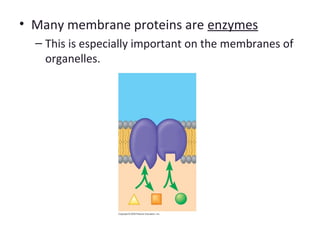
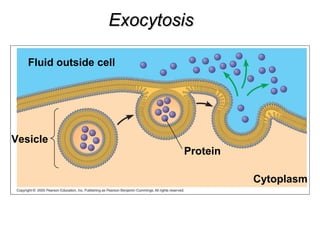
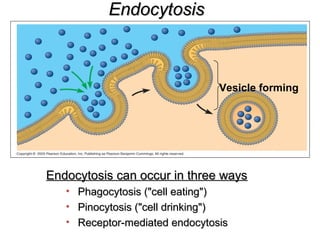
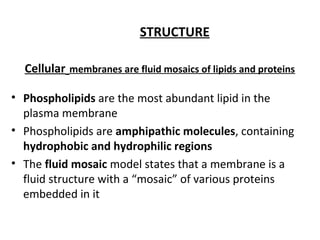
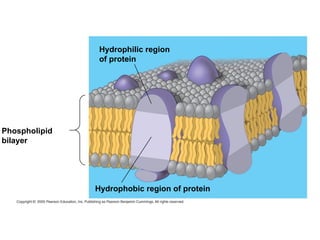
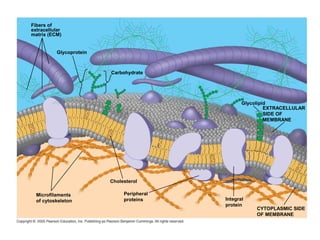
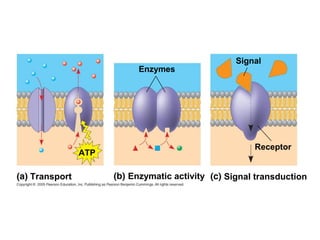
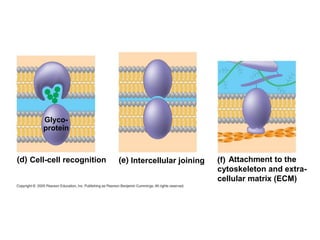
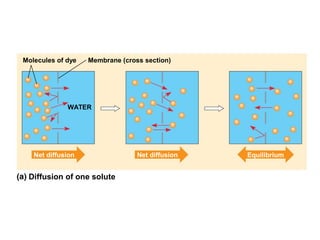
The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable barrier that separates the cell from its external environment. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules with hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads that form a fluid bilayer. The fluid mosaic model describes membranes as a fluid structure with various proteins embedded within. Membranes exhibit selective permeability through diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport. Active transport requires ATP and moves molecules against their concentration gradient. The sodium-potassium pump is an example of active transport that helps maintain membrane potential.

































![Cytoplasmic Na+
bonds to
the sodium-potassium pump
CYTOPLASM
Na+
[Na+
] low
[K+
] high
Na+
Na+
EXTRACELLULAR
FLUID
[Na+
] high
[K+
] low
Na+
Na+
Na+
ATP
ADP
P
Na+
binding stimulates
phosphorylation by ATP.
Na+
Na+
Na+
K+
Phosphorylation causes
the protein to change its
conformation, expelling Na+
to the outside.
P
Extracellular K+
binds
to the protein, triggering
release of the phosphate
group.
P
P
Loss of the phosphate
restores the protein’s
original conformation.
K+
is released and Na+
sites are receptive again;
the cycle repeats.
K+
K+
K+
K+
K+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plasmamembrane-150214210618-conversion-gate01/85/Plasma-membrane-40-320.jpg)