Embed presentation
Downloaded 48 times








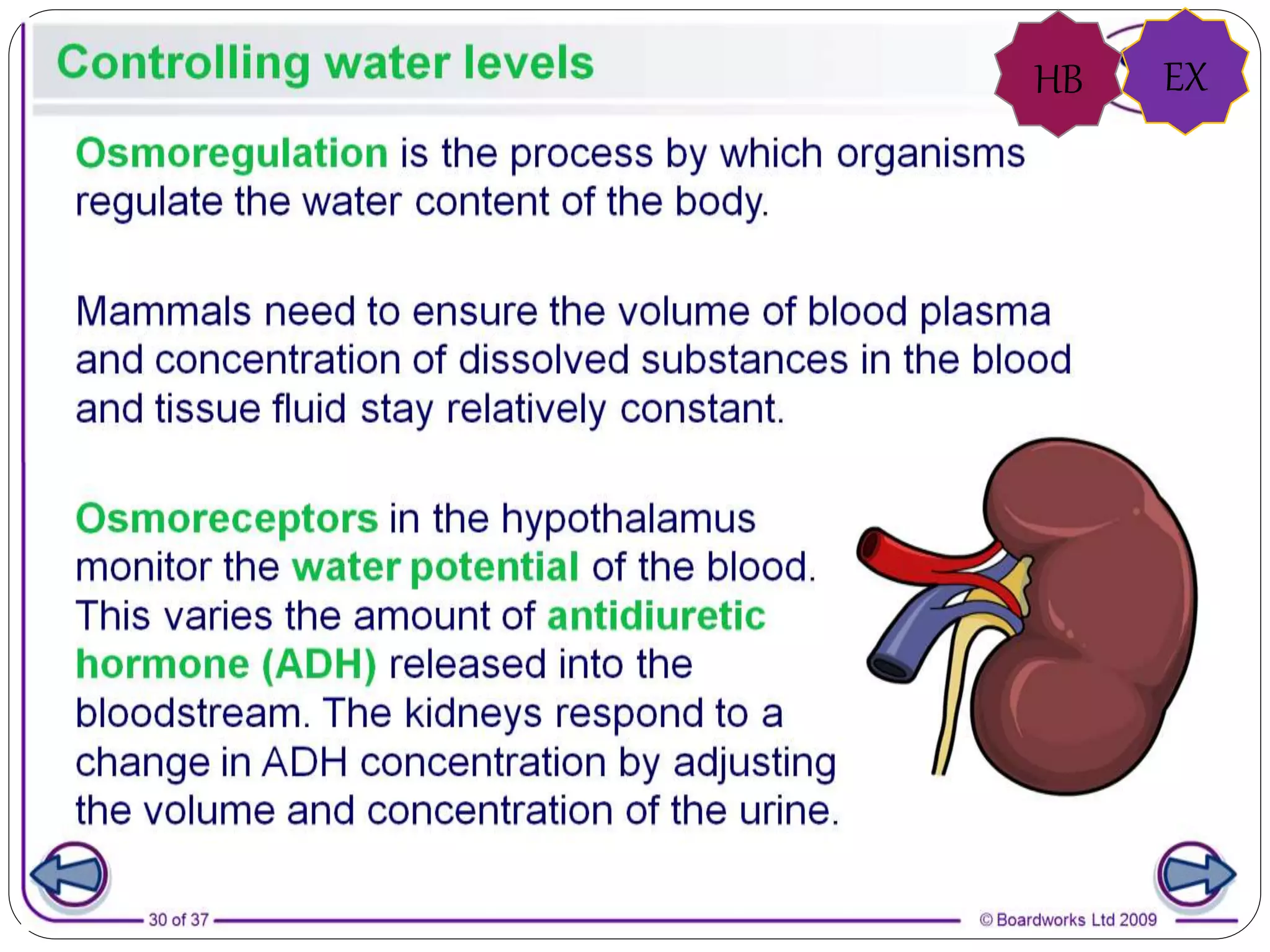




The document discusses excretion and the kidney's role in removing waste from the body. It summarizes that the lungs, skin, and kidneys aid in excretion by removing carbon dioxide, excess water and salts, and urea, excess water, salts, spent hormones and drugs respectively. The nephron, the functional unit of the kidney, filters blood and selectively reabsorbs or secretes substances to produce urine, which normally contains water, urea, salts, spent hormones, alcohol and drugs.











