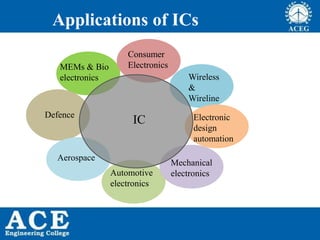
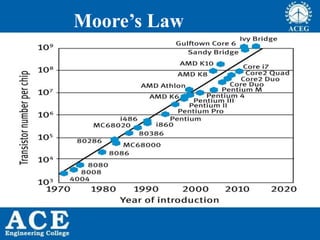
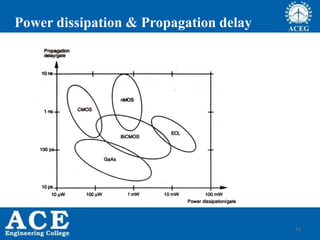
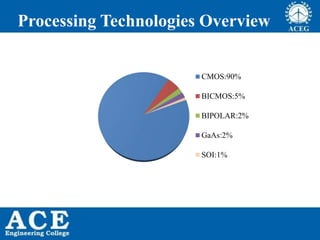
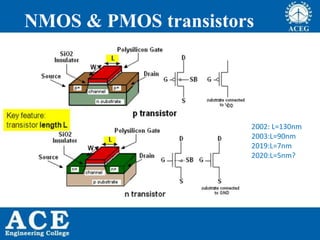
VLSI is the process of integrating millions of transistors on a single chip. It was invented in 1980 and allows for 20,000 to 1,000,000 transistors per chip. VLSI enables devices to be physically smaller, cheaper to produce, faster, more reliable and efficient. Integrated circuits are used in consumer electronics, computers, wireless devices, automotive electronics, aerospace, defense and more. Moore's Law predicts that the number of transistors on a chip will double every 18 months, allowing continued advancement and miniaturization of chips. Common processing technologies for VLSI include CMOS, Bipolar, BiCMOS, GaAs and SOI.