Movement of Substances Across Membrane Plasma
- 1. 3.1 MOVEMENT OF SUBSTANCES ACROSS THE PLASMA MEMBRANE
- 2. substances that are required by cells • Glucose • H2O • O2 • Mineral substances to be eliminated from cells • ammonia • urea • CO2 Cell membranes are like gates.
- 3. The main function of a plasma membrane is to control what enters and what exits a cell. • keeps certain substances inside and other substances on the outside. • This function is critical. If needed molecules (such as those used in protein synthesis) were free to leave, then death of the cell would quickly occur. the necessity for movement of substances across the plasma membrane:
- 4. PLASMA MEMBRANE Membrane lipids are organized in a bilayer (two sheets of lipids making up a single membrane) approximately 60 to 100 Å thick
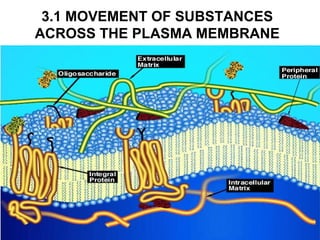
- 5. Plasma Membrane Structure Plasma membrane phospholipid bilayer combination of phospholipids & proteins http://www.bio.davidson.edu/people/macampbell/111/memb-swf/membranes.swf FLUID MOSAIC MODEL • not fixed in any rigid pattern • float around in the membrane Proteins
- 6. These molecules form a phospholipid bilayer • hydrophilic (polar) heads facing their aqueous surroundings (e.g., the cytosol) • hydrophobic tails facing each other Hydrophobic end (repels water) Hydrophilic polar heads (attracted to water) the charges on the phosphate and amino groups (in red) make that portion of the molecule hydrophilic. Amphiphilic lipids~major constituents of cell membranes
- 7. Integral and peripheral membrane proteins PERIPHERAL PROTEINS - lie on the surface of the membrane. INTEGRAL PROTEINS - extend into and sometimes completely through the membrane. • marker proteins ~ like nametags that identify the cell to other cells • transport proteins ~ responsible for shipping and receiving. They move materials in and out of the cell • receptor proteins ~ serve as binding or attachment sites, especially for hormones or other molecular messengers
- 8. thin film on the inside of an egg Semipermeable membrane – lipid bilayer selectively permeable membrane partially permeable membrane differentially permeable membrane • Some materials freely pass - the membrane is permeable to such molecules and whether they are inside or outside of the cell depends on other factors • Some materials are excluded • Some materials enter or leave the cell only by the using cell energy
- 9. 1. Small hydrophobic molecules, such as CO2, O2 and small lipids, dissolve in the membrane and pass through readily. 2. Tiny polar molecules, such as H2O and alcohol, can also slip between the phospholipid molecules. 3. Ions and most nutrient molecules do not move freely through membranes, but are often carried by thetransport protein channels, either with or without the use of energy. 4. Most large molecules are excluded and must be manufactured within the cell, or moved by significant alterations of the membrane itself.
- 10. • Fluid Any substance that can move or change shape in response to external forces without breaking apart. Gases and liquids are fluids. • Concentration The number of molecules of a substance in a given volume • Gradient A physical difference between two regions so that molecules will tend to move from one of the regions toward the other. Concentration, pressure and electrical charge gradients are common in cells.
- 11. Passive Transport involves moving things through membranes without the expenditure of cell energy down gradients. e.g: diffusion. TRANSPORTATION Active Transport the pumping of molecules or ions through a membrane against their concentration gradient.
- 12. to where there is less of it Diffusion the net movement of a substance from where there is more of it along a concentration gradient until molecules are equally distributed (and the gradient no longer exists). Passive Transport
- 13. • passive transport (requires no energy) • without the involvement of specific carrier proteins • The Rate of Diffusion can be affected by:- - Temperature (Higher temperature, faster molecule movement) - Molecule size (Smaller molecules often move more easily) - Concentration (Initial rate faster with higher concentration) - Electrical and pressure gradients of the two regions (Greater the gradient differential, the more rapid the diffusion (again, initially)) • Materials that may move freely through membranes by simple diffusion include: - H20 (water) - CO2 (carbon dioxide) - O2 (oxygen) - Uncharged & some small lipid-soluble molecules (alcohol) http://www.bbc.co.uk/education/asguru/biology/01cellbiology/05pathways/06passivesimple/index.shtml Passive Transport Simple Diffusion
- 14. Simple Diffusion * Small polar molecules cannot readily dissolve in the hydrophobic bilayer but can pass through the membrane via "holes" formed by intrinsic proteins forming channels. * The proteins are thus called channel/ transport proteins. Passive Transport
- 15. Facilitated Diffusion • passive transport (No energy is involved) • with the help of membrane transport proteins, which temporarily bind to the substance to be moved through the membrane • carrier proteins and channel proteins are involved (has a specific receptor site for that substance) • Materials that move through membranes by facilitated diffusion include: - small polar molecules (e.g. glucose) - Many small ions - Amino acids Passive Transport
- 16. the substance being deposited on the other side of the membrane. The protein then returns to its original shape ready to operate again the substance binds to the carrier protein undergoes a conformational (shape) change Passive Transport
- 17. Osmosis • a special case of diffusion. • diffusion of water molecules from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration, • i.e. from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration Passive Transport Water molecule selectively permeable membrane solute
- 19. • A hypotonic solution has a LOWER concentration of solutes • A hypertonic solution has a HIGHER concentration of solutes • An isotonic solution is a solution that has a concentration of solutes equal to its environment So how does this affect cells? Passive Transport
- 20. Human Red Blood Cells Typical Plant Cell HypertonicHypotonic Isotonic HypertonicHypotonic Isotonic The net movement of water is always FROM a hypotonic solution (higher concentration of water) TO a hypertonic solution (lower concentration of water ) There is NO NET MOVEMENT in isotonic solutions Passive Transport
- 21. Active Transport • against the concentration gradient • typically requires two carrier protein active sites:- - to recognize the substance to be carried, and - to release ATP (adenosine triphosphate) to provide the energy for the protein carriers or "pumps". Active Transport http://www.bbc.co.uk/education/asguru/biology/01cellbiology/05pathways/08active/index.shtml
- 22. Active Transport
- 24. Comparison of passive and active transport TELL ME THE ANSWER PLEASE Similarities? Differences?
- 25. Discuss the processes of passive transport and active transport in living organisms: a) gaseous exchange in the alveoli and blood capillaries simple diffusion b) absorption of digested food in the villus facilitated diffusion
- 26. c) absorption of water by root hairs of a plant Discuss the processes of passive transport and active transport in living organisms:
- 27. d) ion intake by root hairs of a plant active transport Discuss the processes of passive transport and active transport in living organisms: