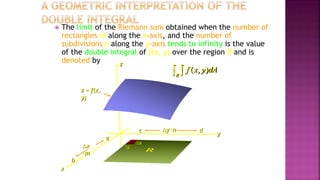
1. Double integrals allow us to calculate the volume of a solid bounded above by a surface z=f(x,y) and below by a plane region R. This is done by setting up a Riemann sum of the volumes of thin rectangular prisms.
2. The limit of the Riemann sum as the number of rectangles goes to infinity gives the double integral, written as ∫∫R f(x,y) dA.
3. Example problems demonstrate calculating the double integral to find the volume in different plane regions R, including those bounded by curves such as y=x2 and y=x.
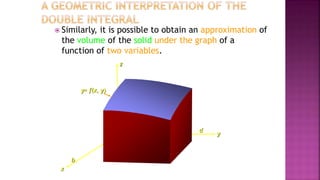
![ You may recall that we can do a Riemann sum to
approximate the area under the graph of a function
of one variable by adding the areas of the
rectangles that form below the graph resulting from
small increments of x (x) within a given interval
[a, b]:
x
y
y= f(x)
a b
x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doubleintegral-221024162612-6b23a964/85/double-integral-pptx-2-320.jpg)
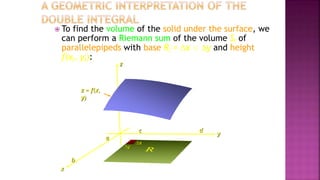
![a. Suppose g1(x) and g2(x) are continuous functions on [a, b] and
the region R is defined by R = {(x, y)| g1(x) y g2(x); a x b}.
Then,
2
1
( )
( )
( , ) ( , )
b g x
R a g x
f x y dA f x y dy dx
x
y
a b
y = g1(x)
y = g2(x)
R](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doubleintegral-221024162612-6b23a964/85/double-integral-pptx-4-320.jpg)


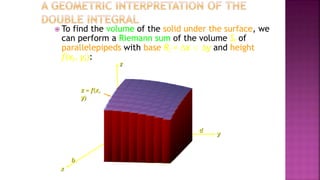
![b. Suppose h1(y) and h2(y) are continuous functions on [c, d]
and the region R is defined by R = {(x, y)| h1(y) x
h2(y); c y d}.
Then, 2
1
( )
( )
( , ) ( , )
d h y
R c h y
f x y dA f x y dx dy
x
y
c
d
x = h1(y) x = h2(y)
R](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doubleintegral-221024162612-6b23a964/85/double-integral-pptx-10-320.jpg)






