1. Processor performance is determined by frequency and instructions per cycle (IPC), with the goal of higher performance and lower power efficiency.
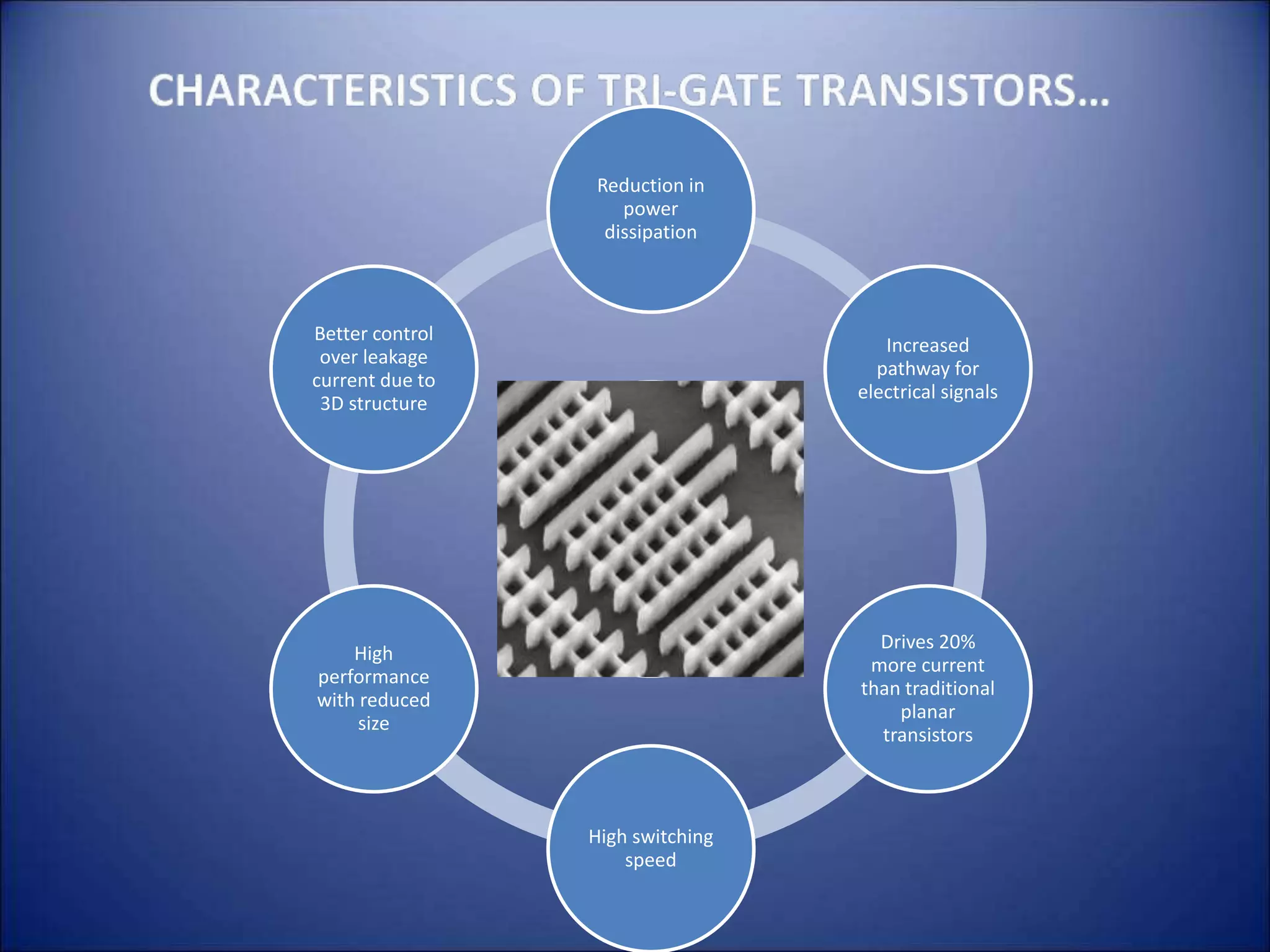
2. Higher IPC usually results in wider data paths and more performance, but also impacts power through leakage current and transistor switching ability.
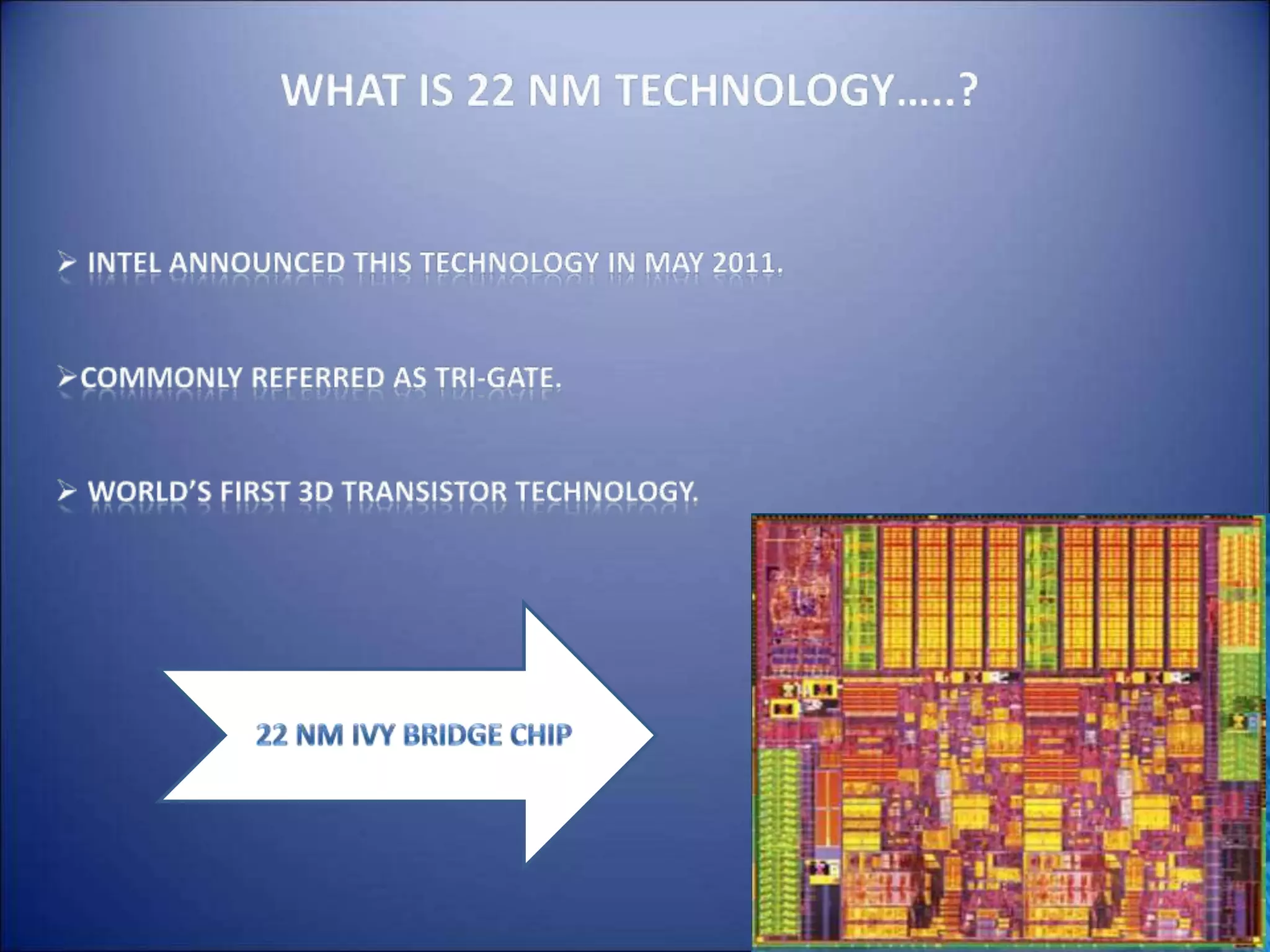
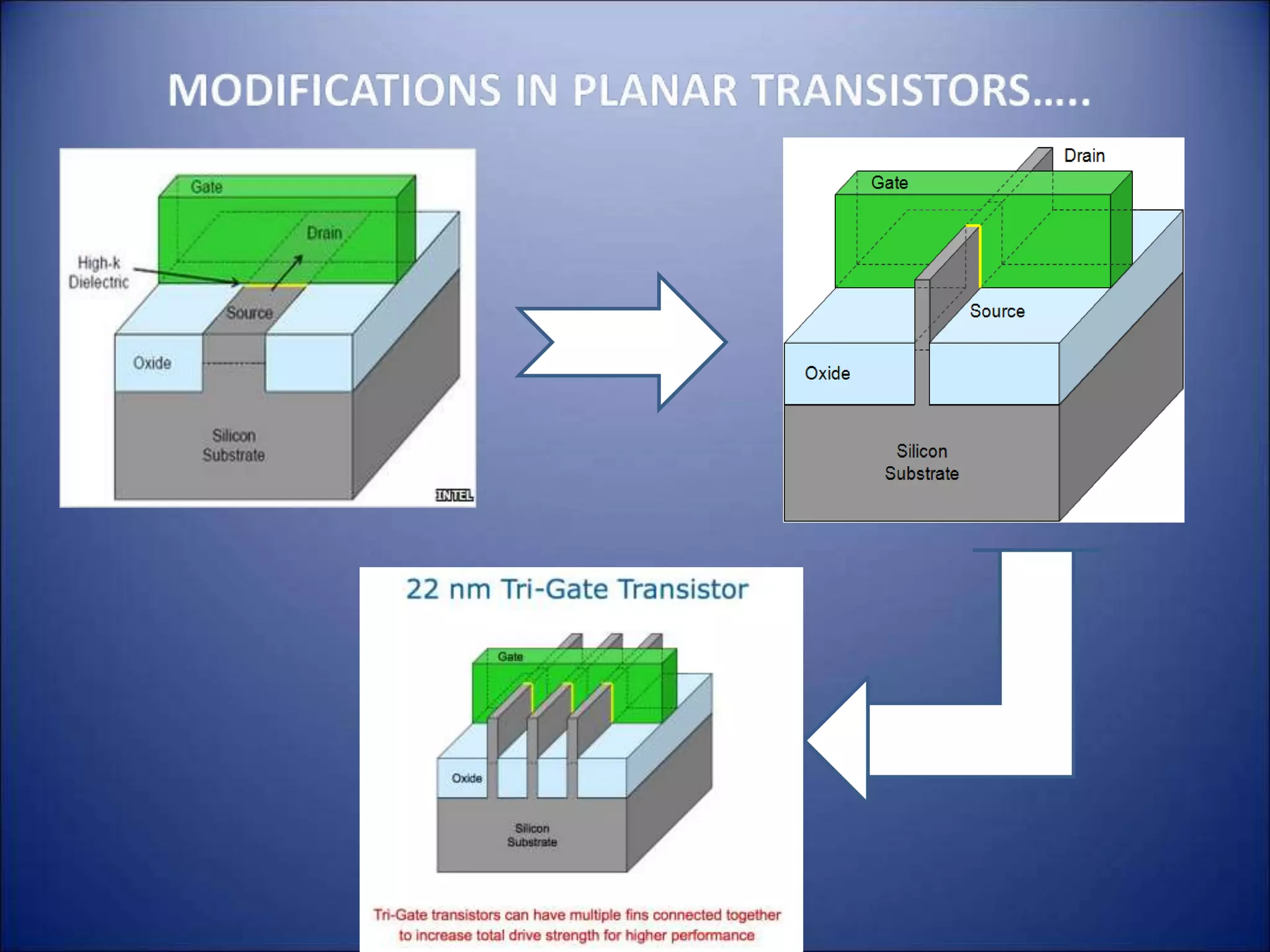
3. Advances in silicon technology like smaller transistor sizes have driven increases in processor performance and reductions in power dissipation over time, with the next steps being 22nm and 32nm transistors.