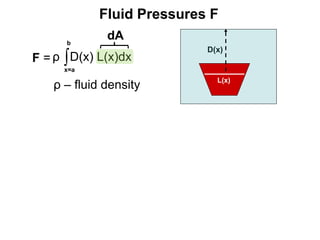
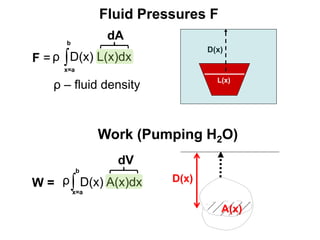
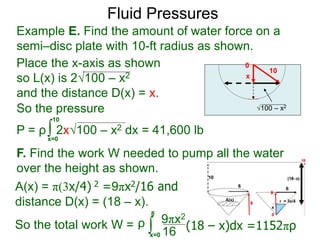
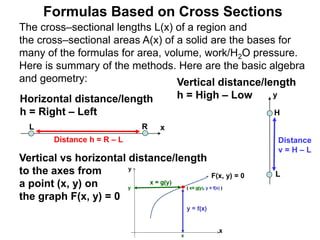
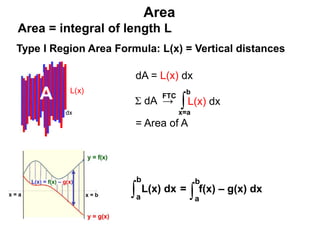
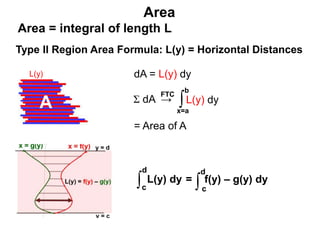
1) The document discusses formulas for calculating area, volume, fluid pressure, and work based on the cross-sectional lengths and areas of regions and solids.
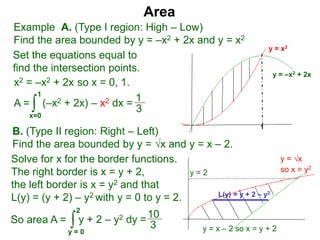
2) It provides examples of calculating the area of regions bounded by functions, the volume of solids of revolution, fluid pressure on a plate, and work needed to pump water.
3) The key concepts are using integrals to calculate quantities by summing cross-sectional lengths or areas and defining these lengths and areas based on the geometry of regions and solids.

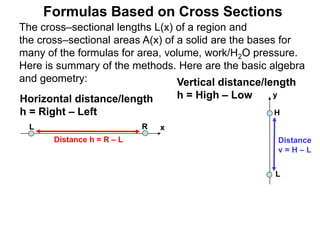
![dV = A(x) dx
V A(x)
dx
Σ dV → ∫
x=a
b
A(x) dx
= Volume of V
FTC
Volume = integral of area
Volume of revolution–solid
Solids of Revolution
∫
x=a
b
dx
V = π [f (x)]2
Cross–section–area A(x) = π [f (x)]2:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10-breview-cross-sectionalformula-210904002332/85/10-b-review-cross-sectional-formula-7-320.jpg)
![dV = A(y) dy
V
A(y)
dy
Σ dV → ∫
x=a
b
A(y) dy
= Volume of V
FTC
∫y=a
dy
π [f (y)]2
V =
Solids of Revolution
Volume = integral of area
Volume of revolution–solid
Cross–section–area A(x) = π [f (y)]2:
b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10-breview-cross-sectionalformula-210904002332/85/10-b-review-cross-sectional-formula-8-320.jpg)
![Solids of Revolution
Example C. Find the volume of revolution around the
x axis formed by the curve y = √x from x = 0 to x = 2.
The cross–sections are discs with
radius r = √x so A(x) = π (√x)2.
∫
x=0
2
dx
So the volume V = πx = 2π
∫
y=1
π [(1/2 + y–1/2)2 – 1/2 2] dy
4
So the volume V =
D. Find the volume of revolution around
the axis x = –½ formed by the template as shown.
The inner radius r = ½,
outer radius R = ½ + y –1/2.
2
=19π](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10-breview-cross-sectionalformula-210904002332/85/10-b-review-cross-sectional-formula-9-320.jpg)