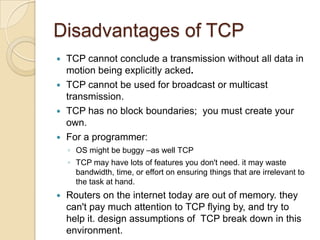
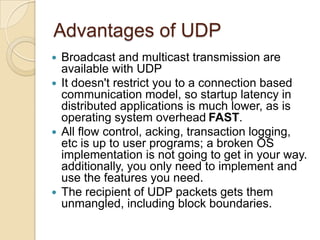
TCP guarantees reliable delivery of data packets in the correct order, while UDP does not provide these guarantees. TCP is commonly used for applications that require reliable data transfer like HTTP and FTP. UDP is used for applications that prioritize speed over reliability, such as media streaming, VoIP, and online games. While TCP ensures error-free transmission, it introduces more overhead and latency than UDP. The choice between TCP and UDP depends on an application's requirements for reliability versus speed.