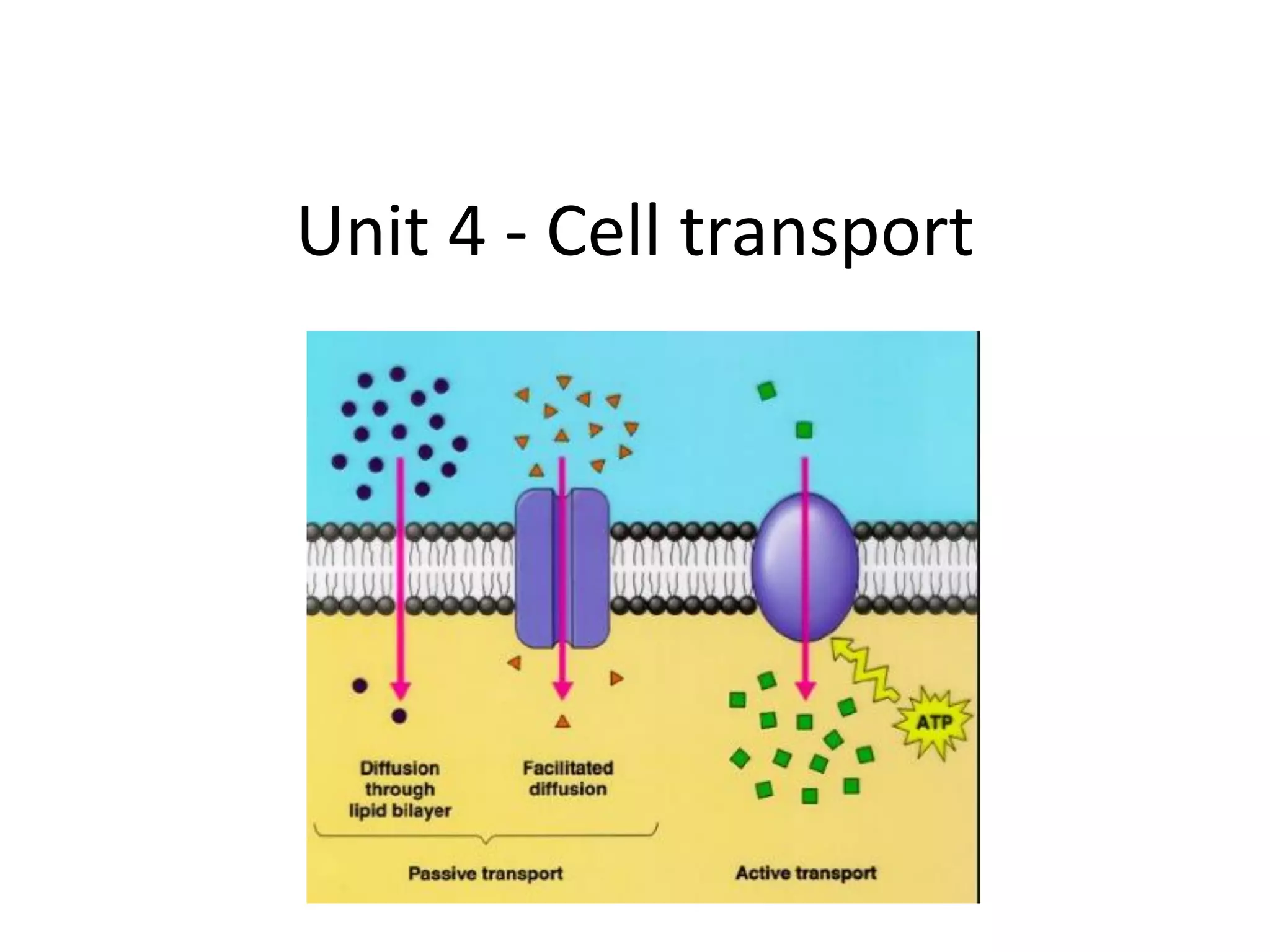
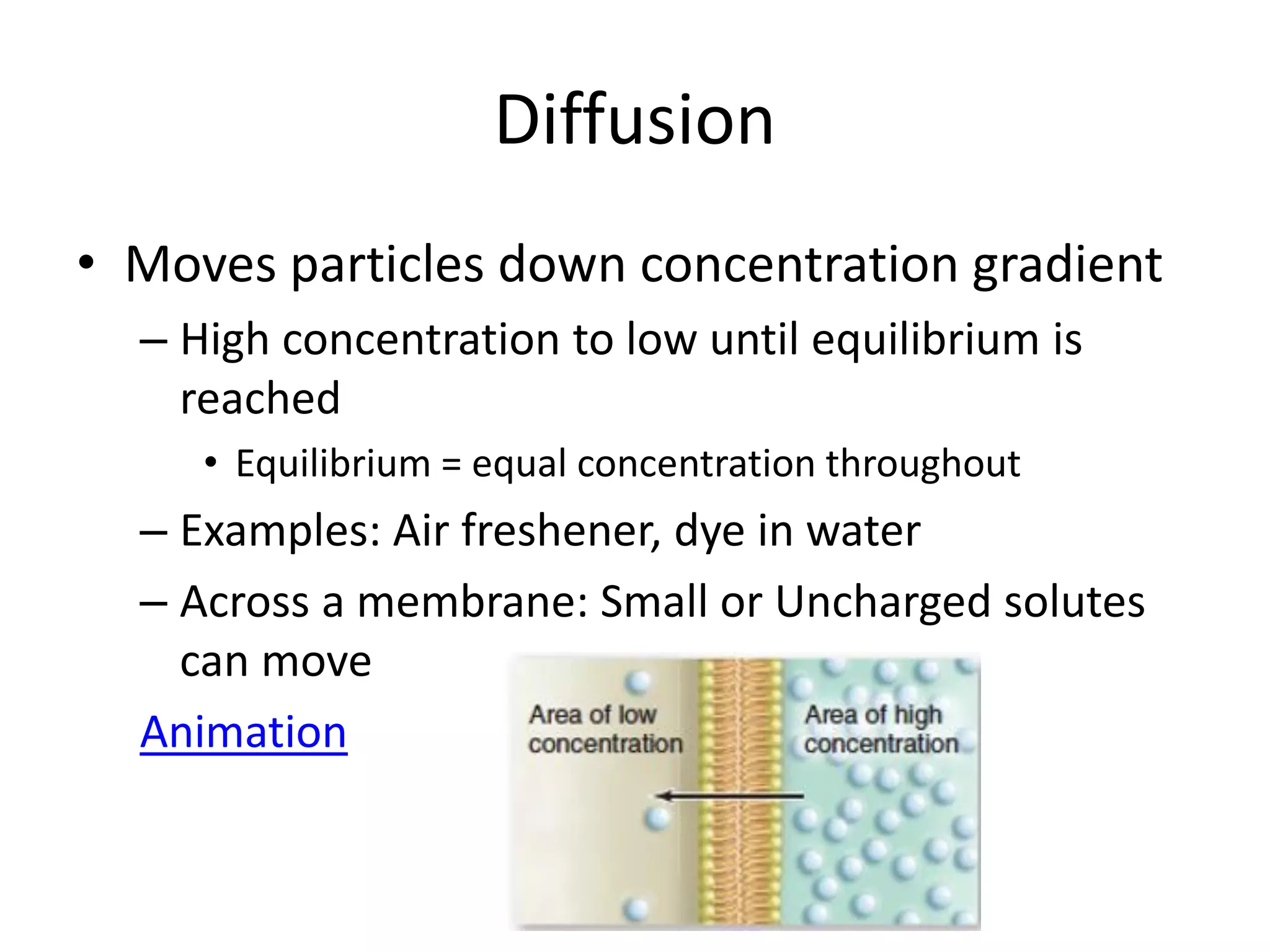
The cell membrane regulates what enters and exits the cell through selective permeability. Small, uncharged molecules can pass through the phospholipid bilayer via diffusion. Larger or charged molecules require transport proteins to cross via facilitated diffusion. Water moves in and out of cells through osmosis in order to balance solute concentrations; it will diffuse into areas of higher solute concentration. The membrane also uses active transport and bulk transport like exocytosis and endocytosis to move molecules against gradients or transport larger particles, requiring energy in the form of ATP.