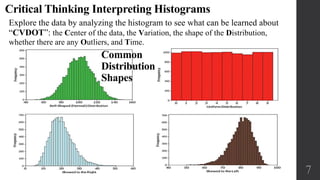
This document discusses histograms and frequency distributions for organizing and summarizing data. It defines key terms like frequency distribution, class limits, and histograms. Histograms are described as bar graphs that visually display the shape, center, and spread of data distribution. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to construct histograms and interpret their features. Different common distribution shapes like normal, skewed left, and skewed right are illustrated. The document also introduces normal quantile plots as another tool to assess normality of data distribution by examining how closely the points follow a straight line pattern.