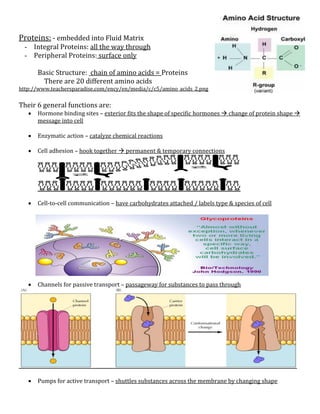
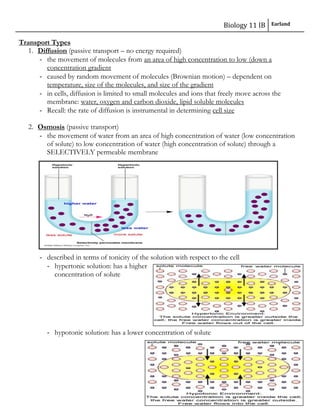
The document discusses cell membranes and transport across membranes. It begins by explaining the structure of membranes, noting they are composed of a phospholipid bilayer with hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions. Membrane proteins embedded in the bilayer perform various functions and transport roles. The document then describes six types of transport across membranes: diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, active transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis. It explains the differences between passive and active transport, and provides examples of protein transporters involved in each.