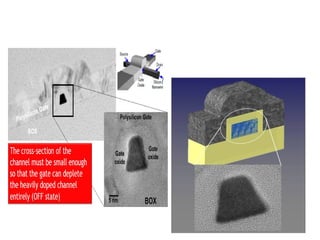
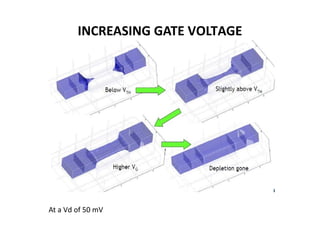
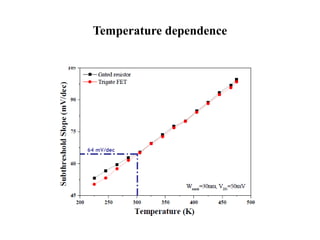
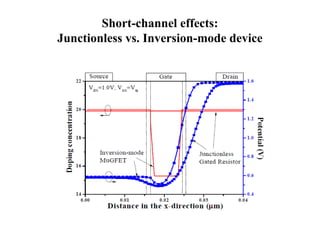
The document discusses junctionless transistors, which are transistors without PN junctions. Junctionless transistors have uniformly doped channels without doping concentration gradients. They have advantages over traditional transistors like near-ideal subthreshold slopes and lower leakage currents. The document describes the structure, fabrication process, electrical characteristics, and types of junctionless transistors. It notes that junctionless transistors could help enable the continued scaling of transistors to smaller sizes.