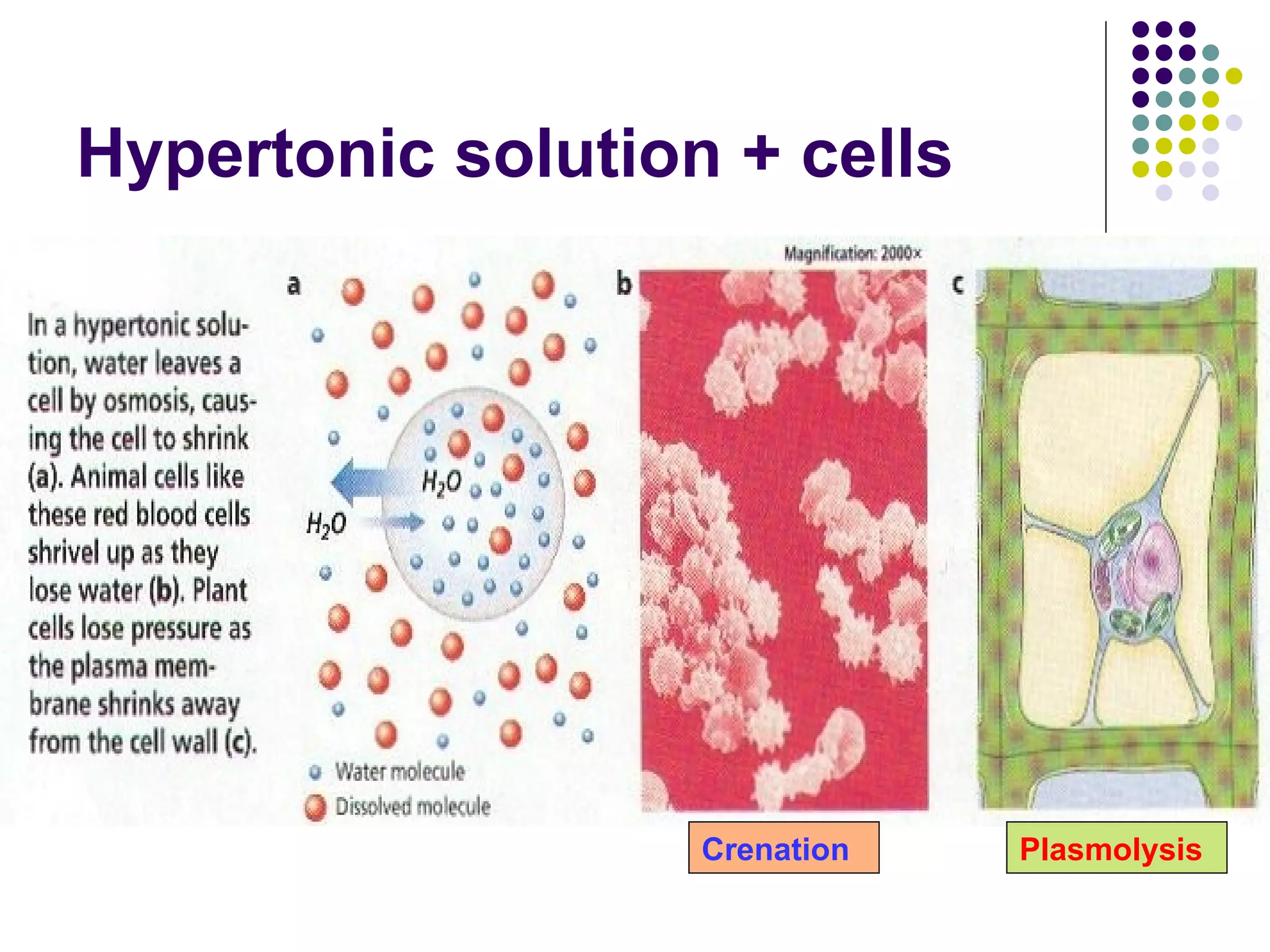
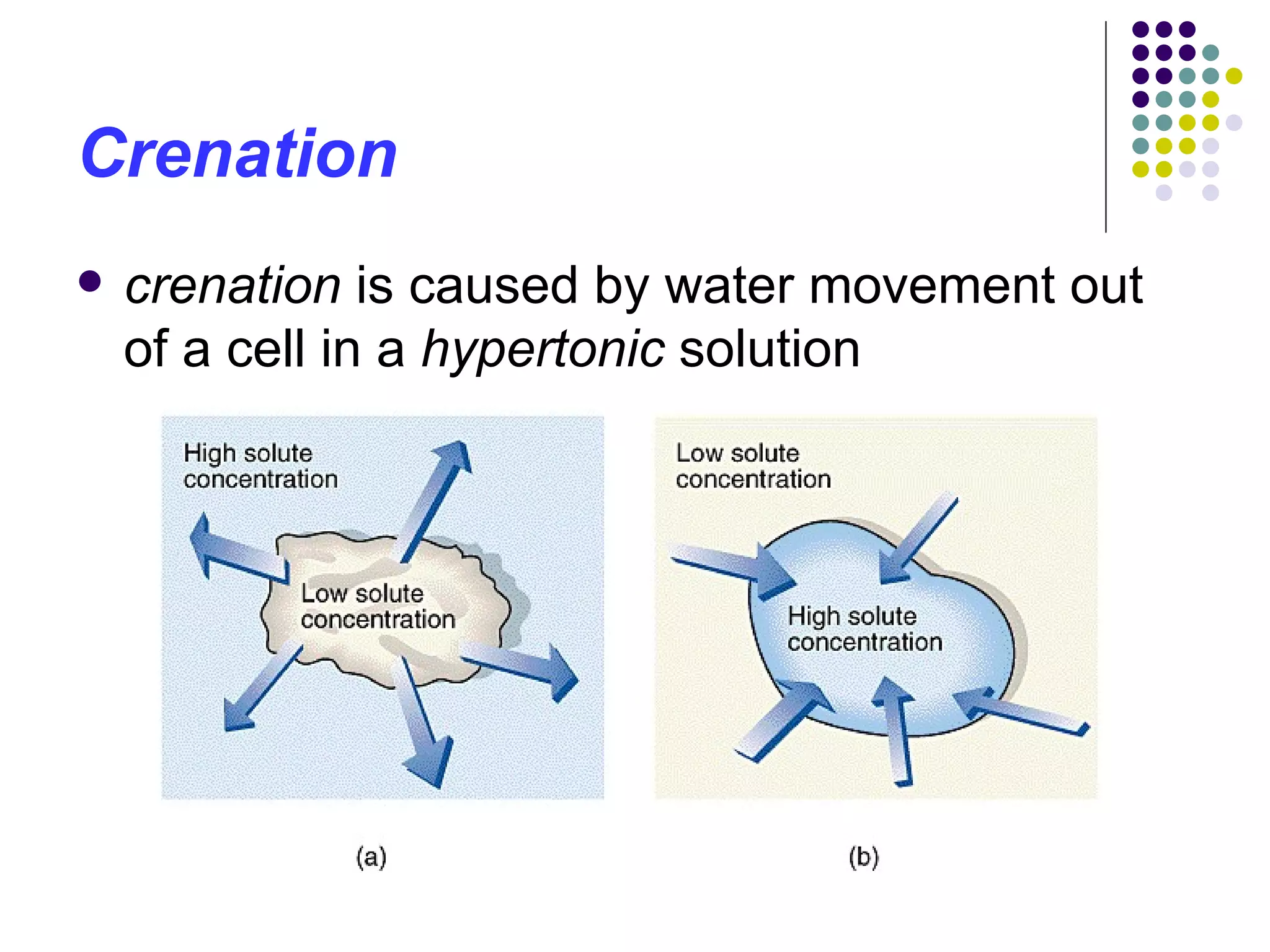
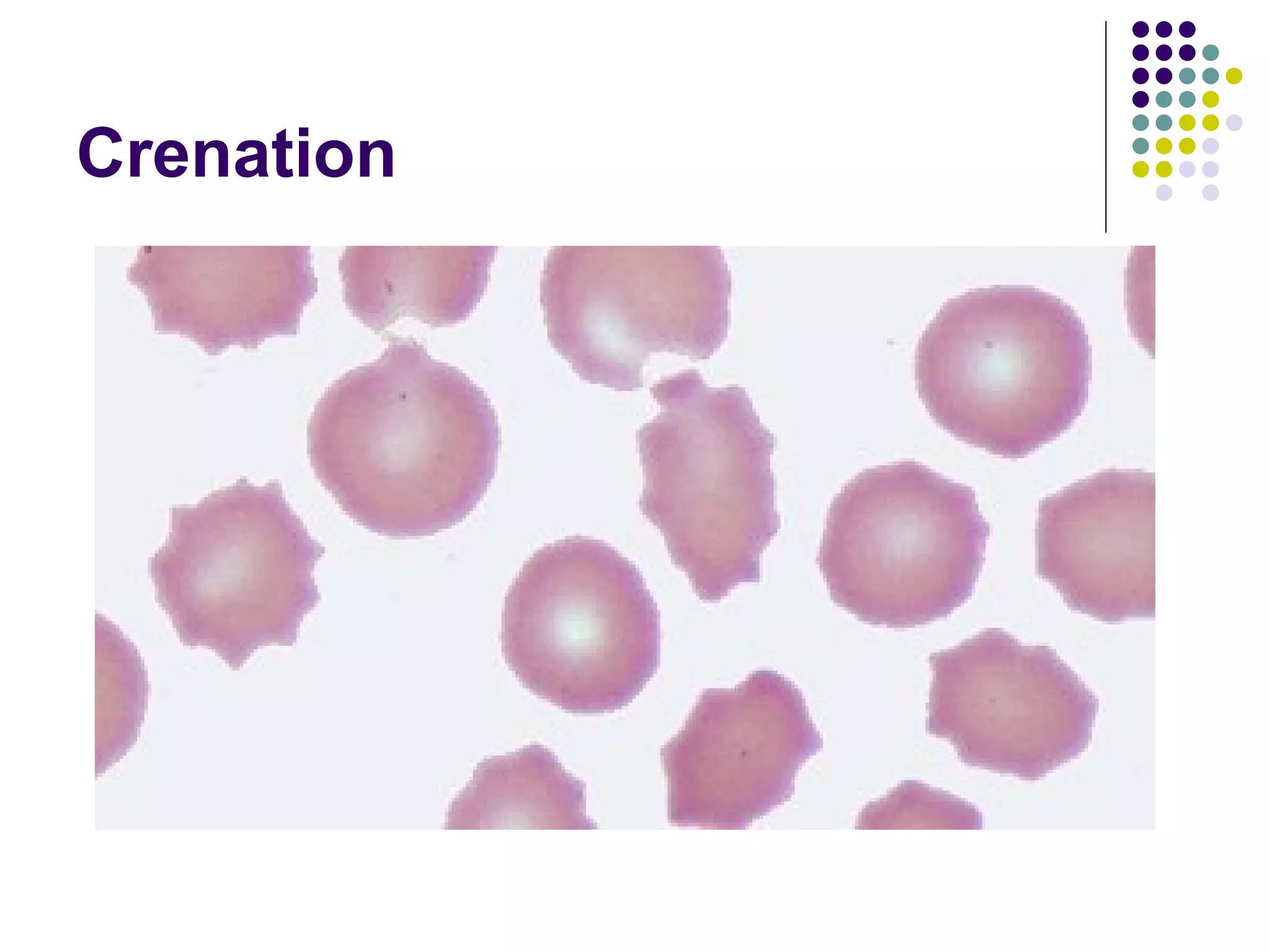
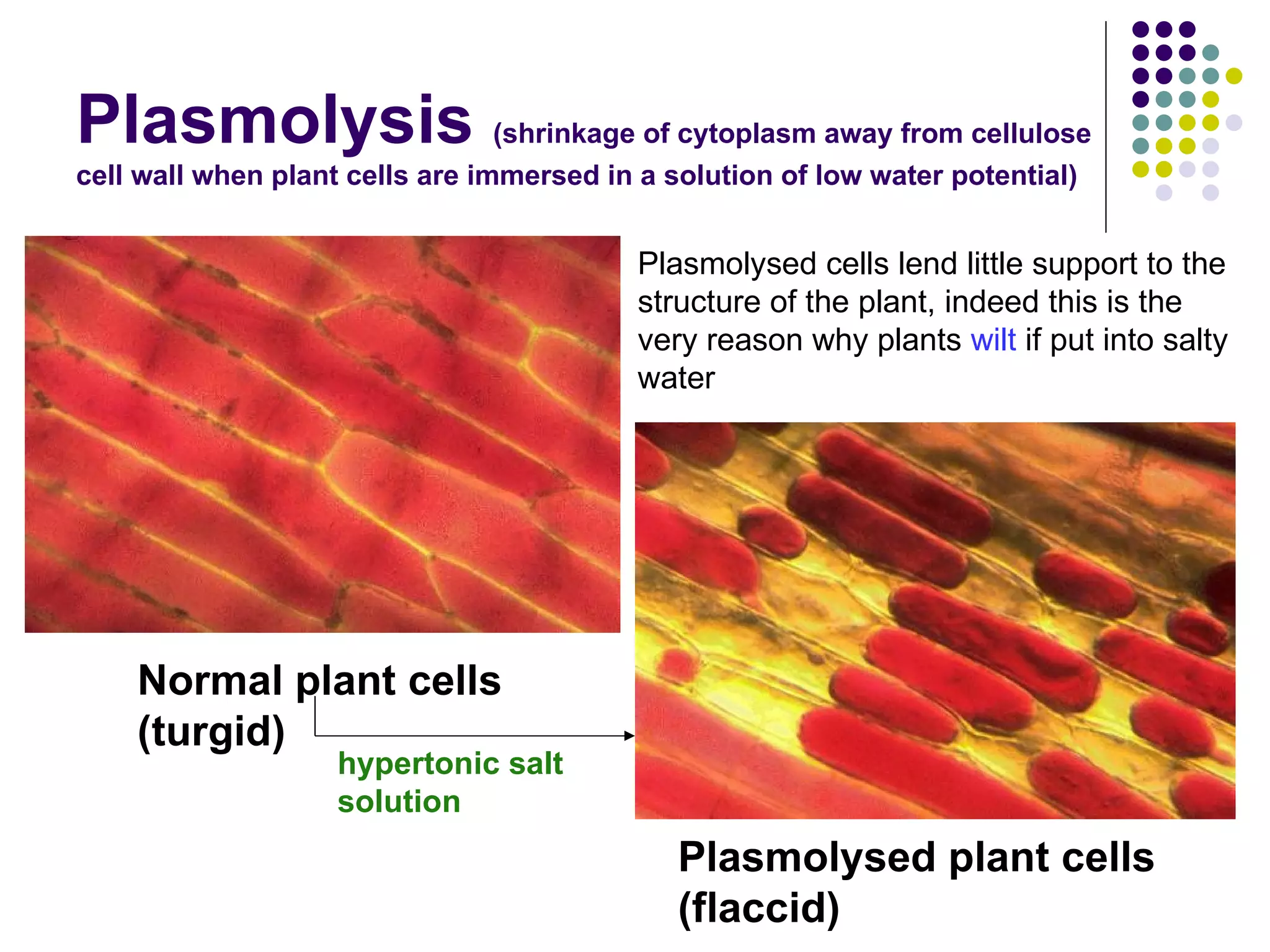
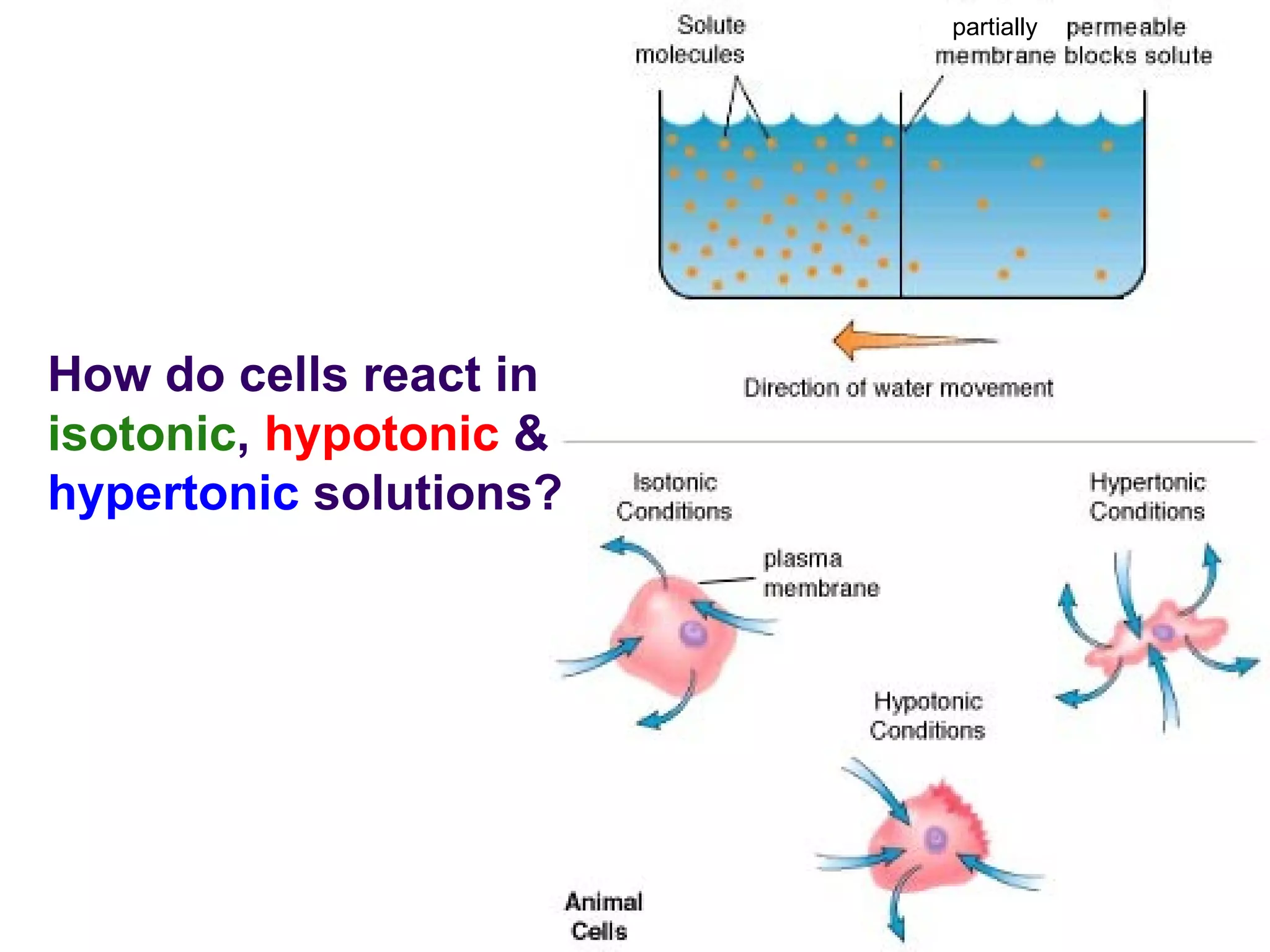
The document discusses isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solutions and their effects on cells.
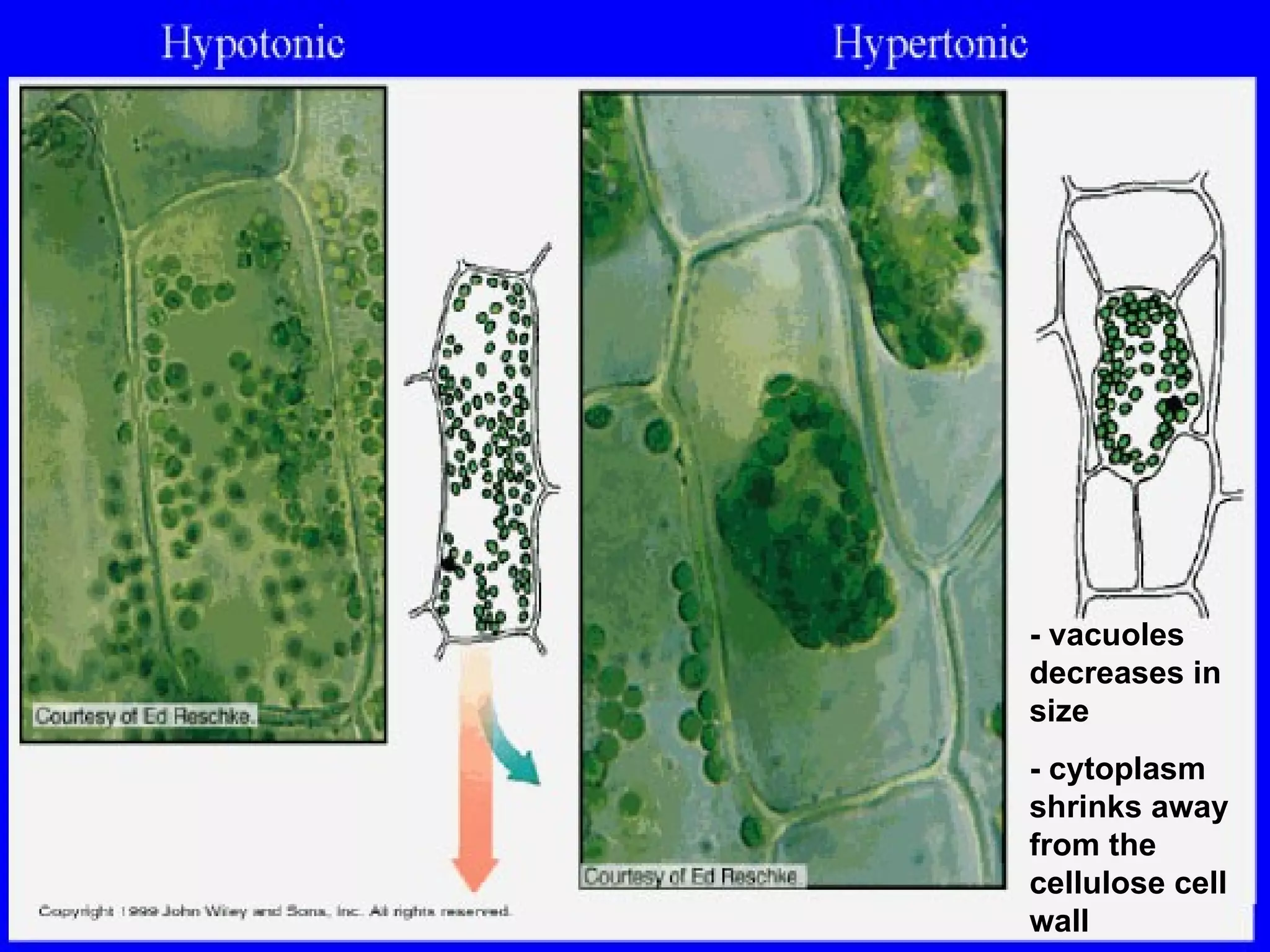
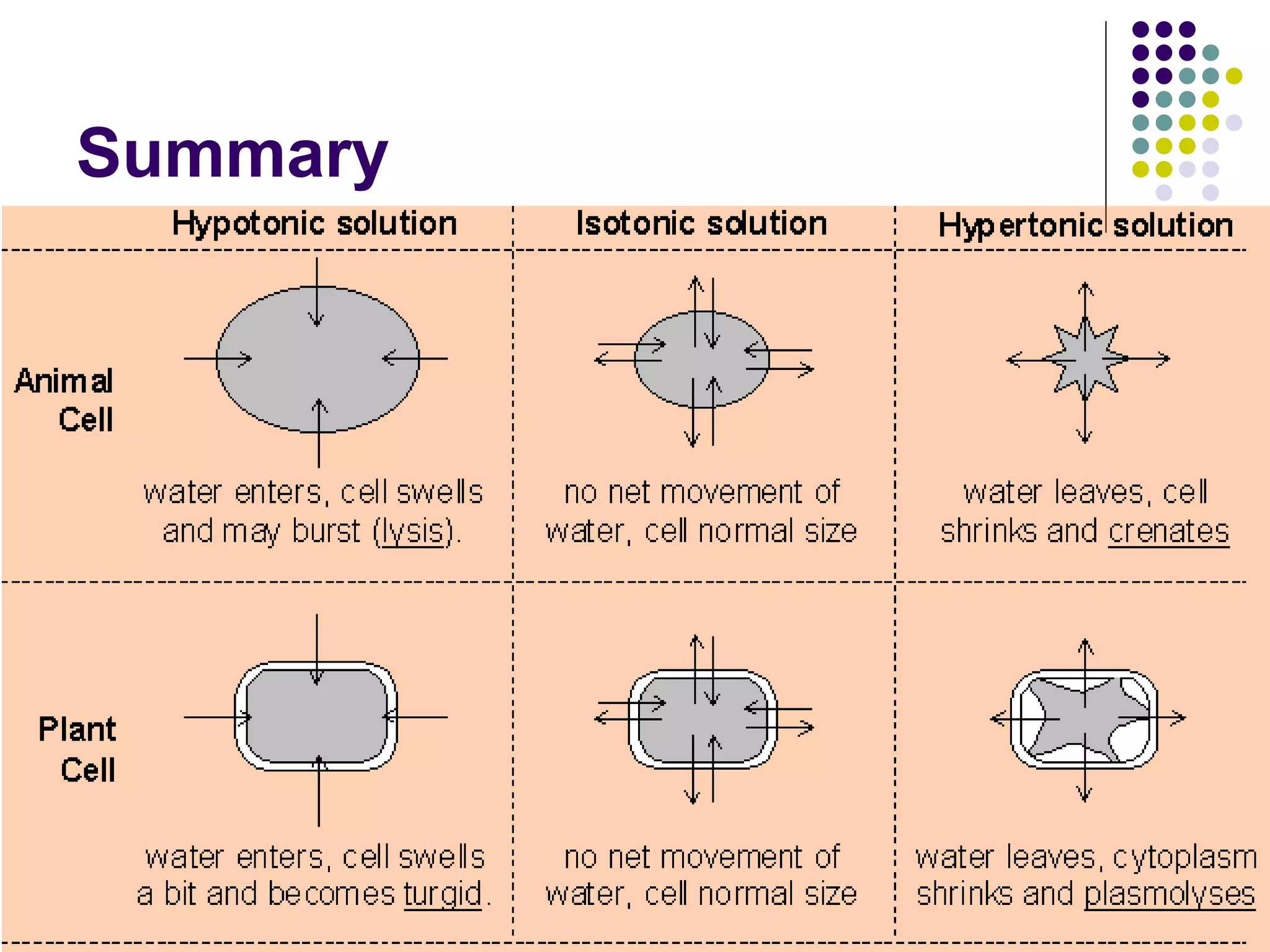
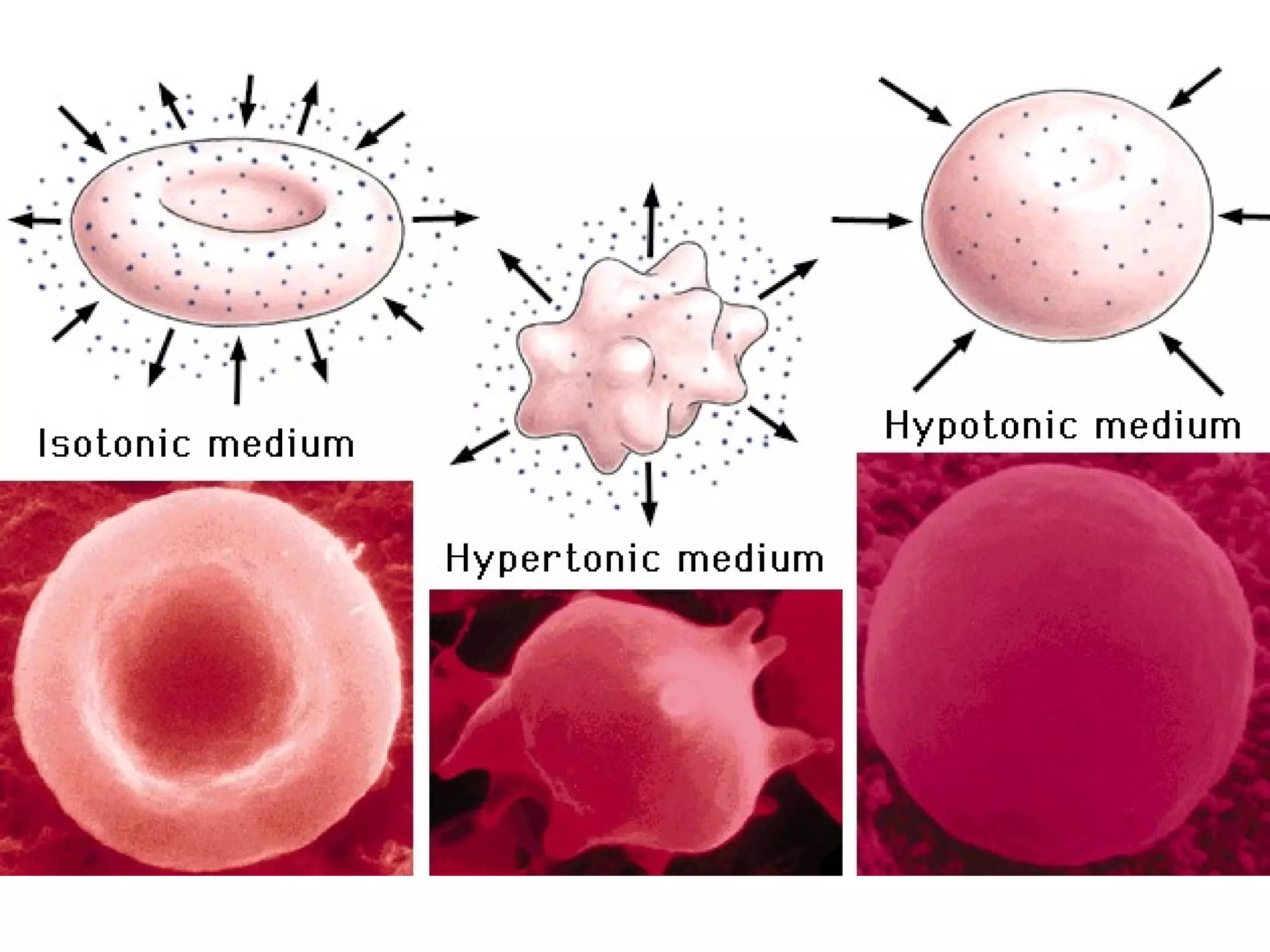
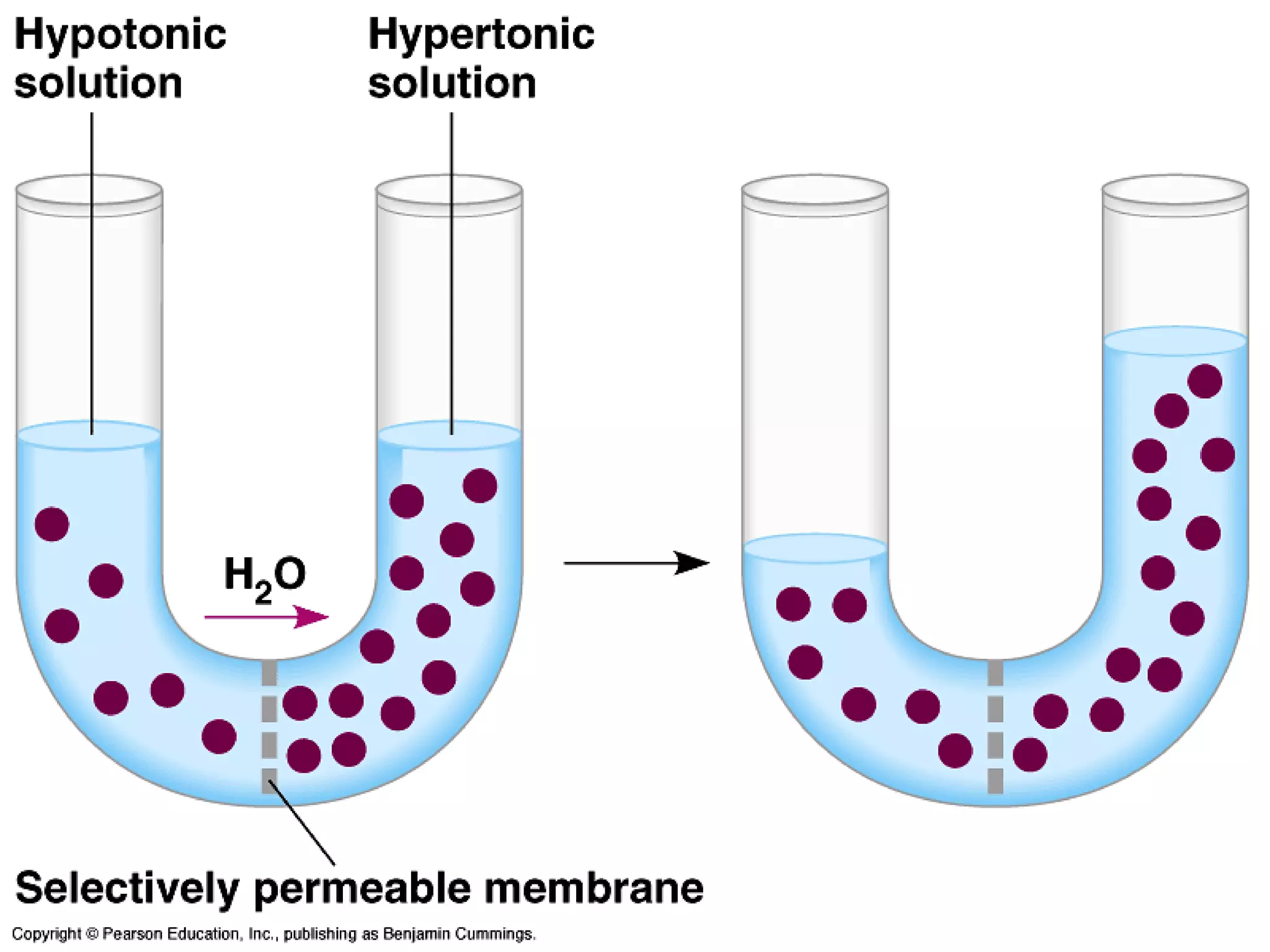
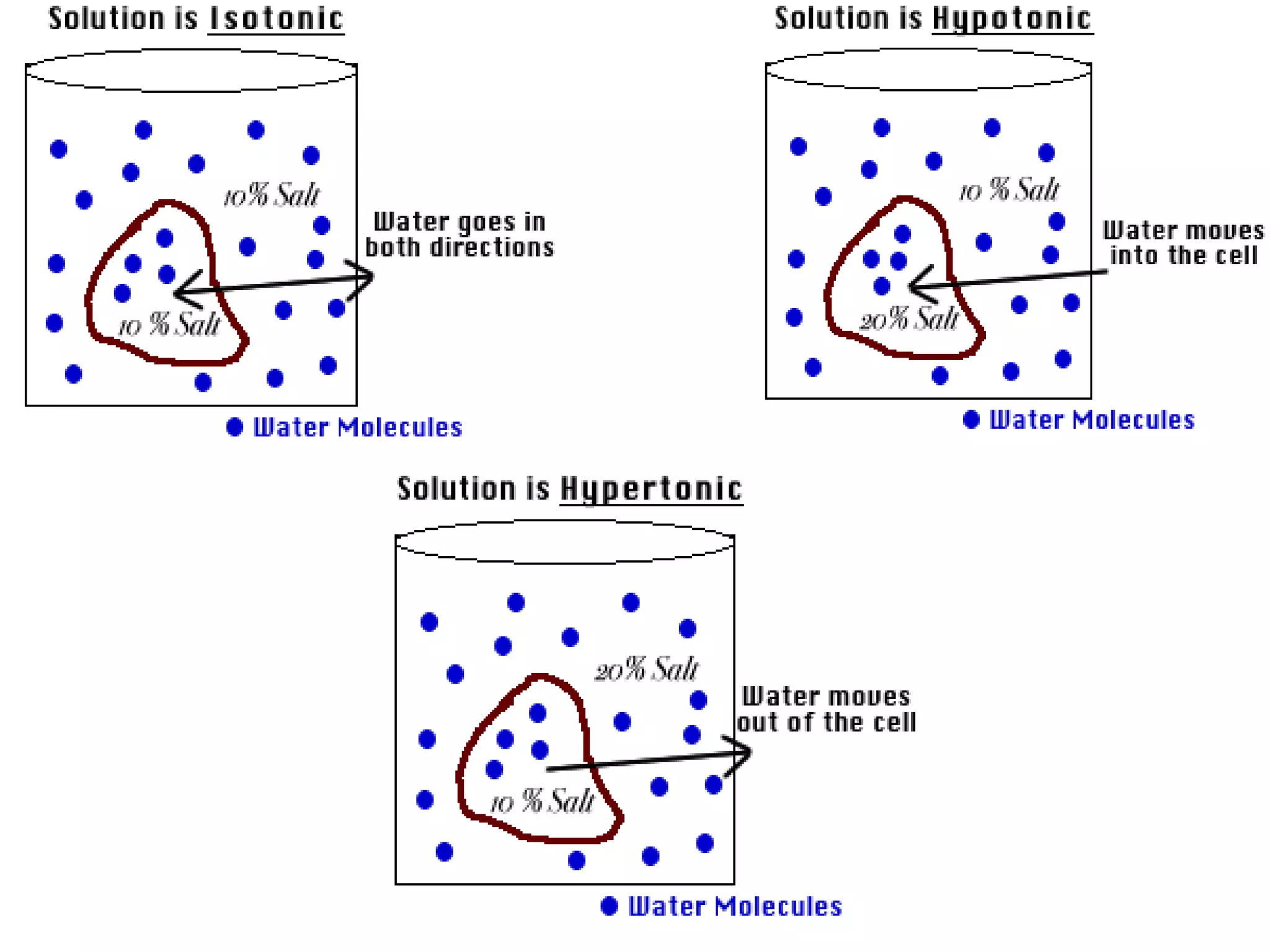
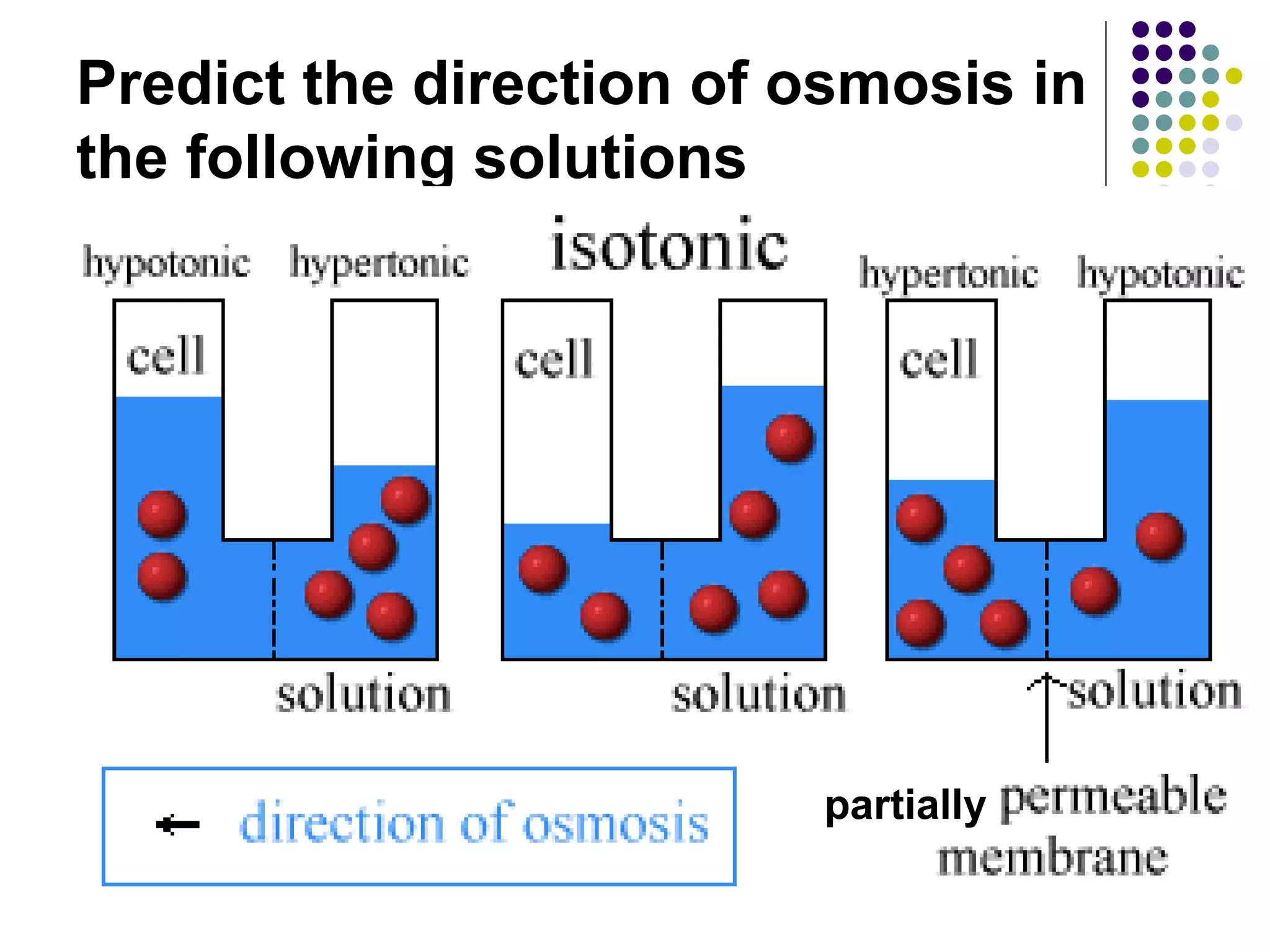
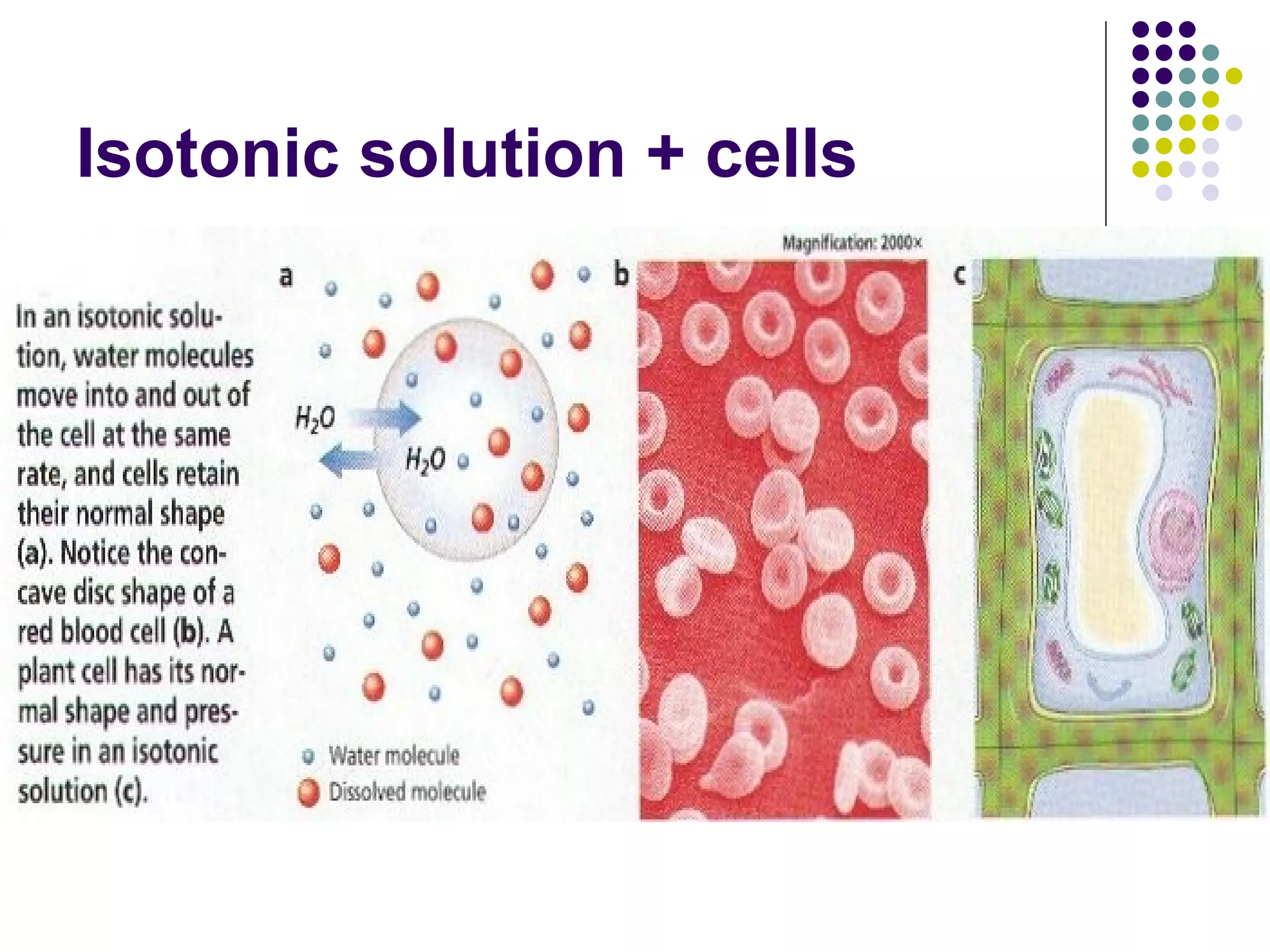
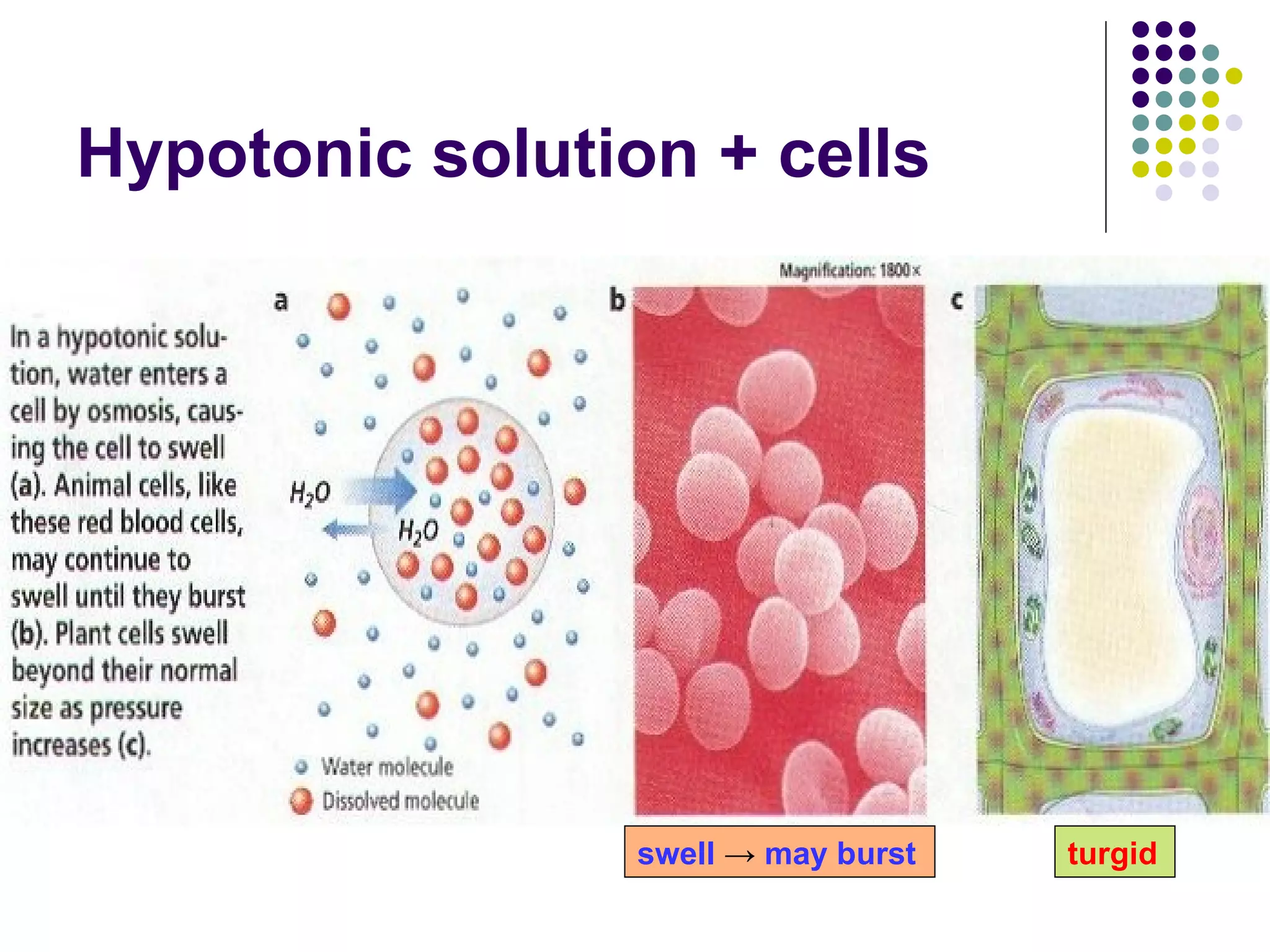
An isotonic solution has an equal concentration to a cell, so there is no net movement of water into or out of the cell. A hypotonic solution has a lower concentration than a cell, so water will move into the cell by osmosis, causing it to swell. A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration than a cell, so water will move out of the cell by osmosis, causing it to shrink or crenate.

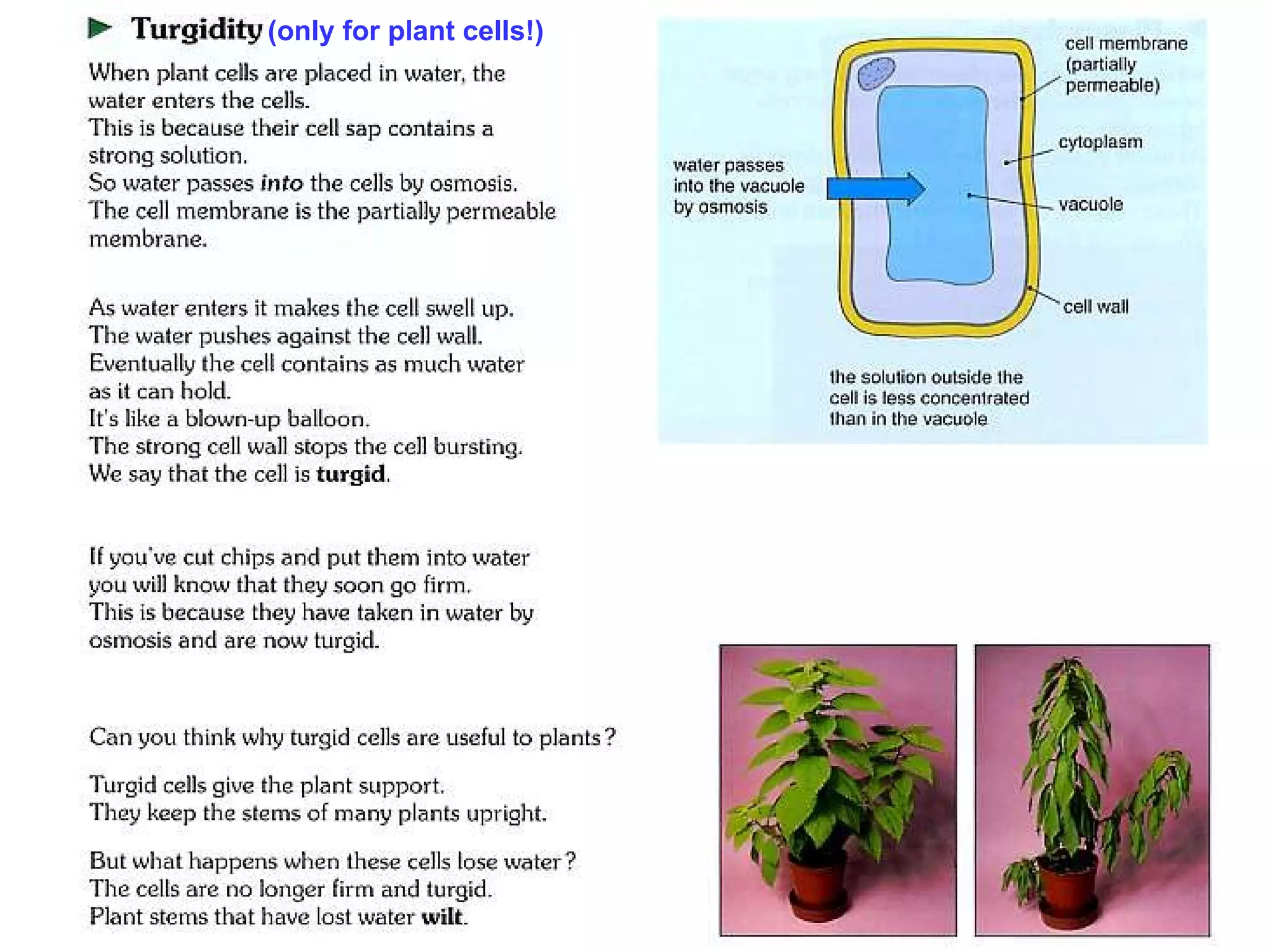
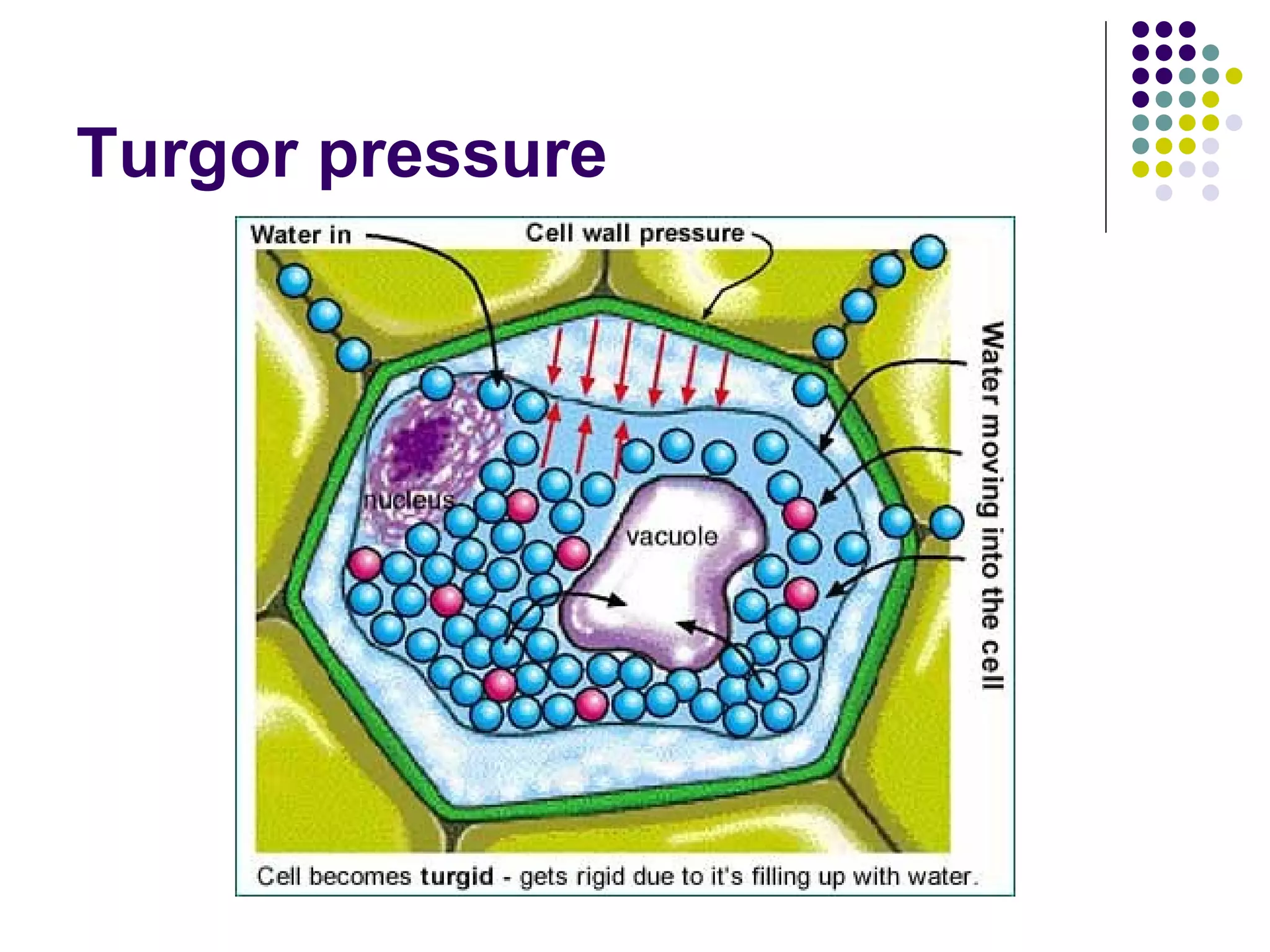
![Turgidity Maintains shape of soft plant tissues [provides support (water sufficient)/ wilts (lack of water -> control fertilizer input )] Responsible for movement in plants e.g. mimosa -> changes in turgor in small swellings at the base of leaflets e.g. flowers opening in day and closing at night/ bending of petals](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2isotonichypotonichypertonicsolns-101012005348-phpapp01/75/Chapter-3-Movement-of-Substances-Lesson-2-Effects-of-isotonic-hypotonic-hypertonic-solutions-on-cells-12-2048.jpg)