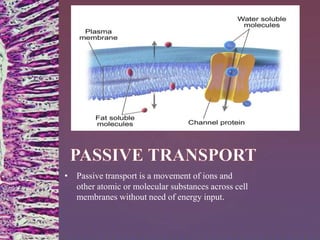
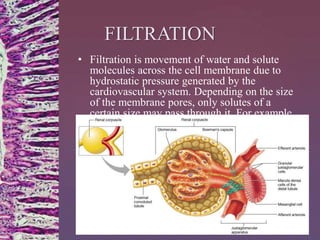
The document discusses membrane transport mechanisms in biology, detailing categories such as passive and active transport, as well as various processes like diffusion, facilitated diffusion, filtration, and osmosis. It explains key concepts related to each transport type, including concentration gradients and the behavior of water in different solute conditions (hypertonic, hypotonic, isotonic). The author, Ruhid Hasan, invites readers to reach out with any questions.