Embed presentation
Downloaded 159 times
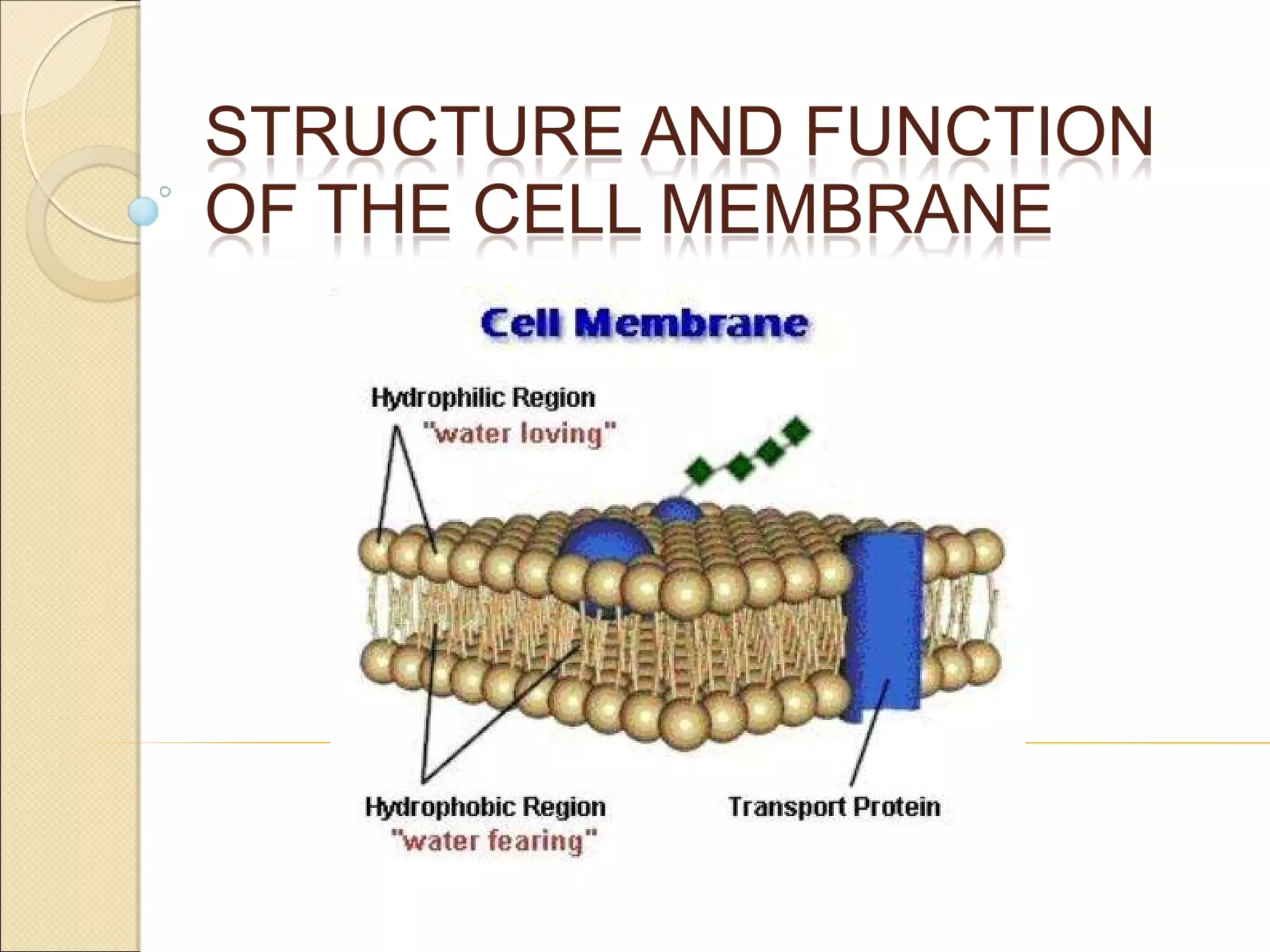

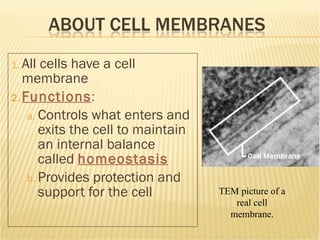
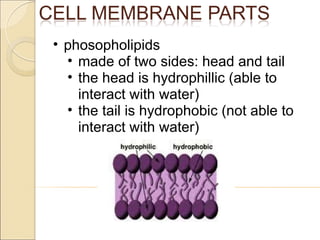
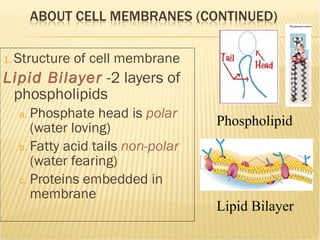
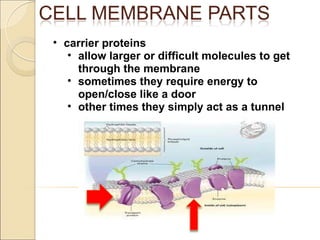
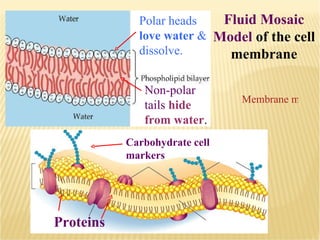
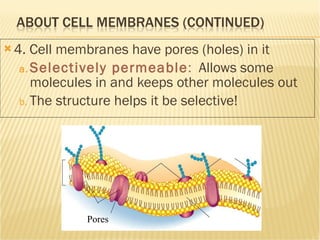
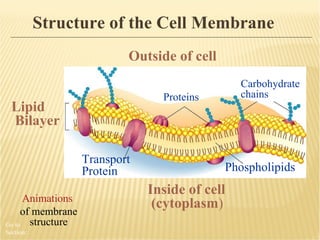

The document summarizes key aspects of the cell membrane. The cell membrane is selectively permeable, controlling what enters and exits the cell to maintain homeostasis. It is composed of a lipid bilayer with phospholipids that have hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails. Proteins are embedded throughout the membrane and act as transporters, sometimes requiring energy to move molecules across. The fluid mosaic model best depicts the structure of the cell membrane.









