Embed presentation
Downloaded 24 times

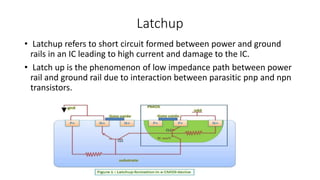
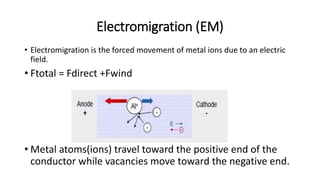

The document discusses four topics related to transistors: 1. Threshold voltage is the minimum gate voltage needed to create a conducting path between source and drain, and depends on oxide thickness, temperature, and random dopant fluctuations. 2. Latchup refers to a short circuit formed between power and ground rails in an integrated circuit, caused by interaction between parasitic bipolar transistors. 3. Electromigration is the forced movement of metal ions due to an electric field, with atoms traveling toward the positive conductor end and vacancies toward the negative end. 4. Mobility degradation occurs due to lateral and vertical electric fields scattering carriers, reducing surface mobility as channel lengths shrink.



