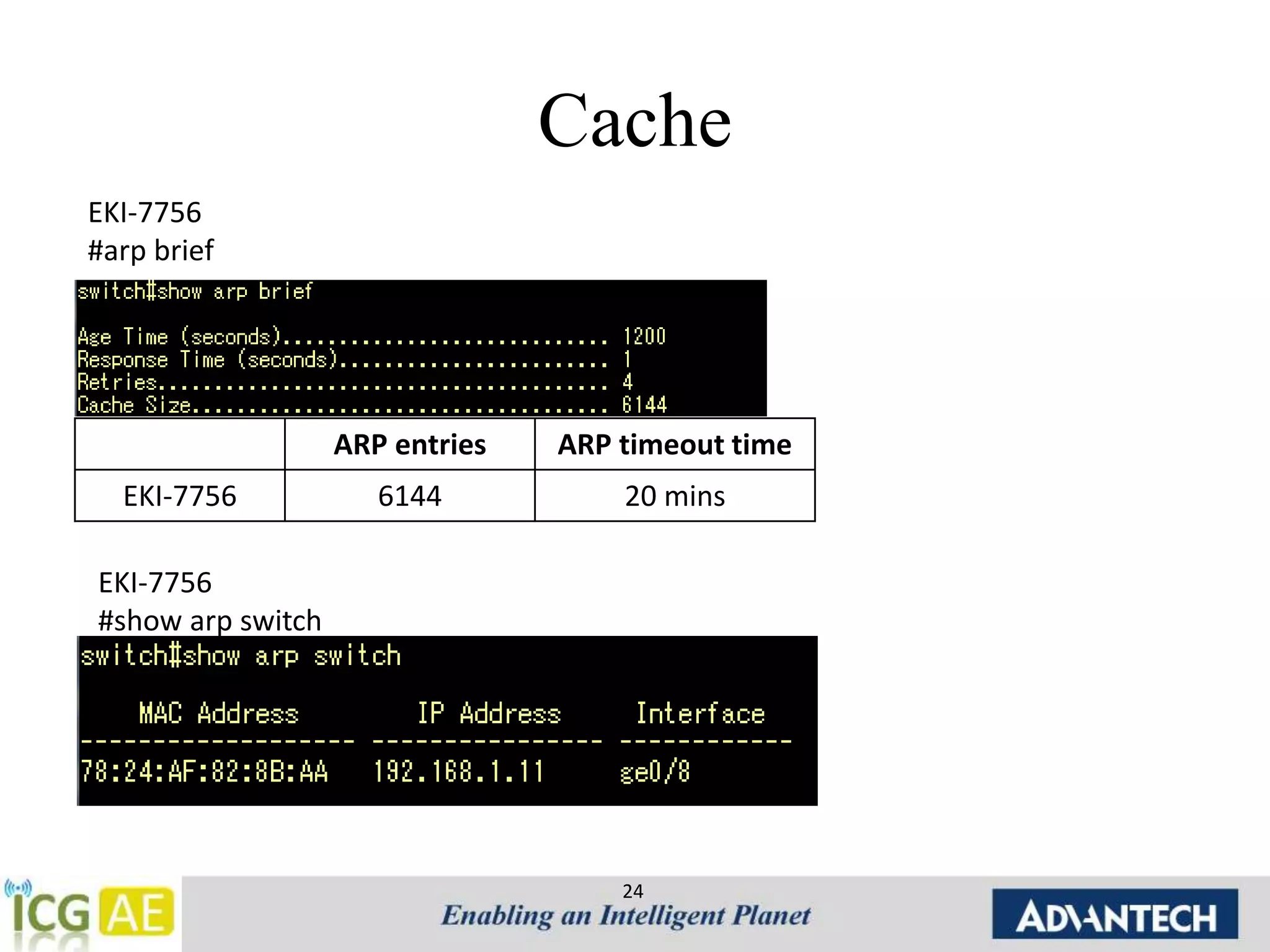
![Cache
• Requires more bandwidth for every outgoing
packet sending ARP request and waiting for
responses
• ARP cache maintained at each node
ARP entries ARP timeout time
windows 256 10 mins
Linux fedora 1024 60 s
23
arp -a to show
arp -d [IP] to delete
arp –s [IP] [MAC] to add](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap2-141119002448-conversion-gate02/75/Chap2-ipv4-arp-icmp-23-2048.jpg)
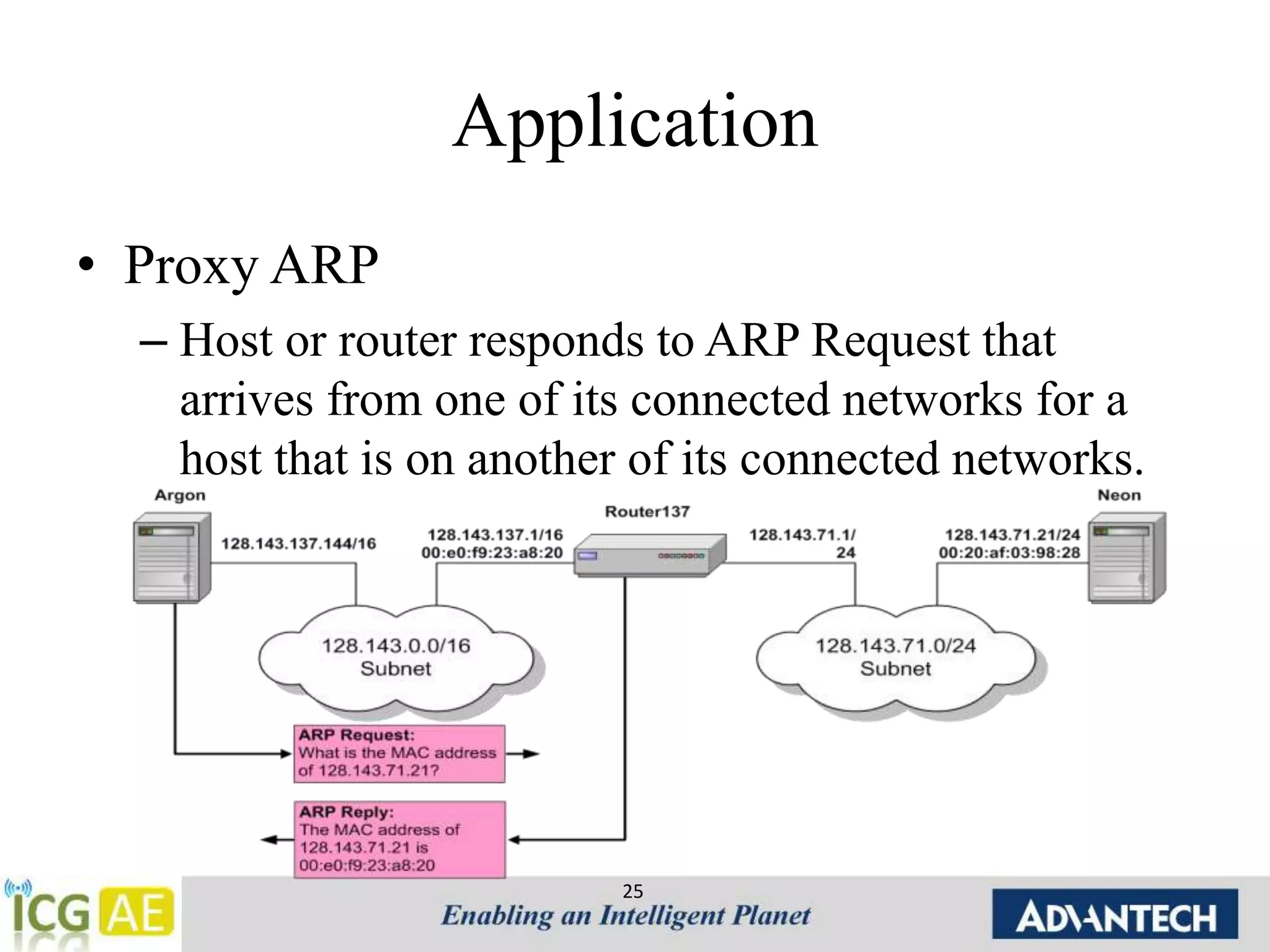



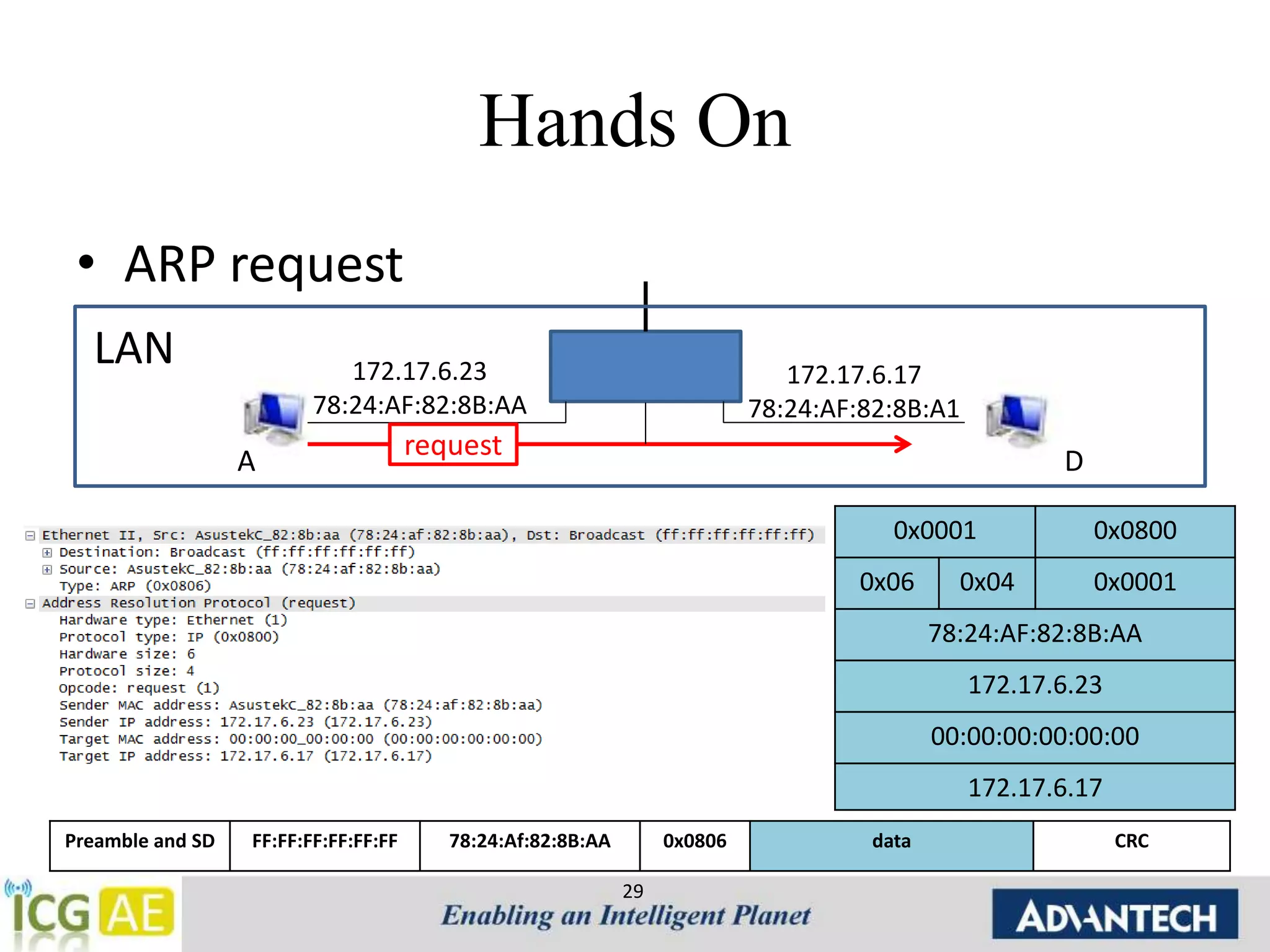
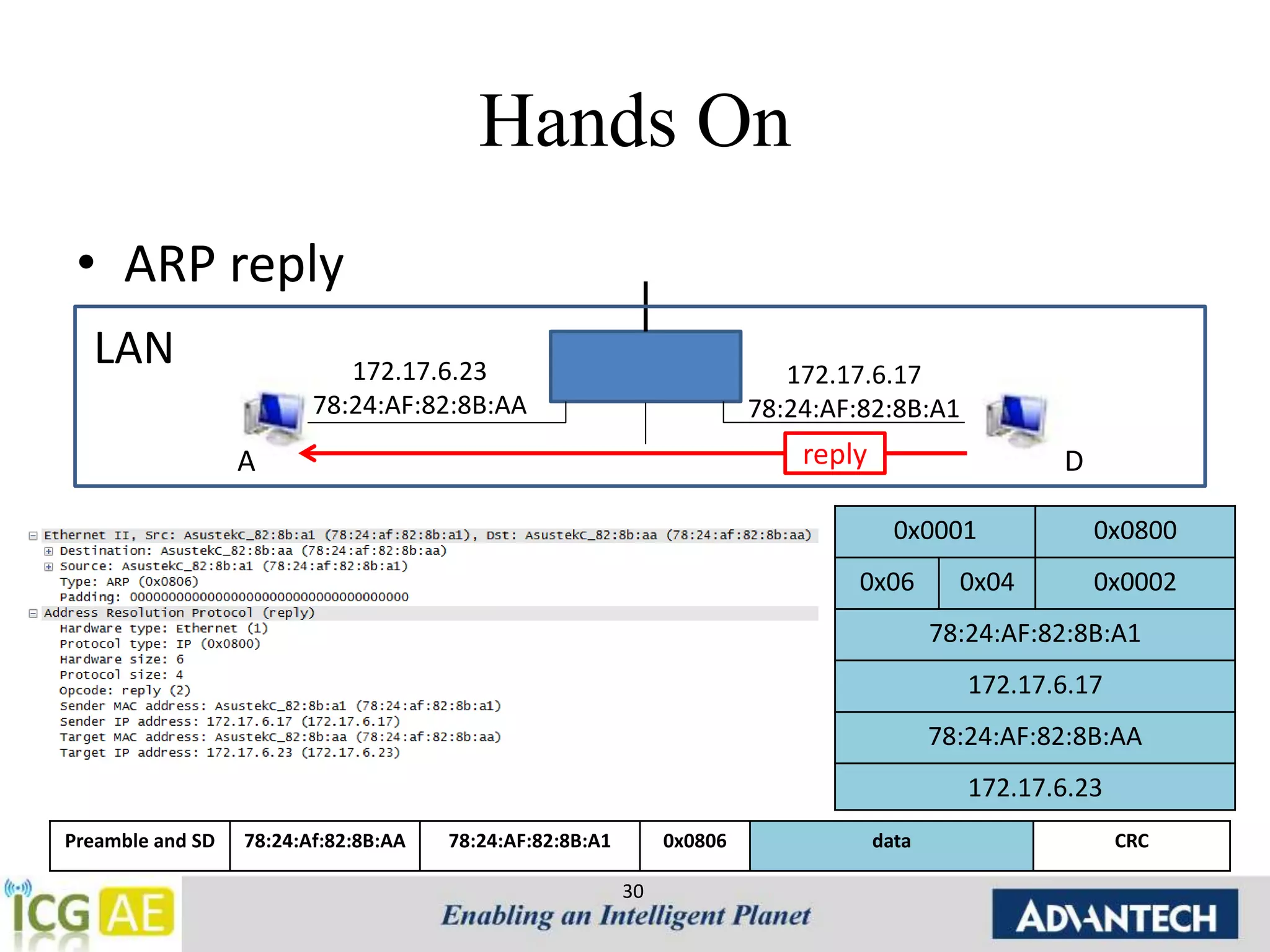




![Tools
• Ping, packet Internet groper
– sends an ICMP echo request to a remote host,
which then return an ICMP echo reply to the
sender
Windows ping program
Ping [IP] [-t] [-n Count] [-l Size] [-w Timeout]
-t Sends Echoes until interrupted
-n Count Specifies the number of Echo Request messages sent
-l Size Specifies the length, in bytes, of the Data field in the
Echo Request messages sent(Default is 32Bytes)
-w Timeout Specifies the amount of time, in milliseconds to wait
for the Echo Reply(Default is 1000=1s)
46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap2-141119002448-conversion-gate02/75/Chap2-ipv4-arp-icmp-46-2048.jpg)