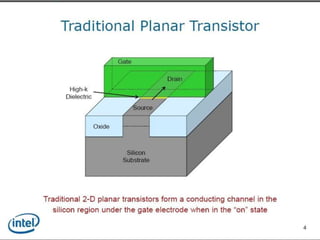
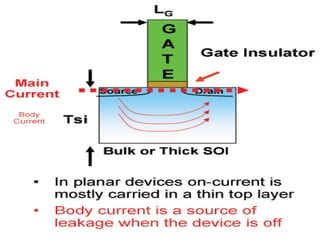
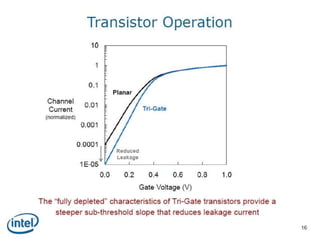
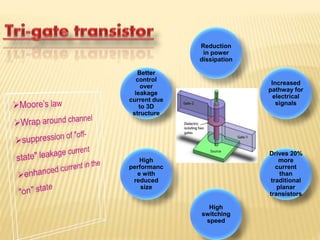
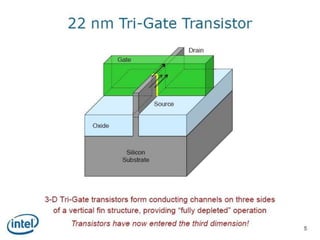
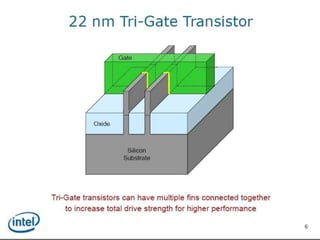
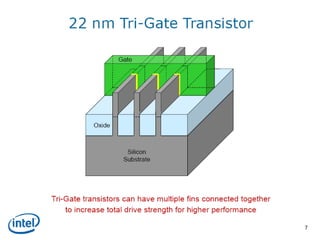
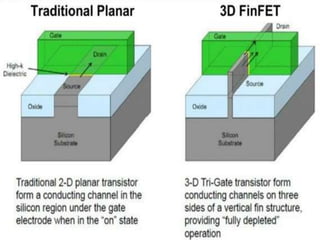
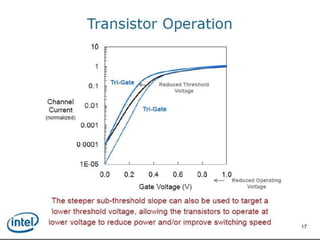
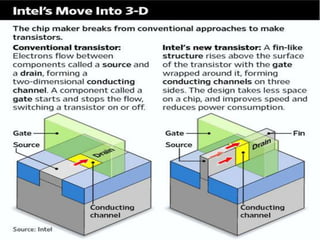
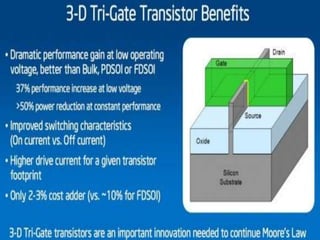
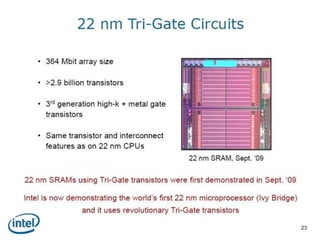
This document discusses the evolution of transistor technology, focusing on the development of tri-gate transistors. It describes how tri-gate transistors allow Moore's Law to continue by addressing issues like short channel effects that arise at smaller scales. The document outlines different types of multigate transistors and explains the advantages of tri-gate transistors, such as reduced power dissipation and better control over leakage current. It also provides some examples of how small 22nm transistors are in comparison to everyday objects.