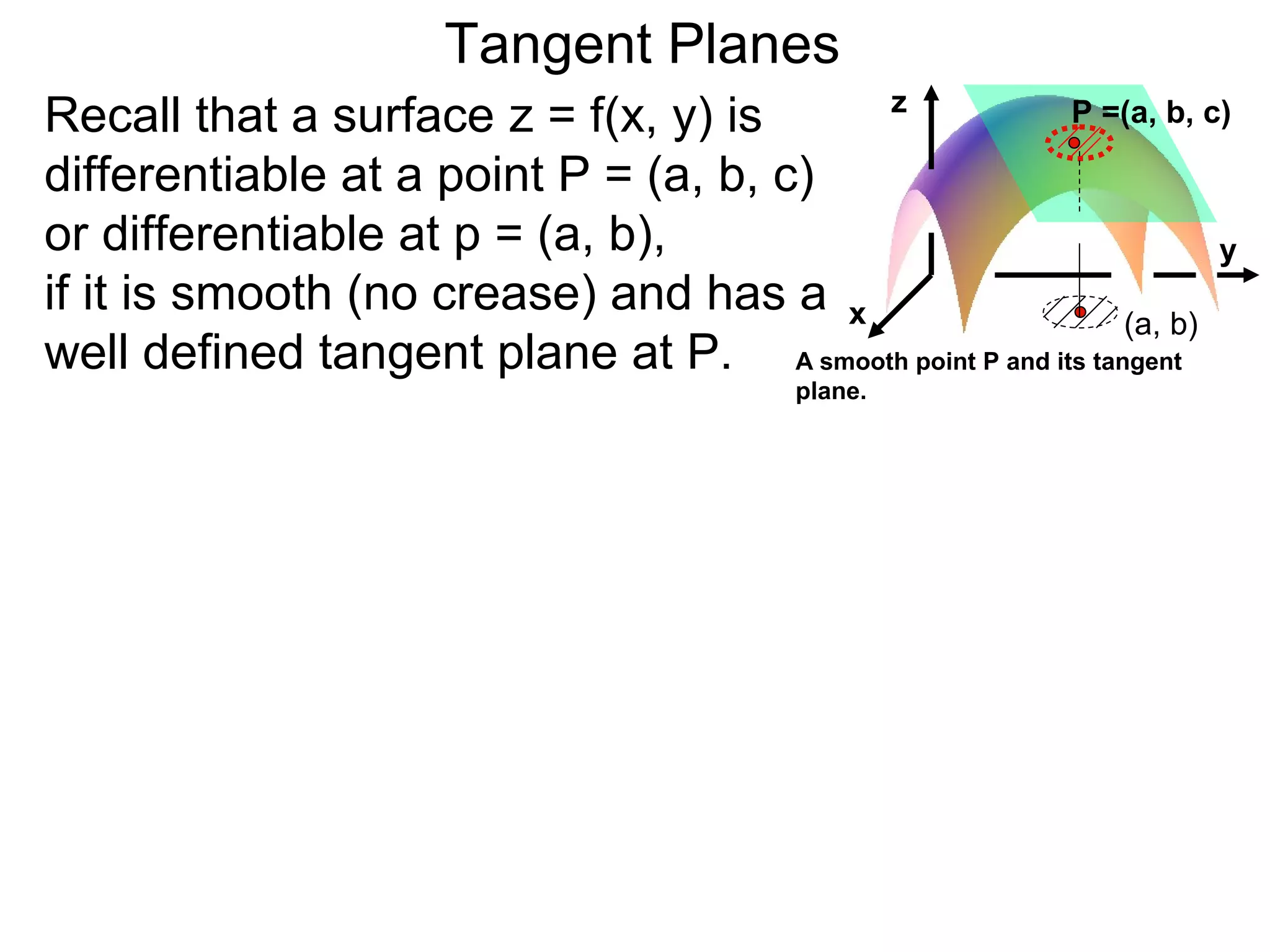
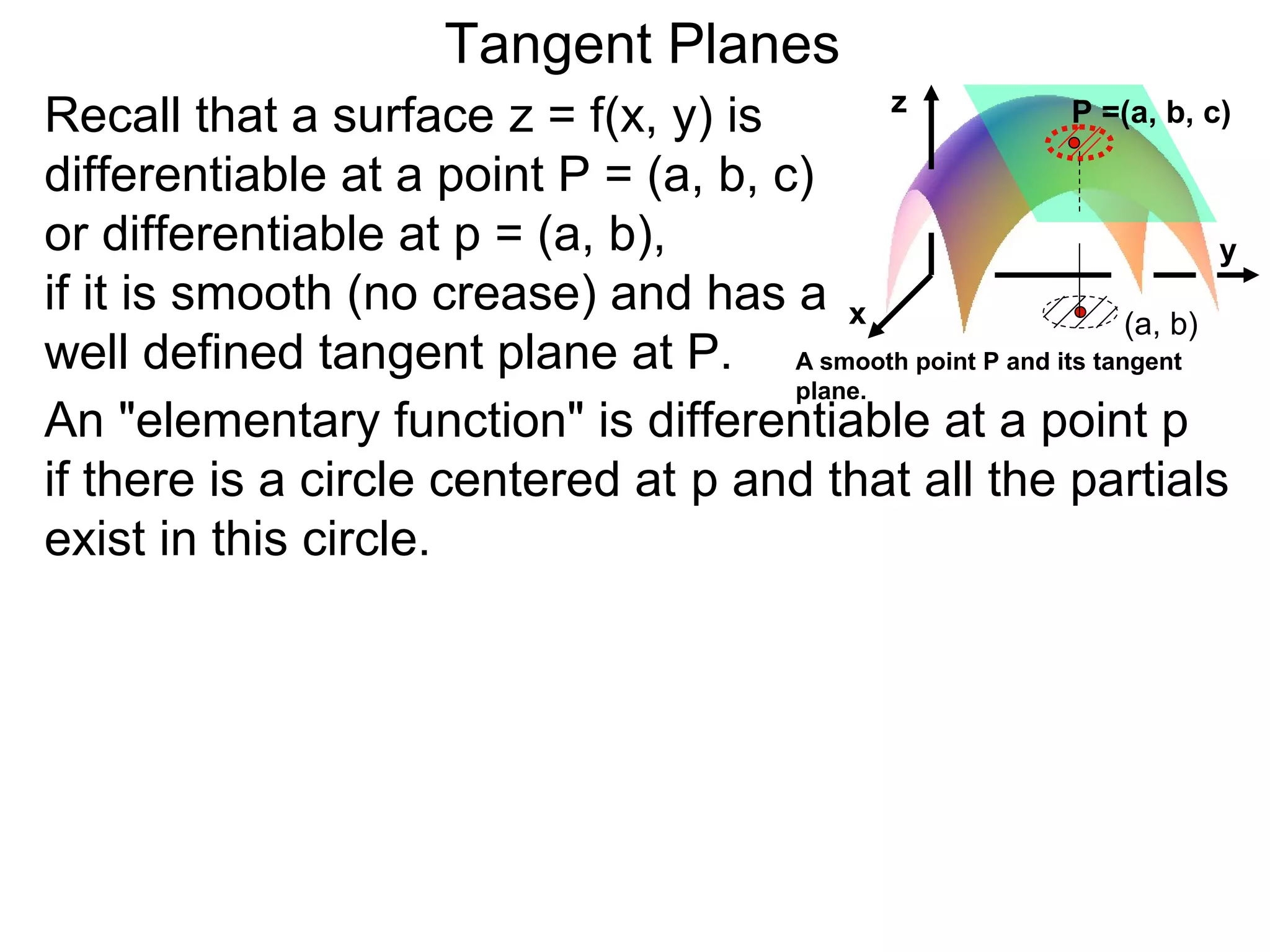
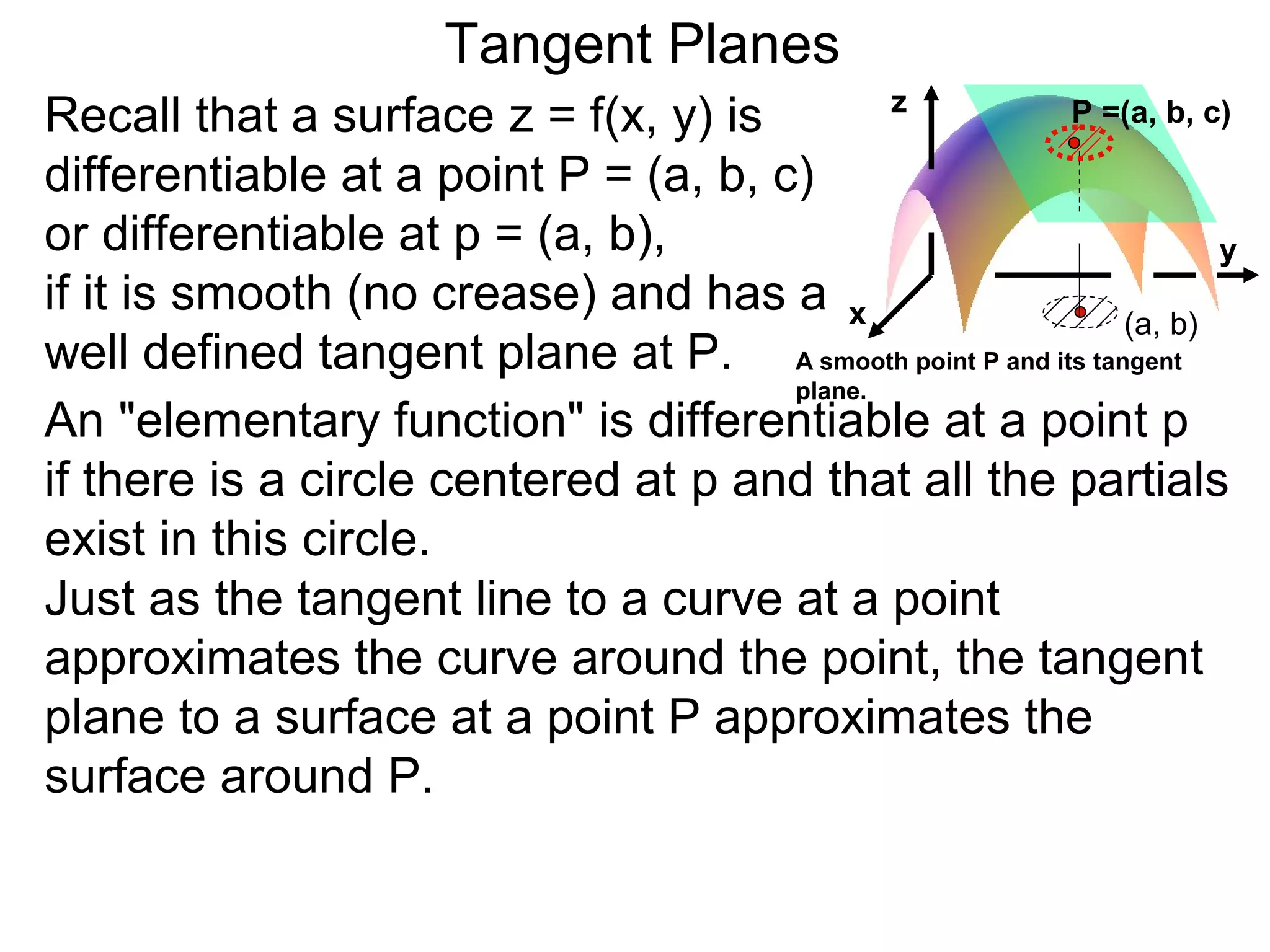
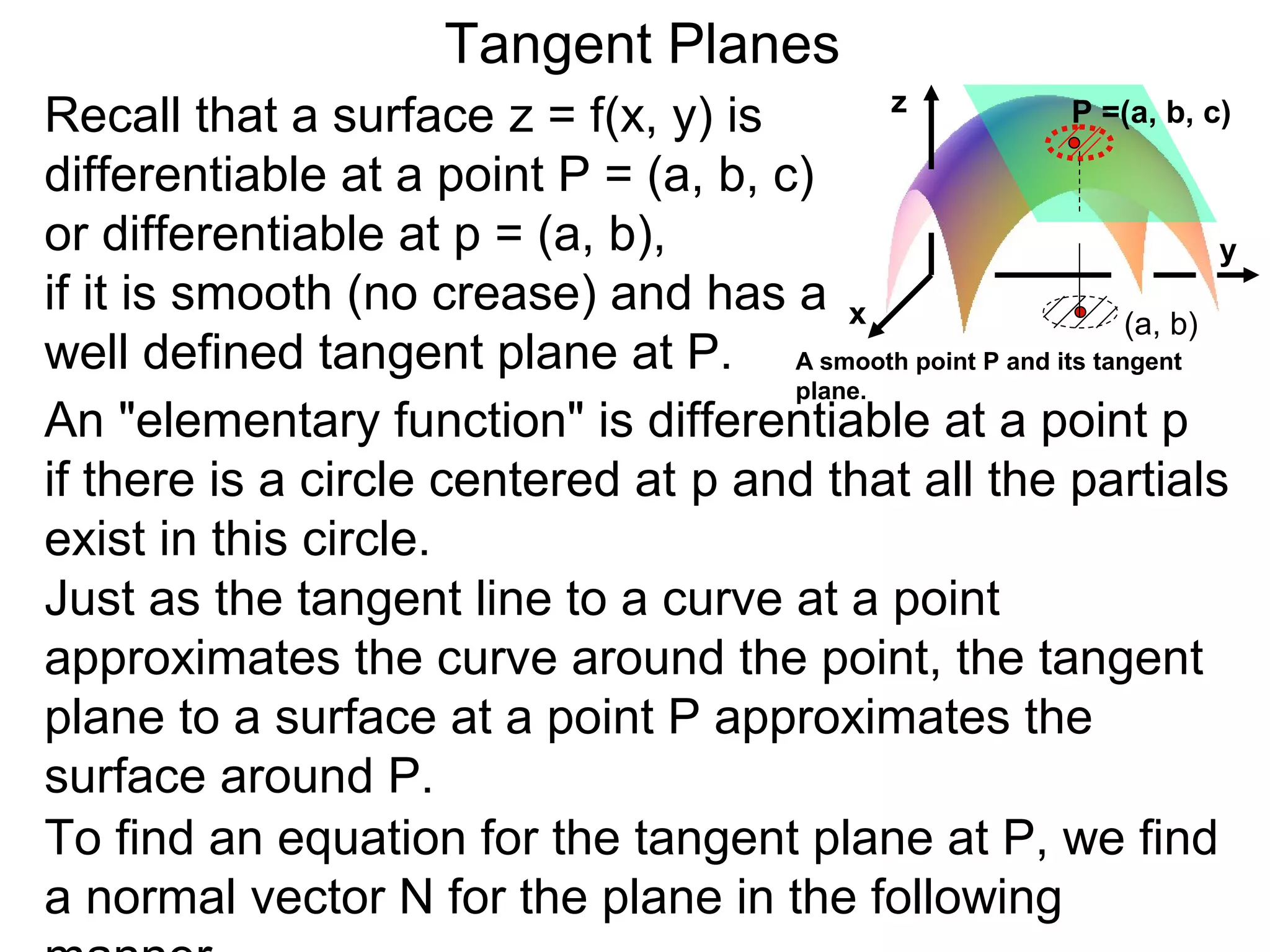
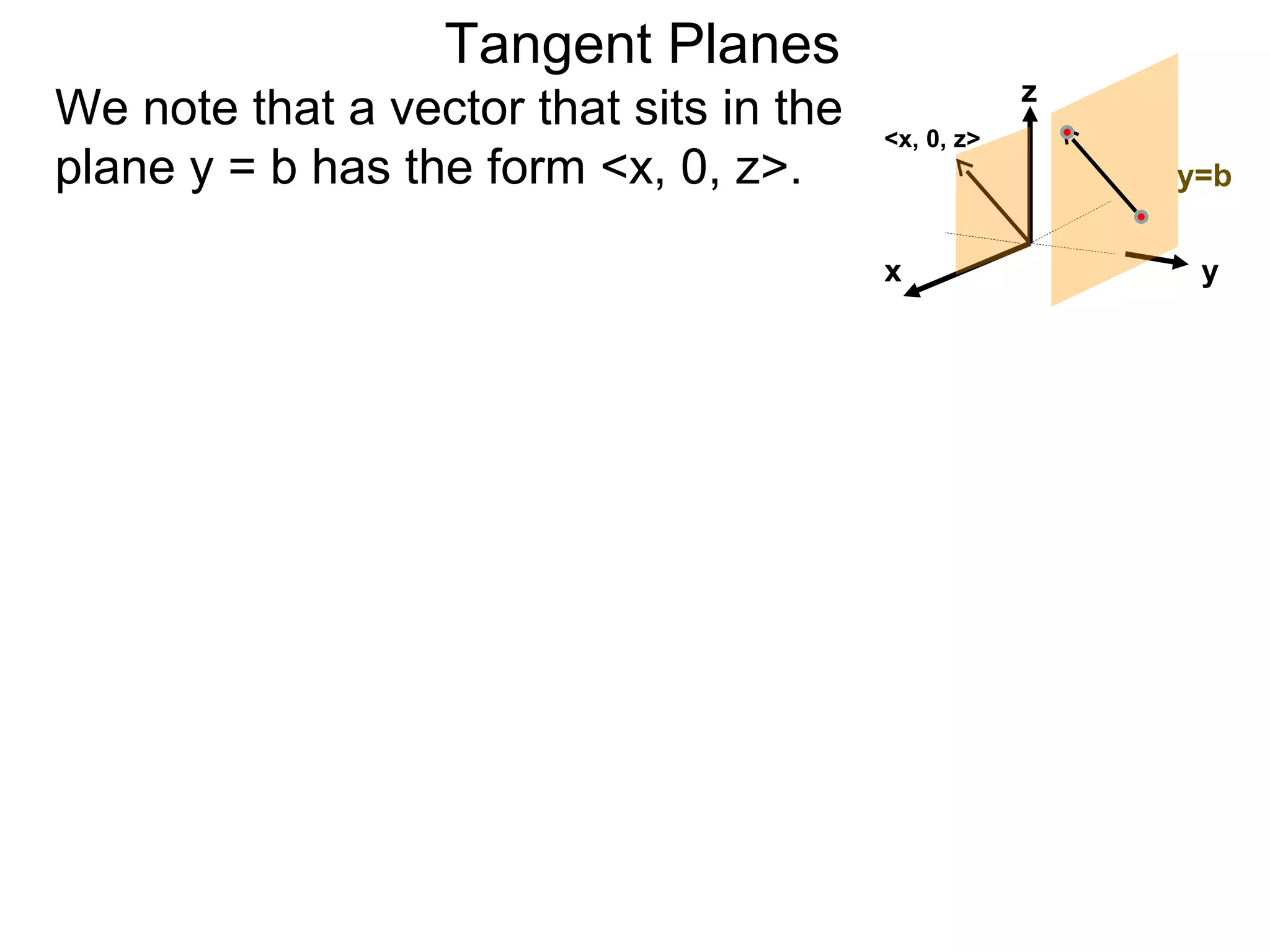
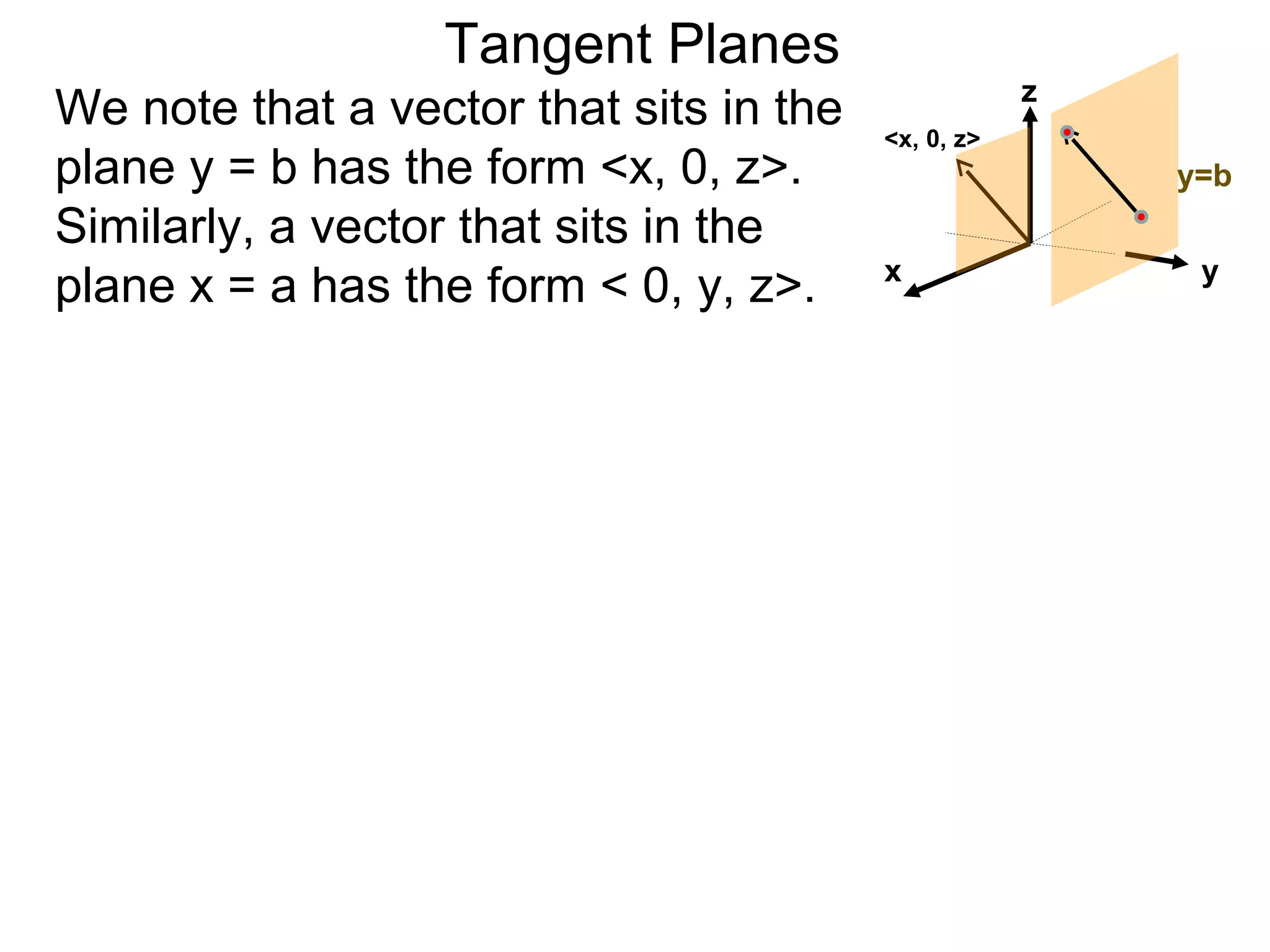
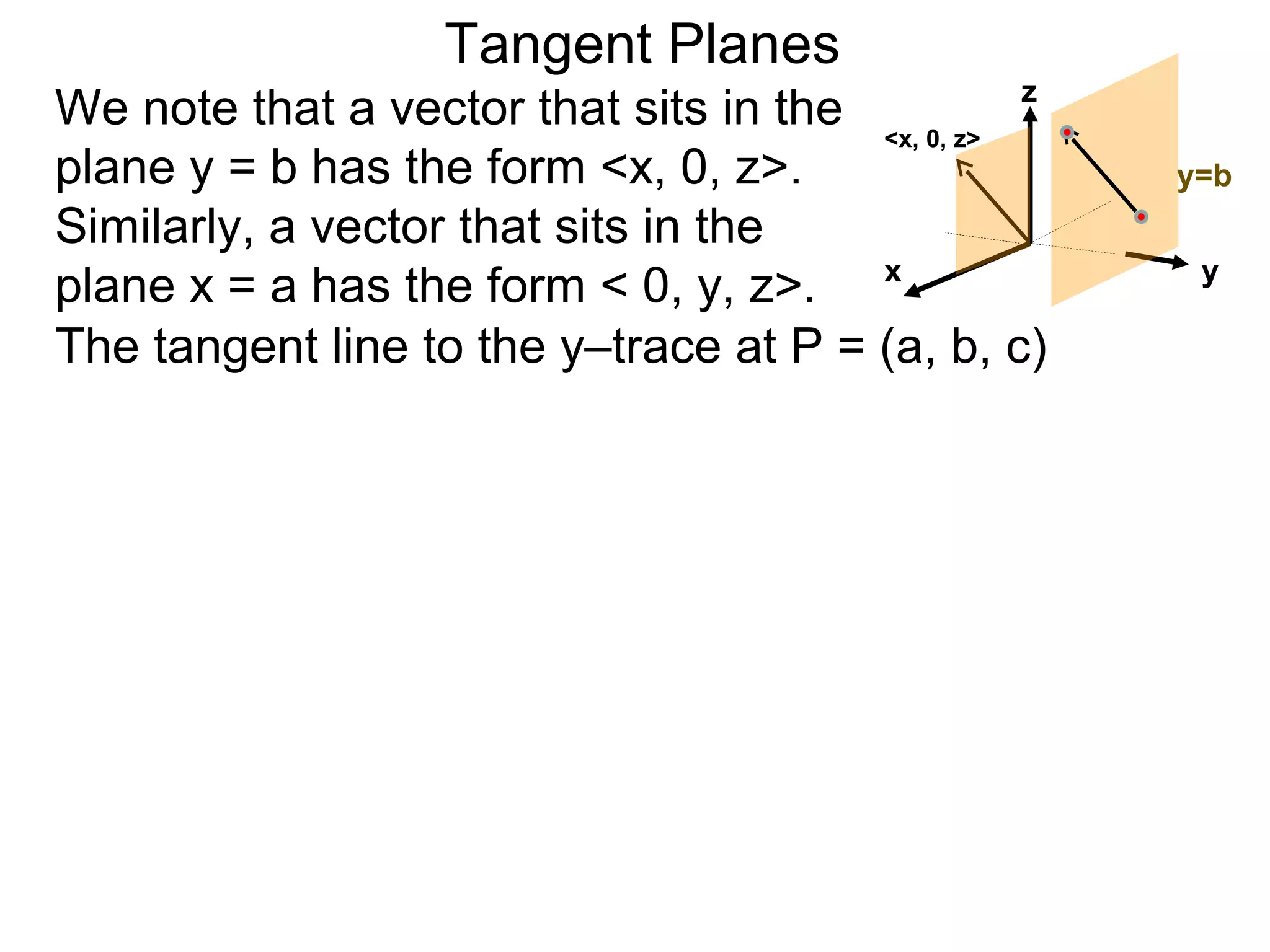
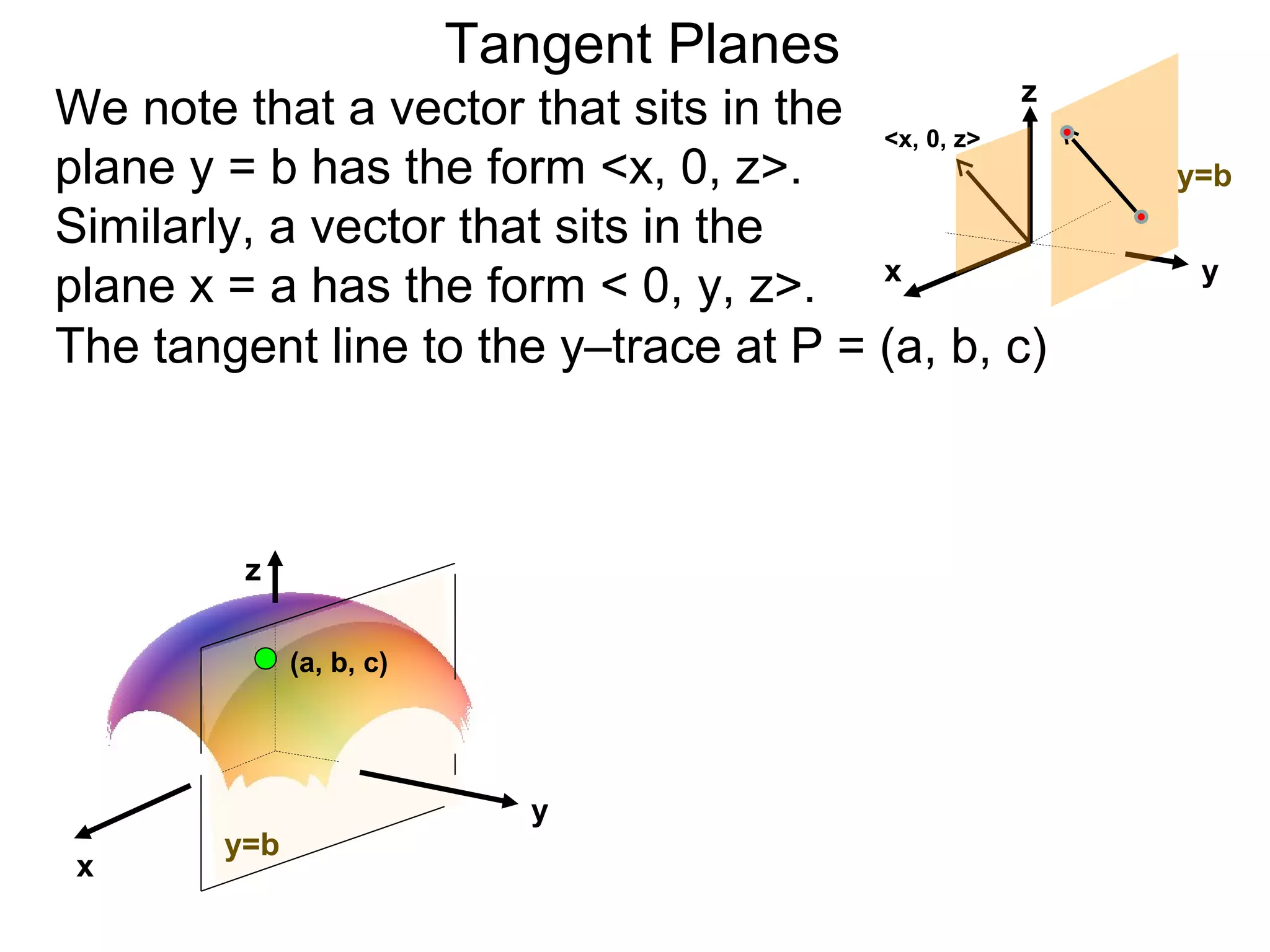
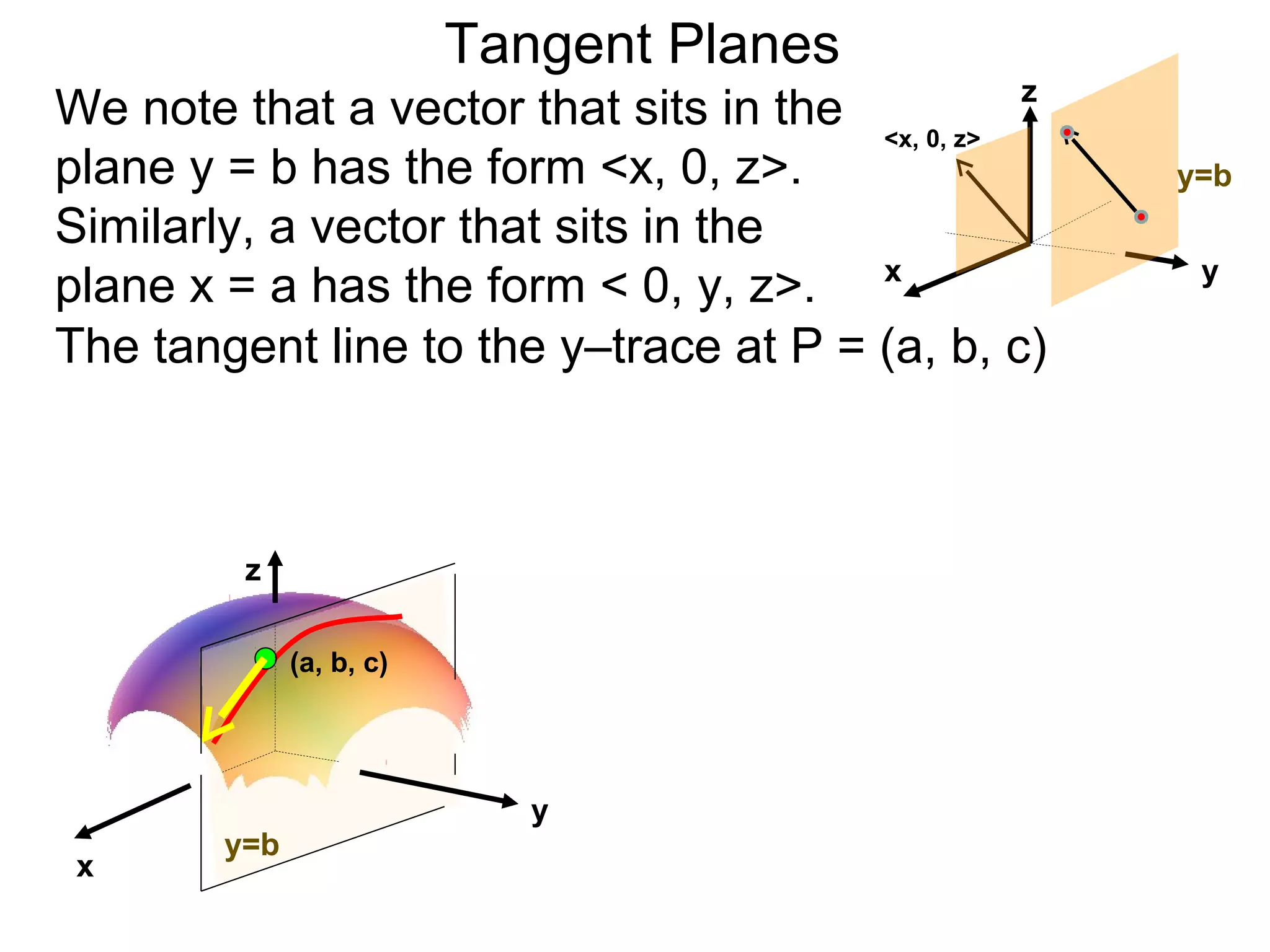
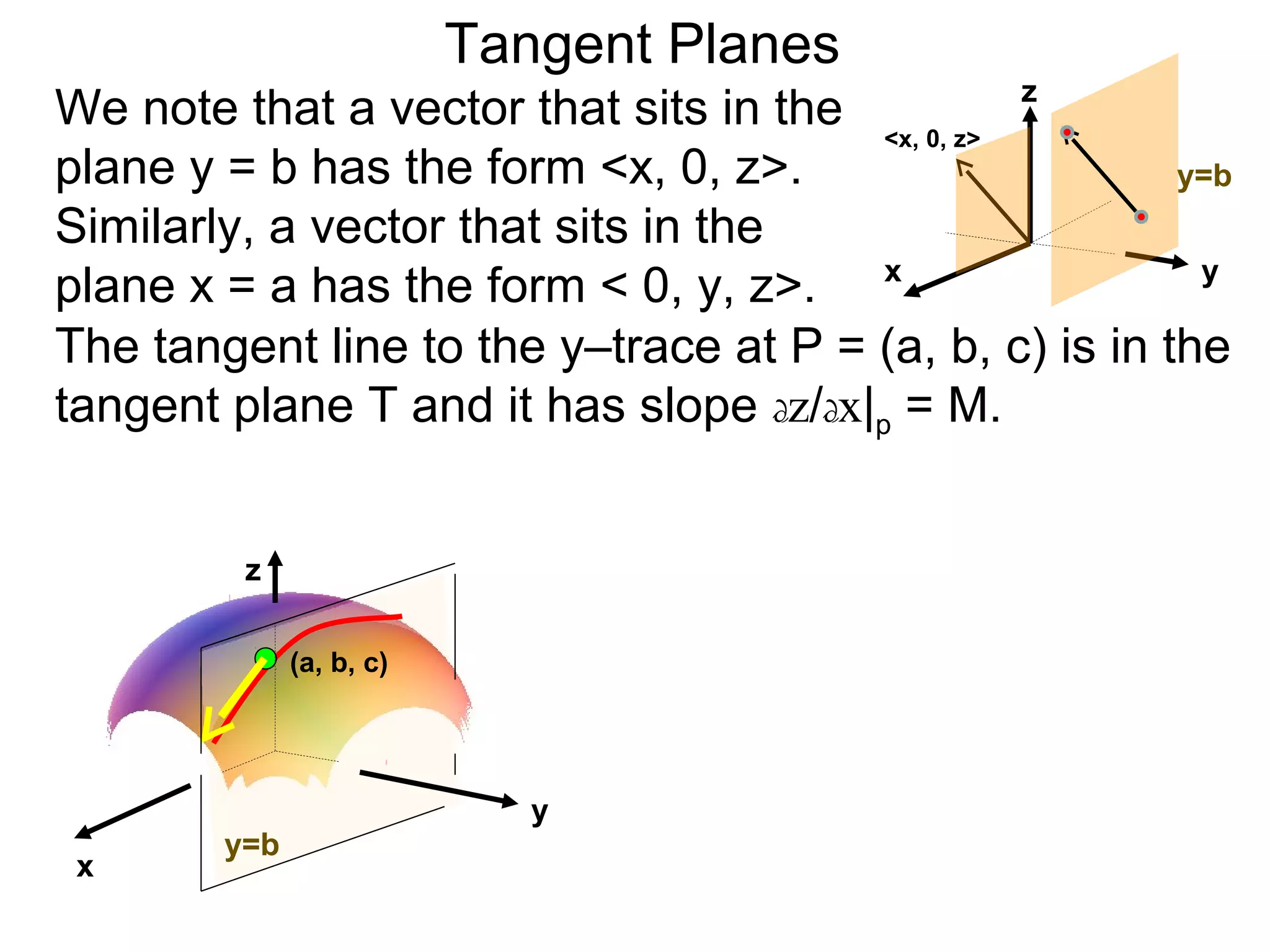
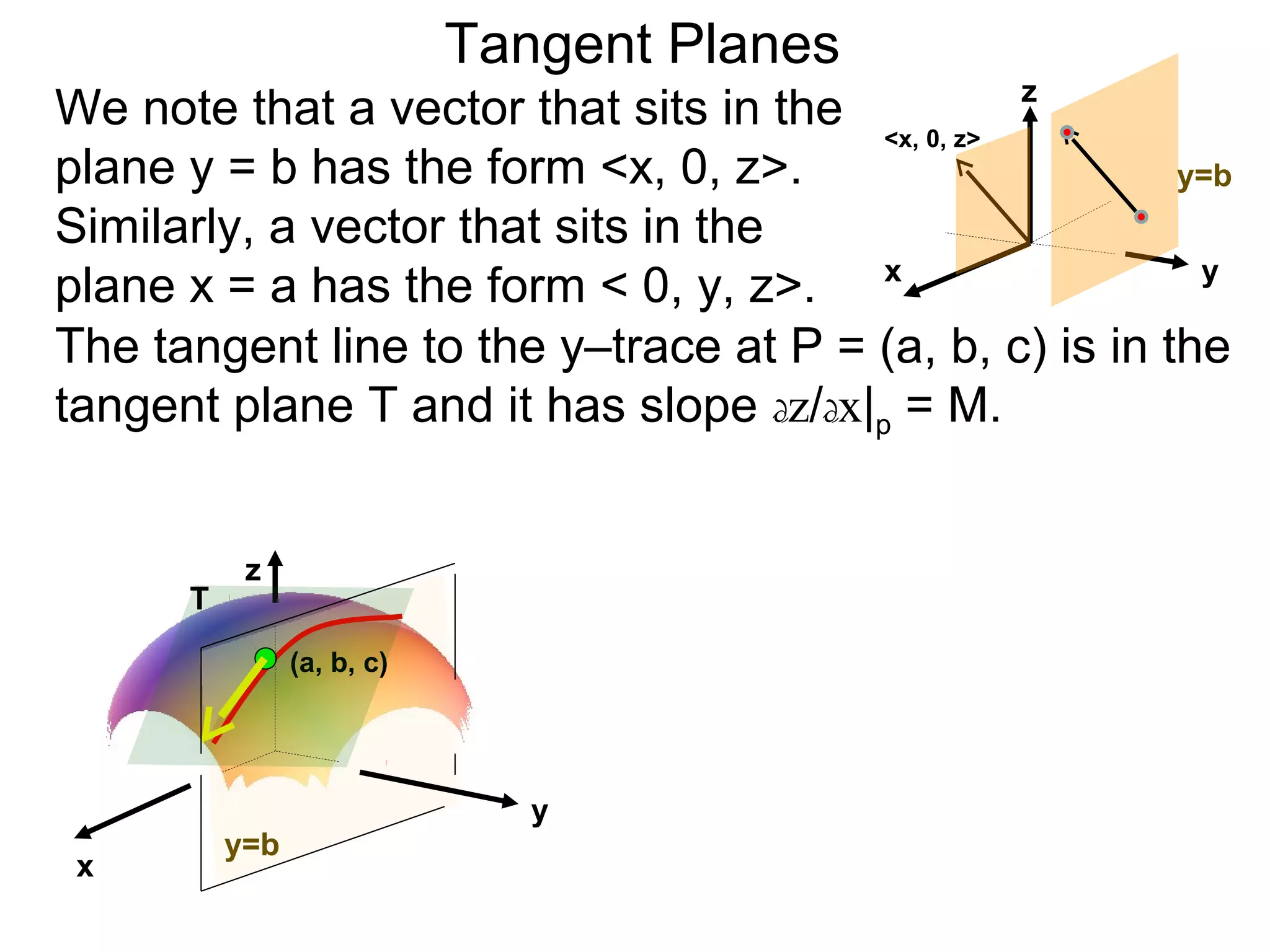
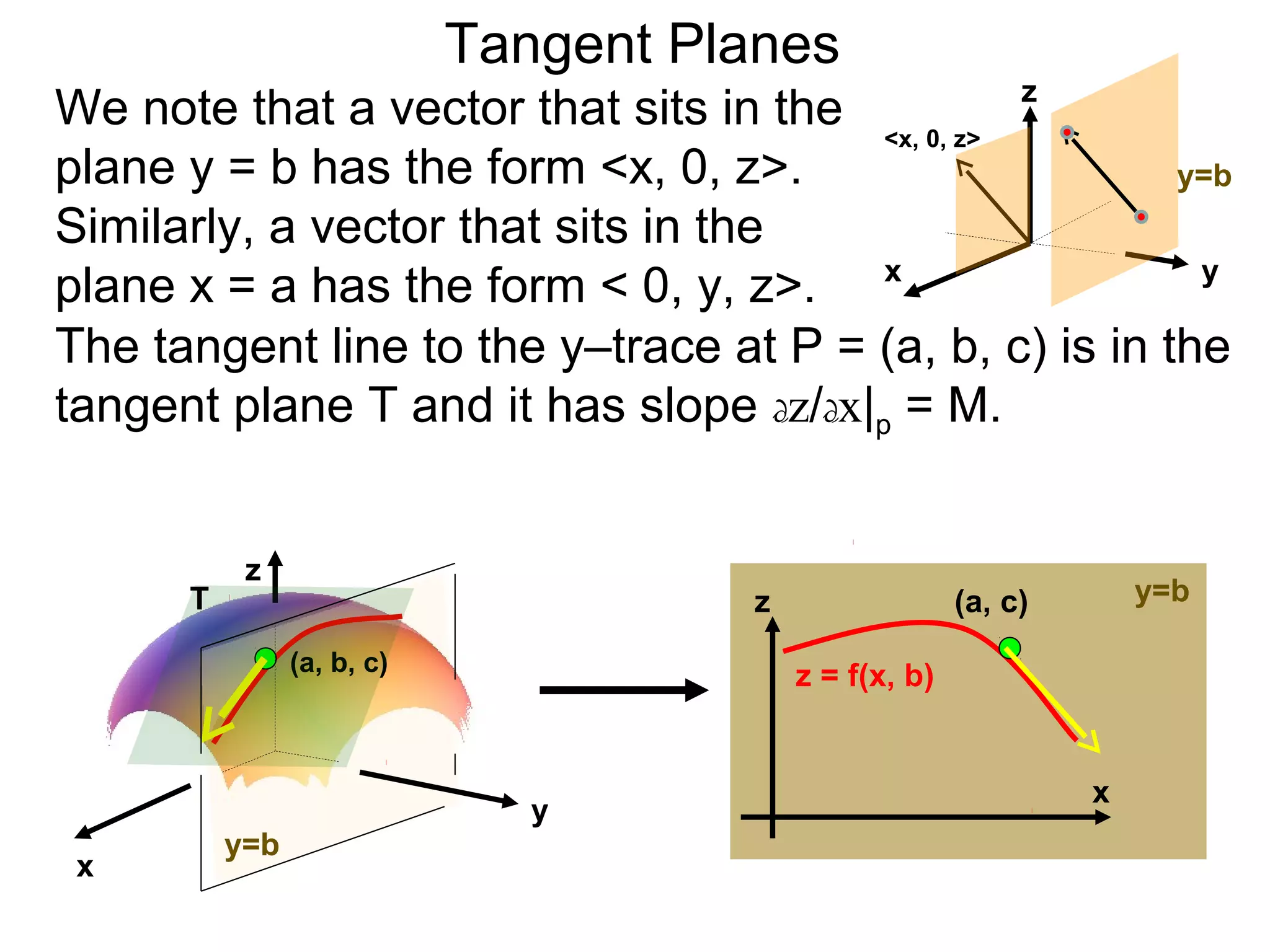
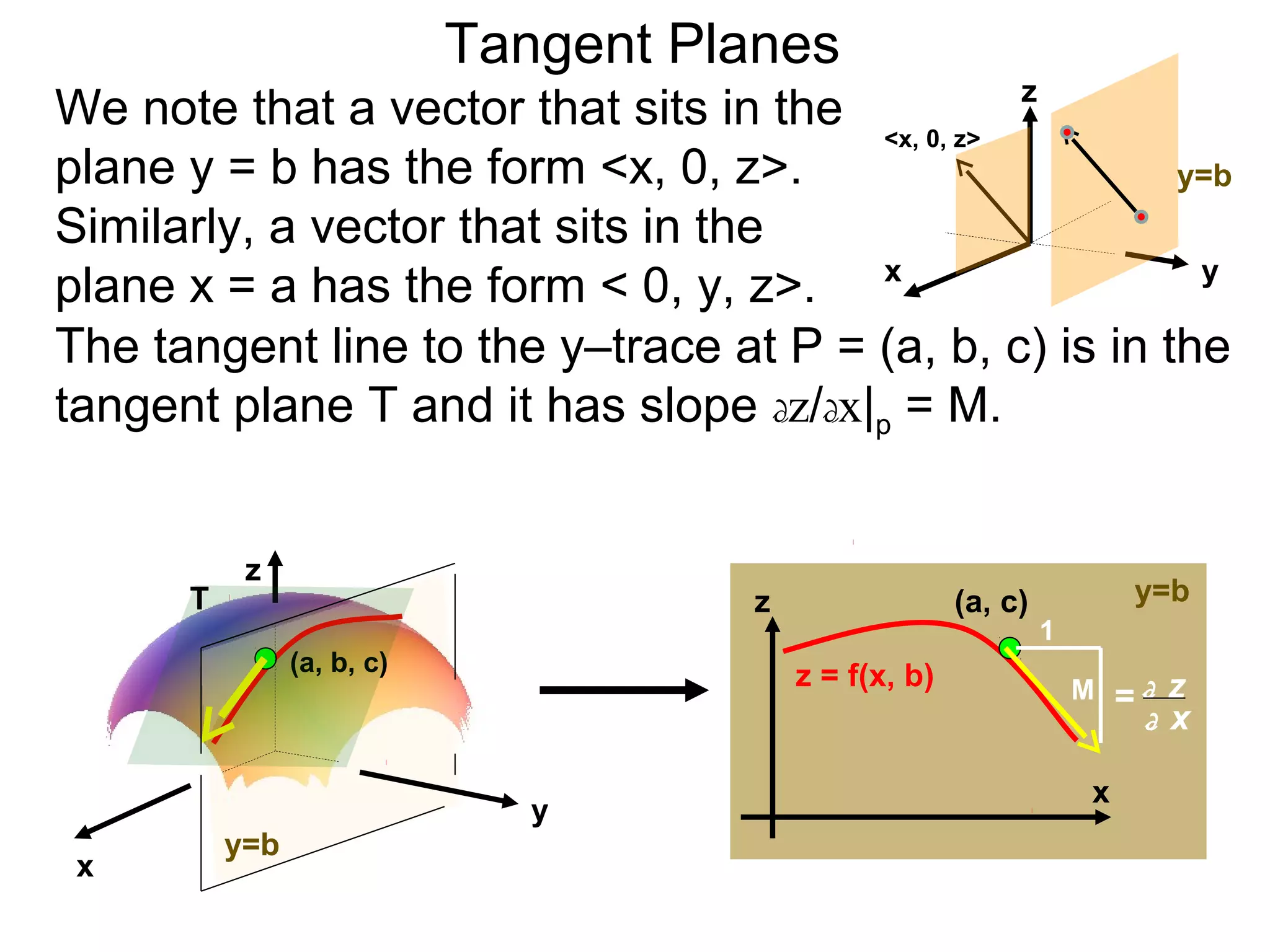
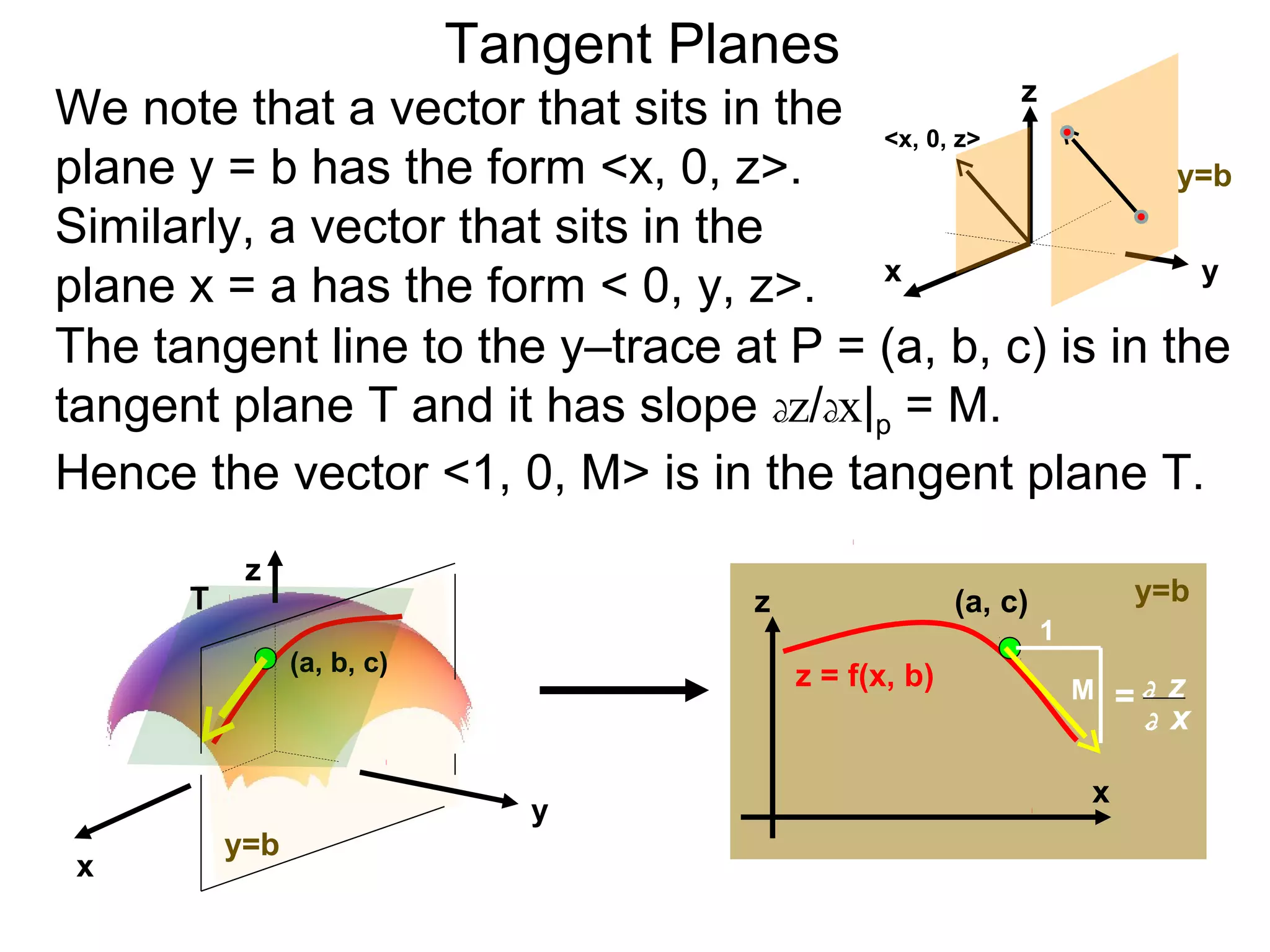
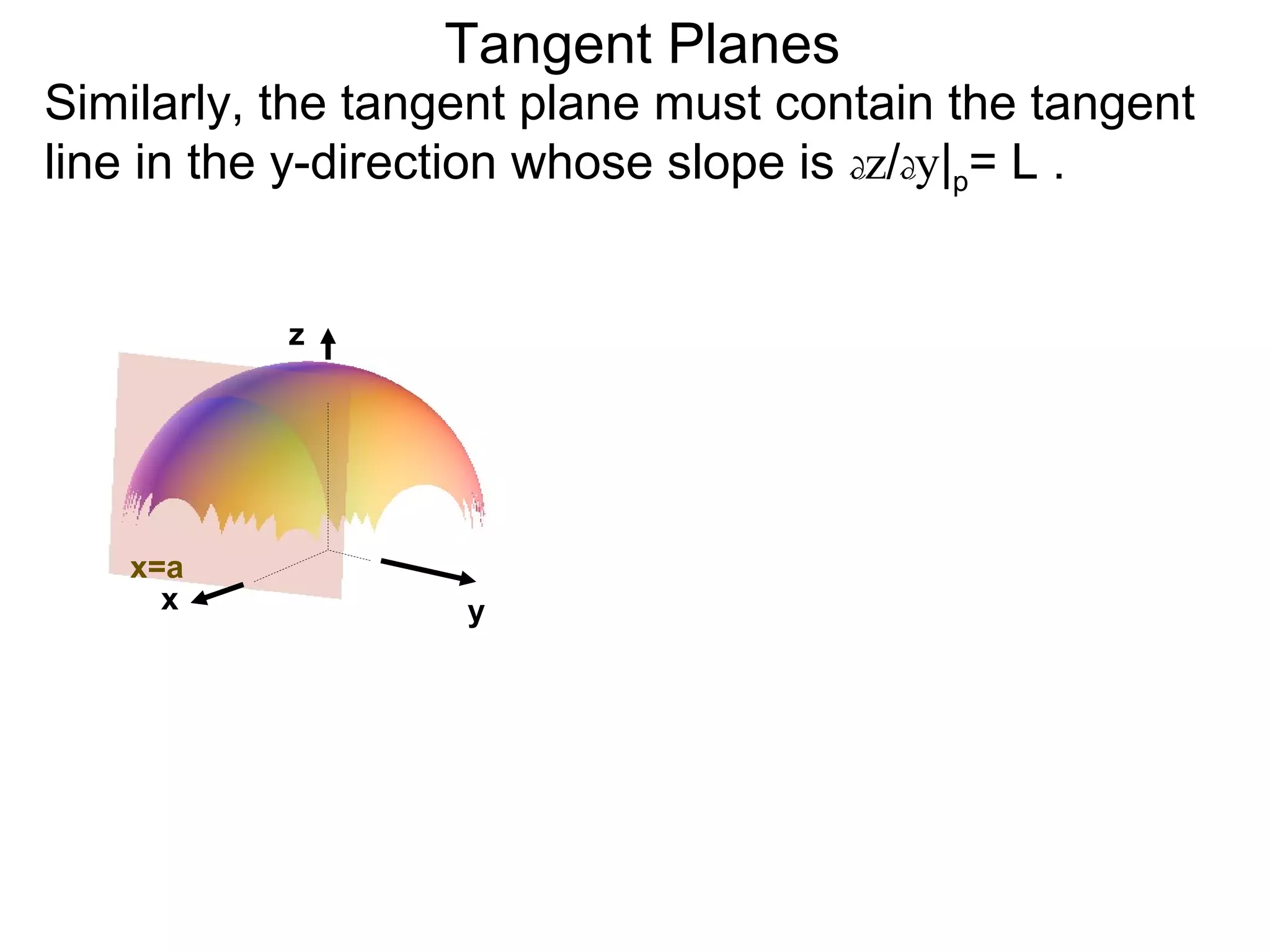
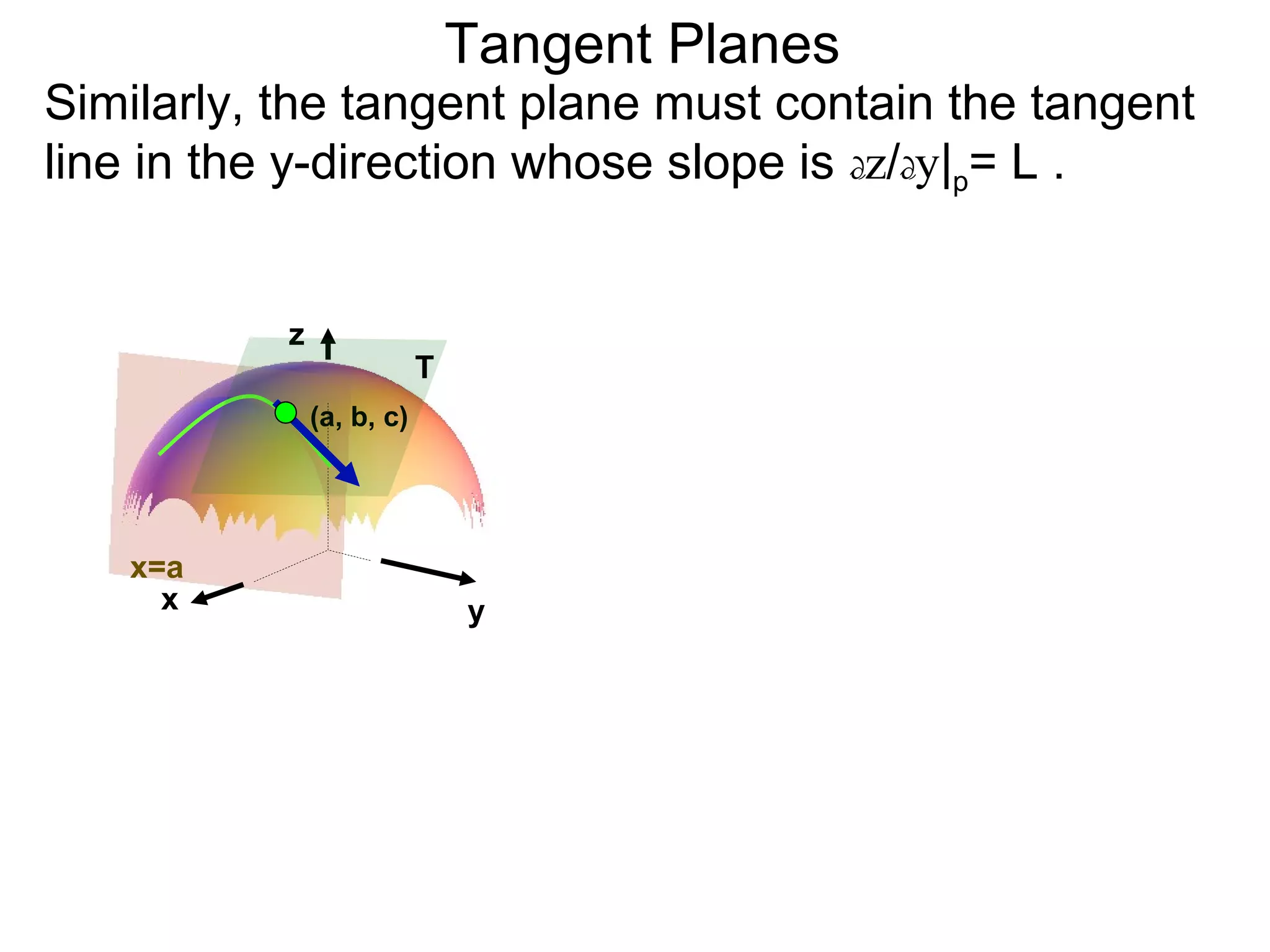
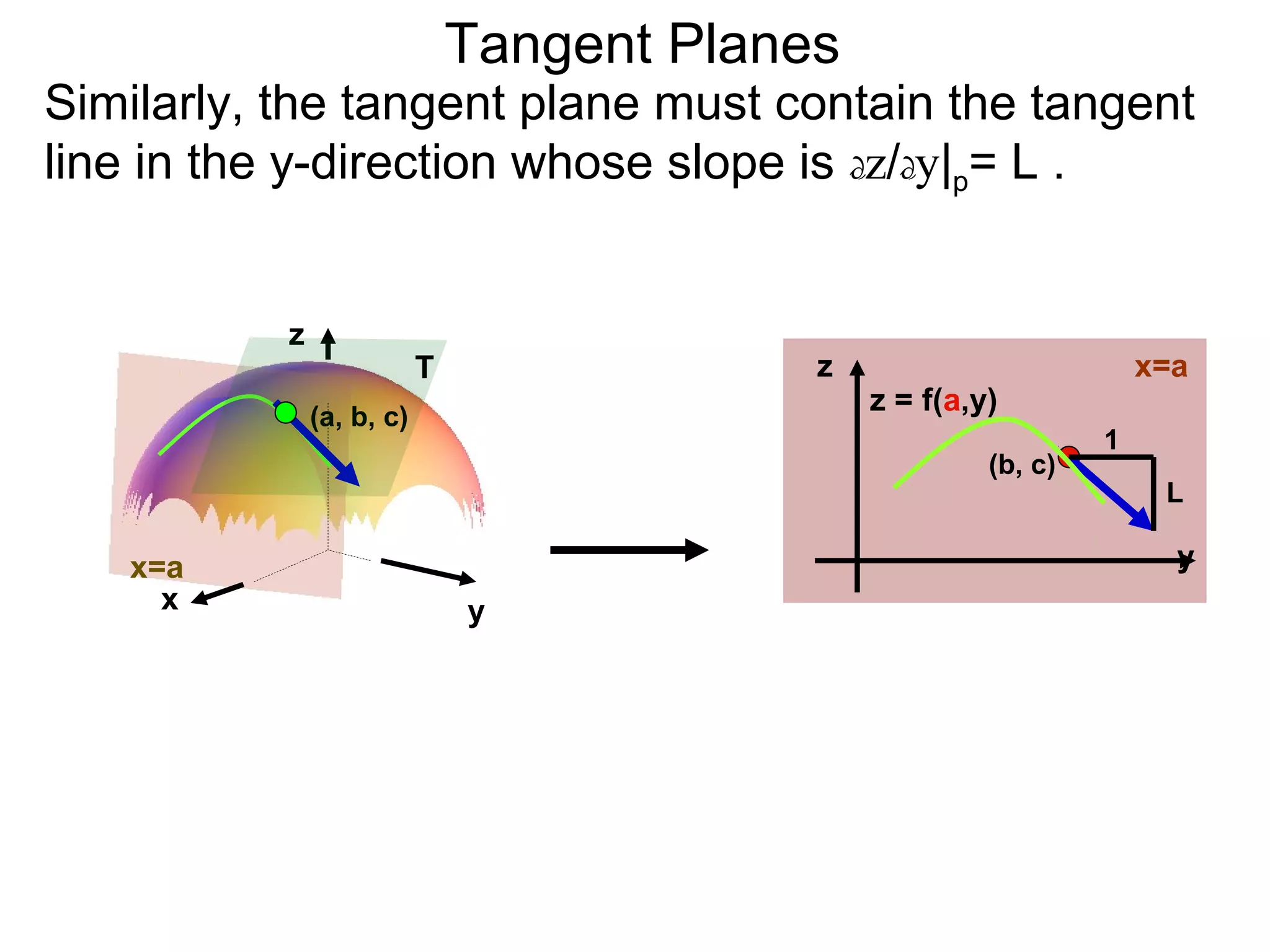
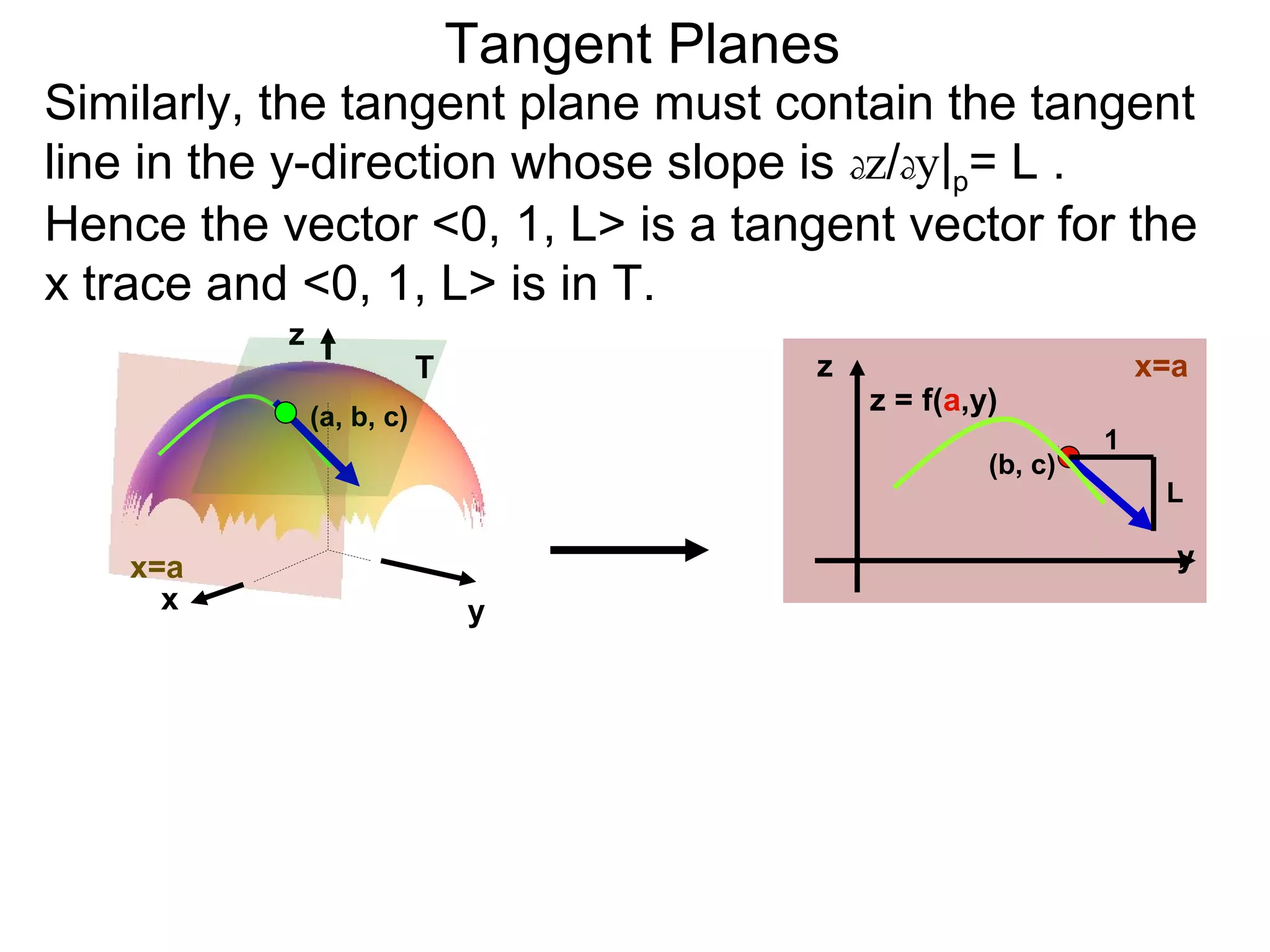
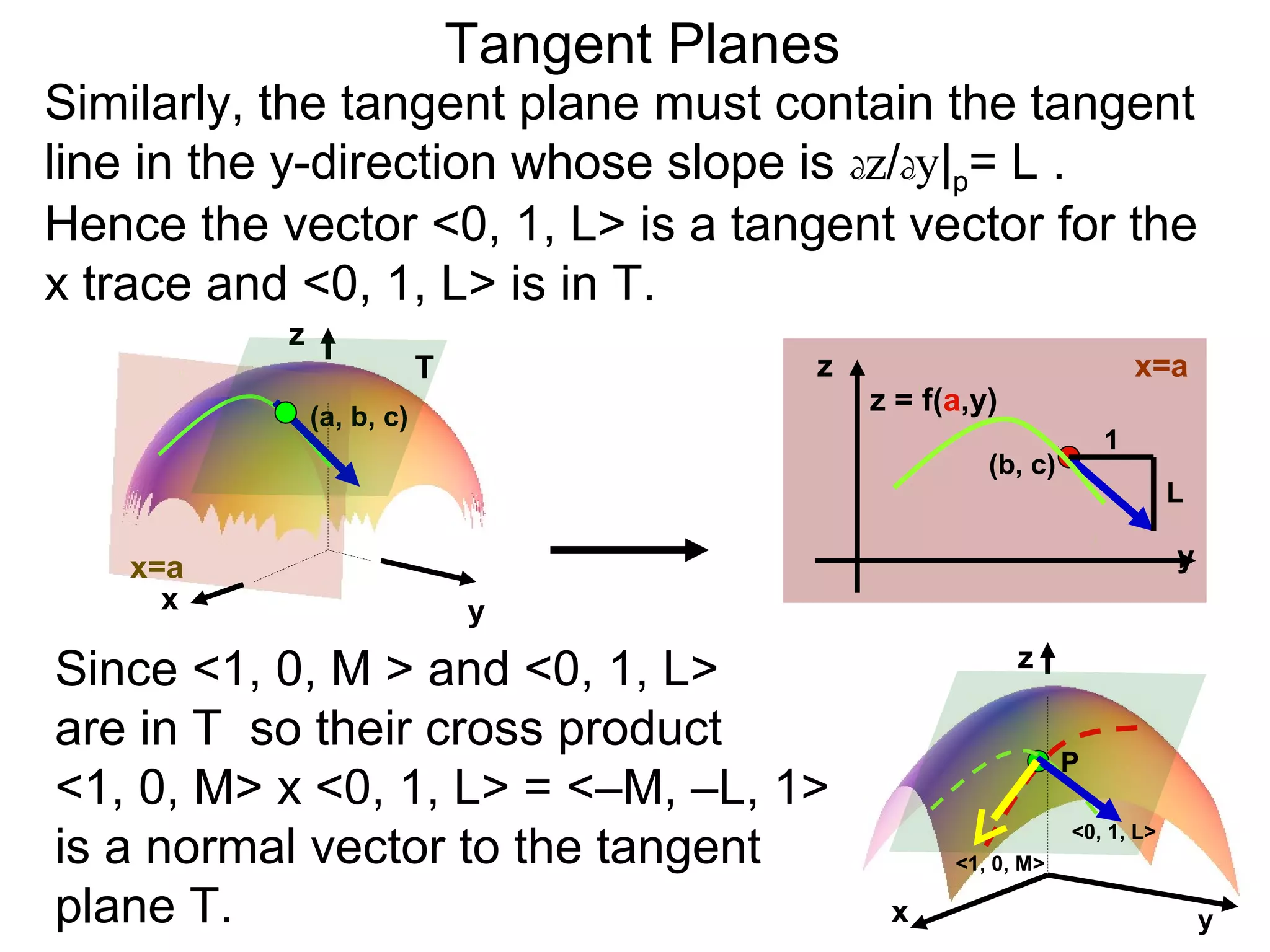
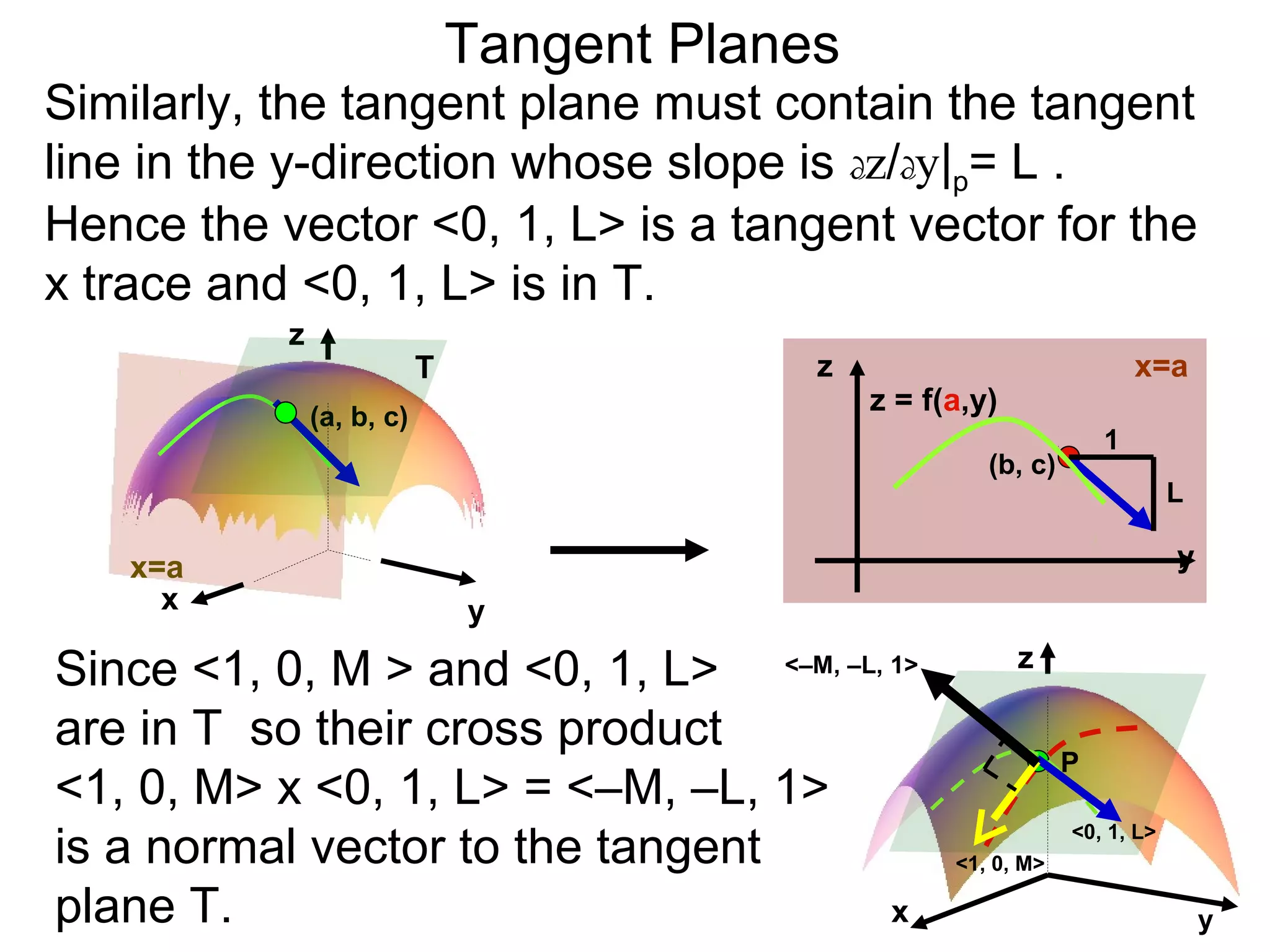
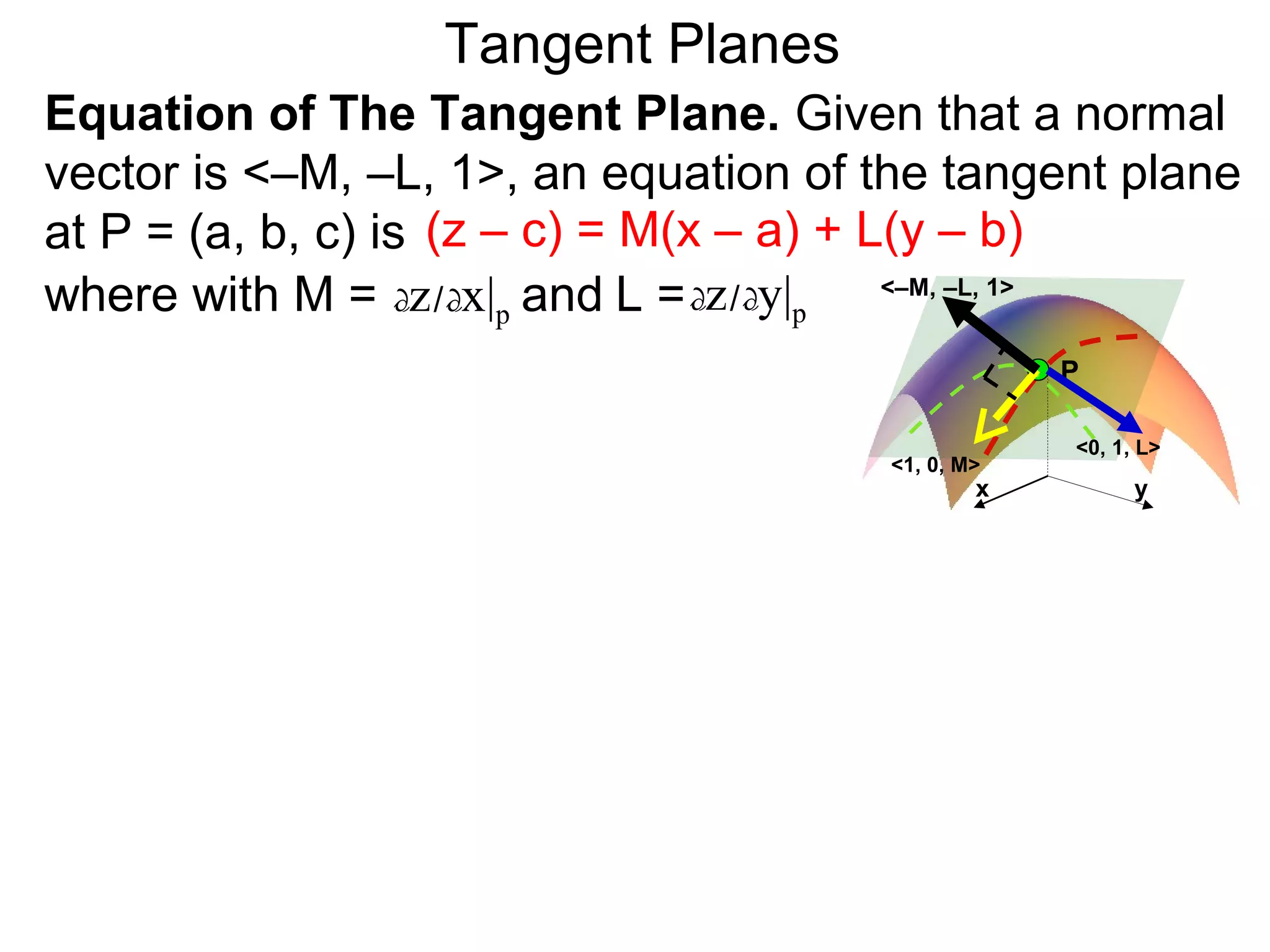
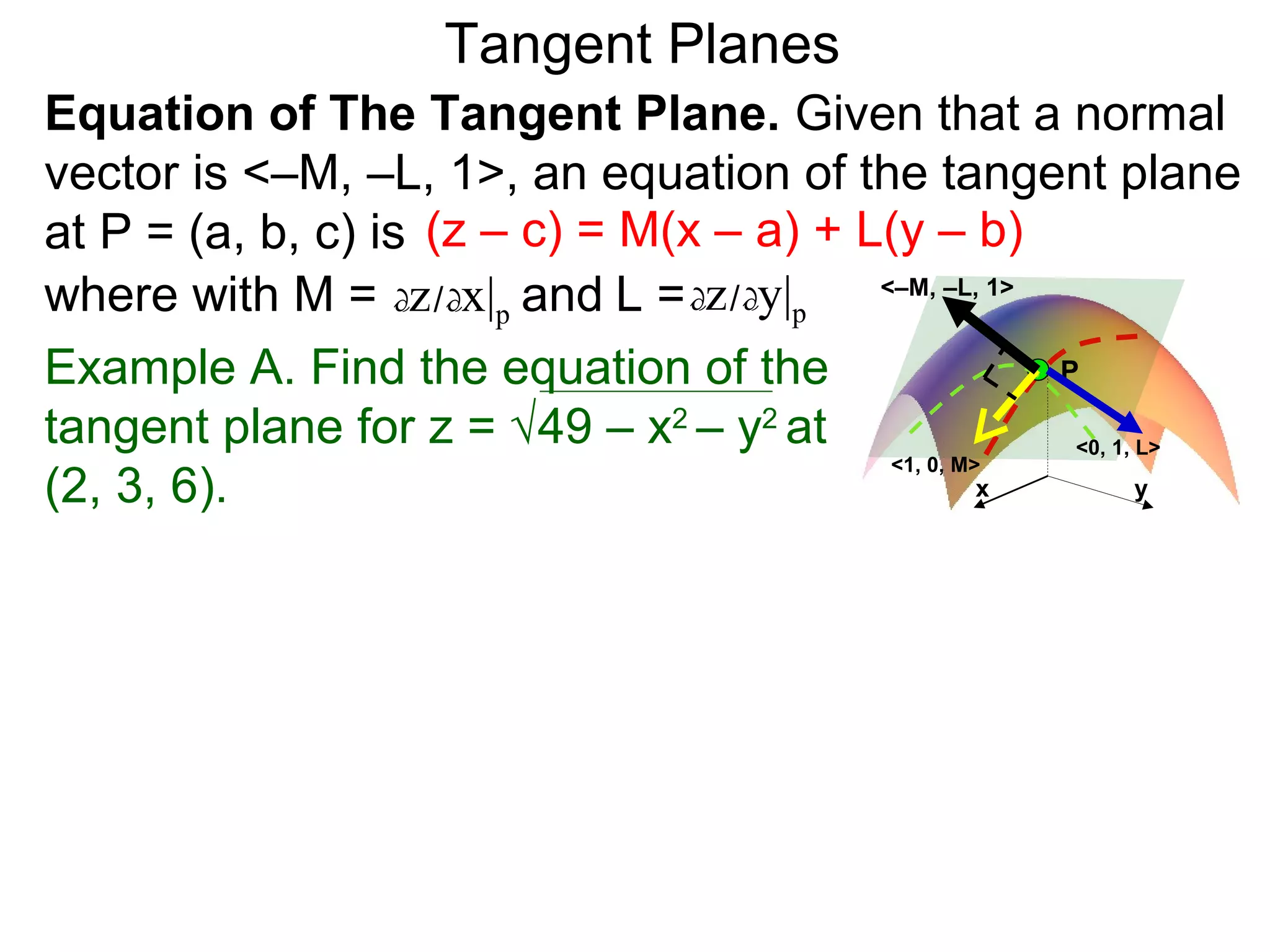
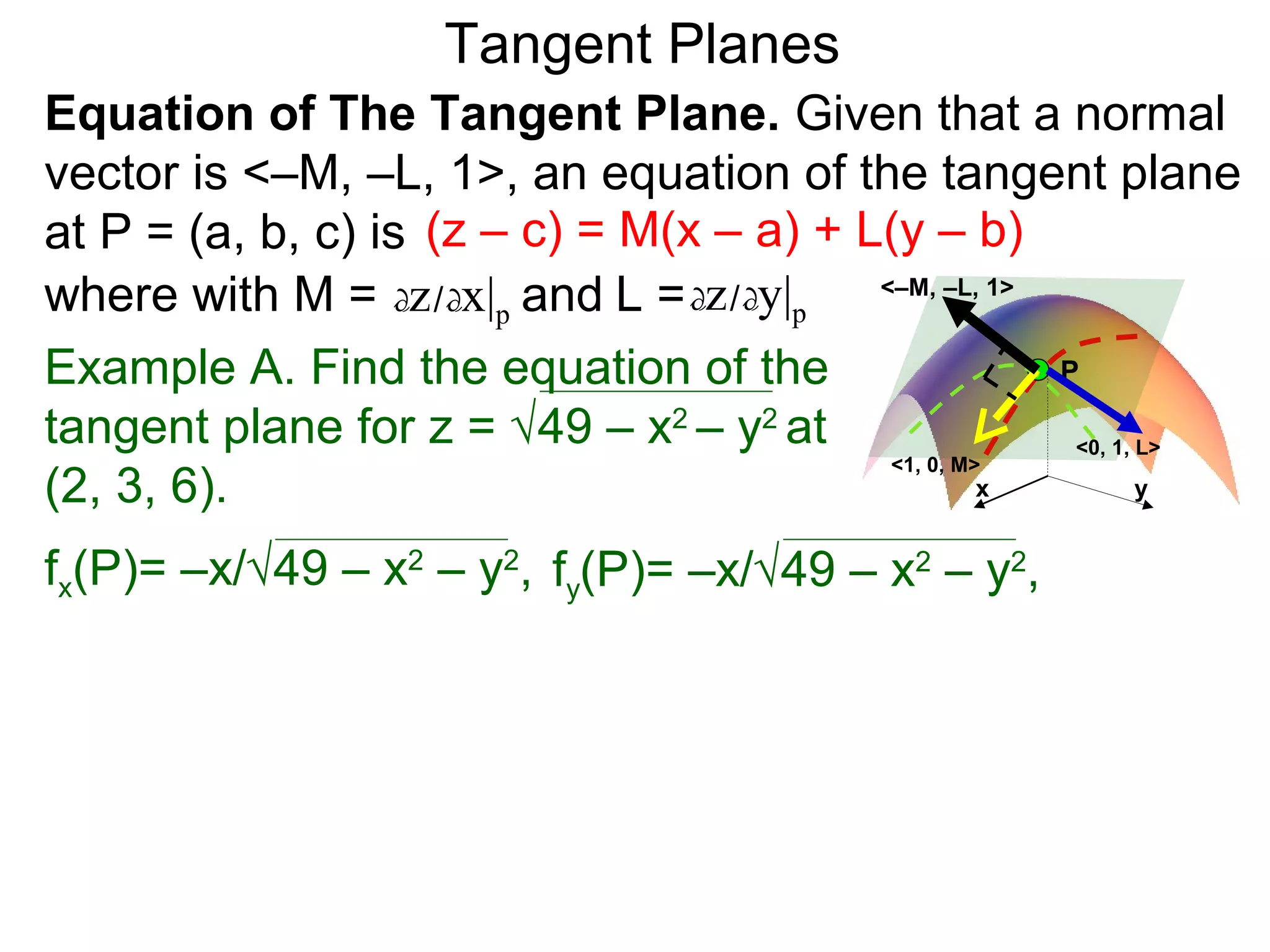
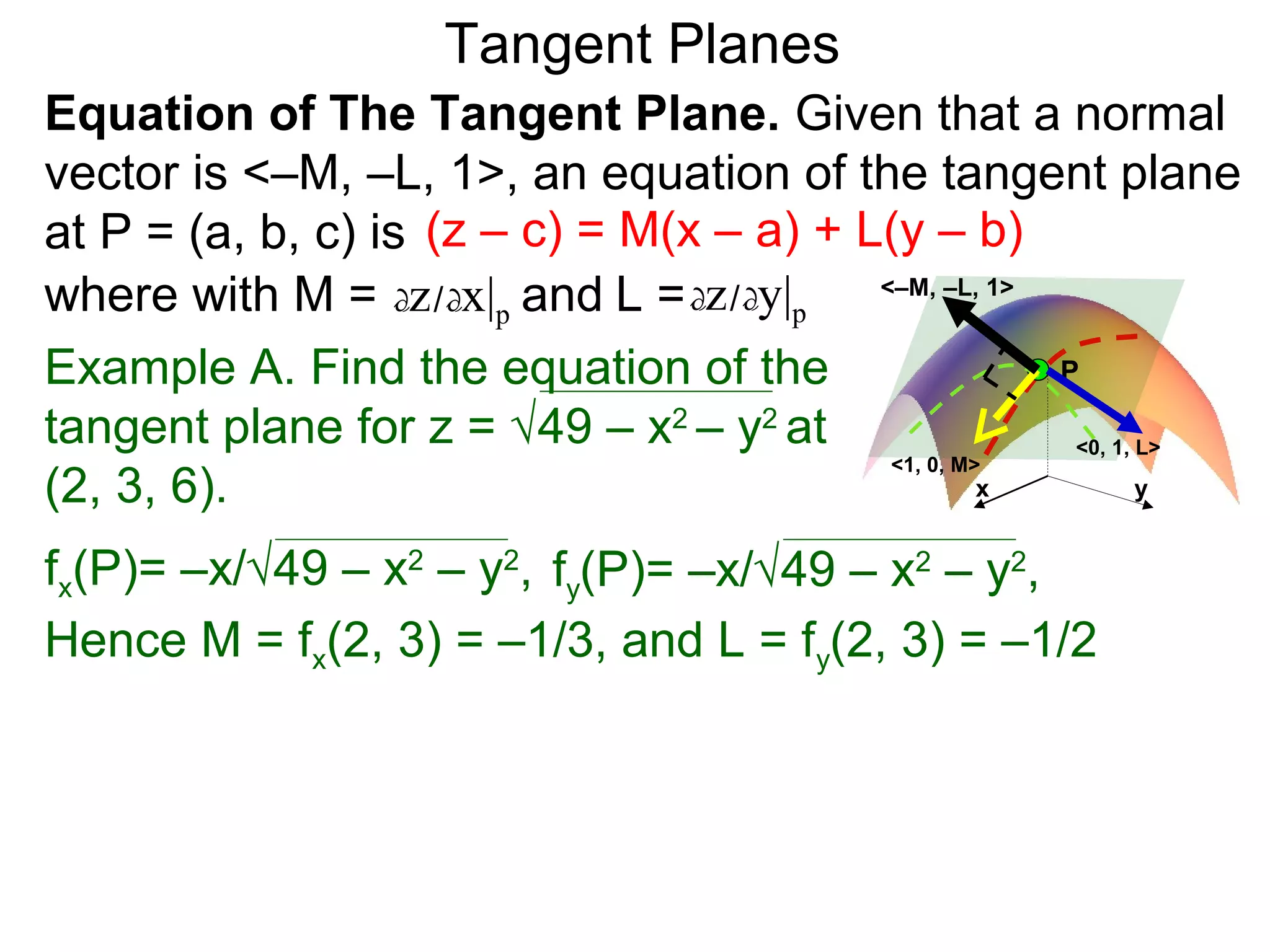
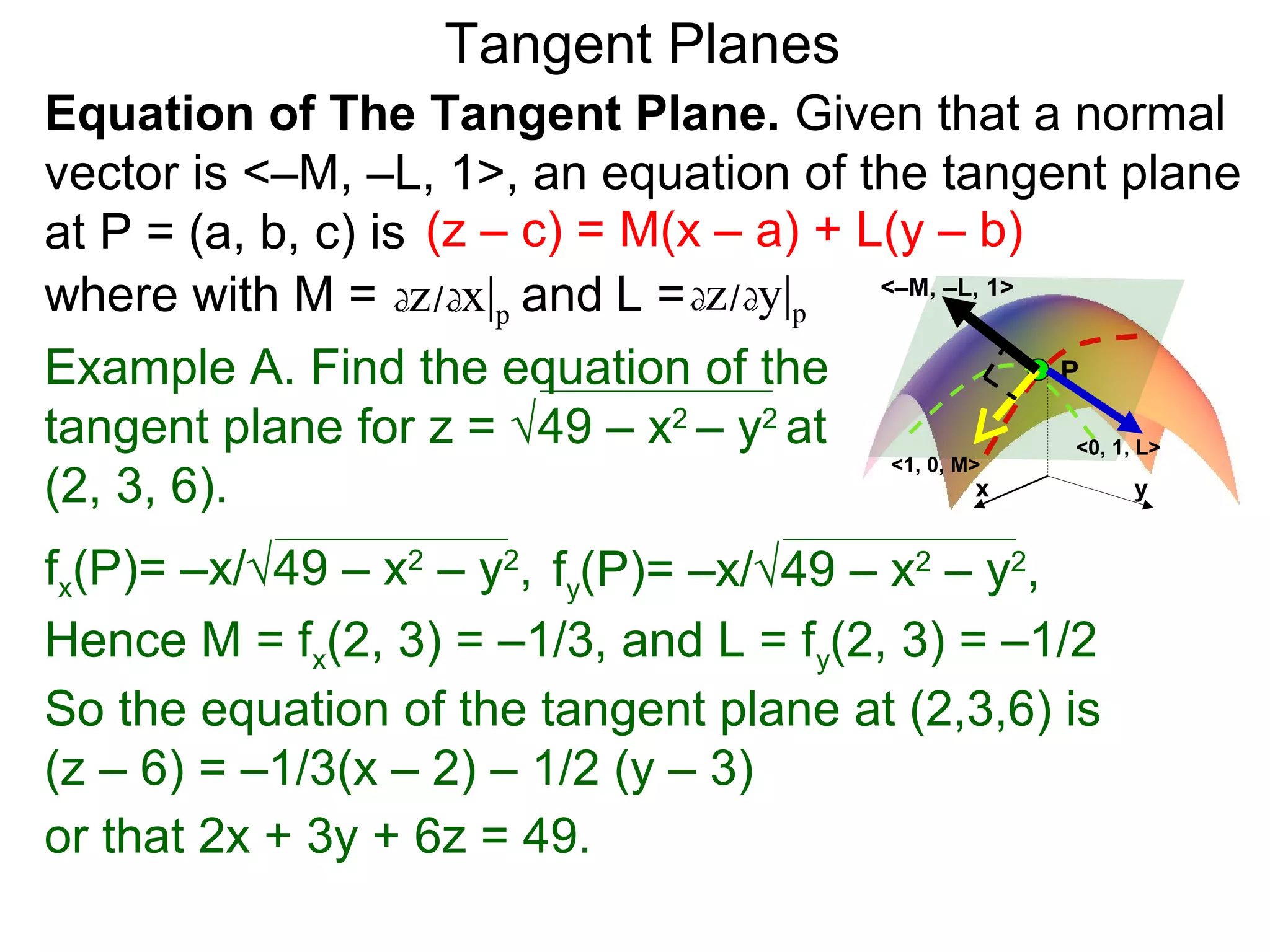
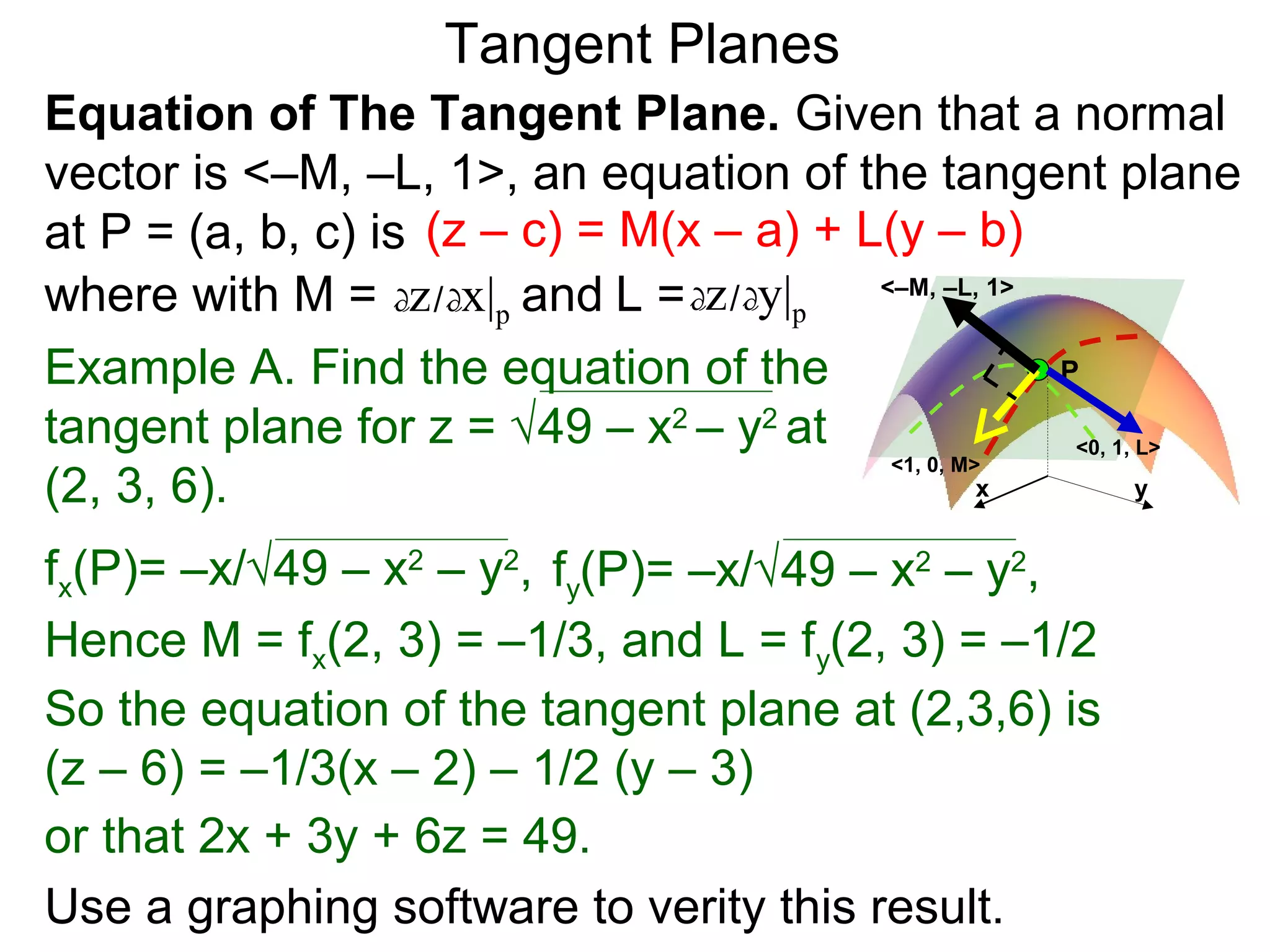
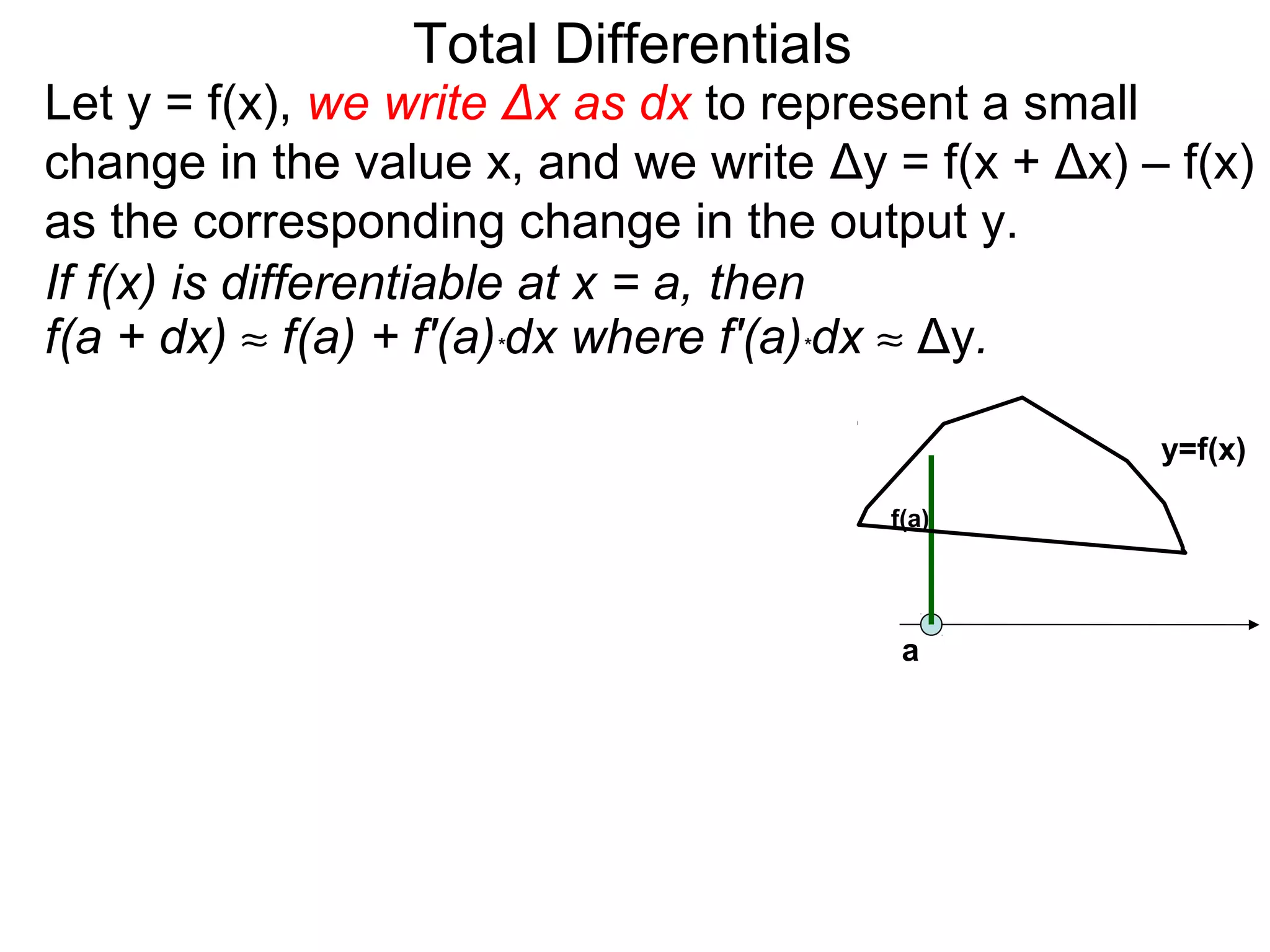
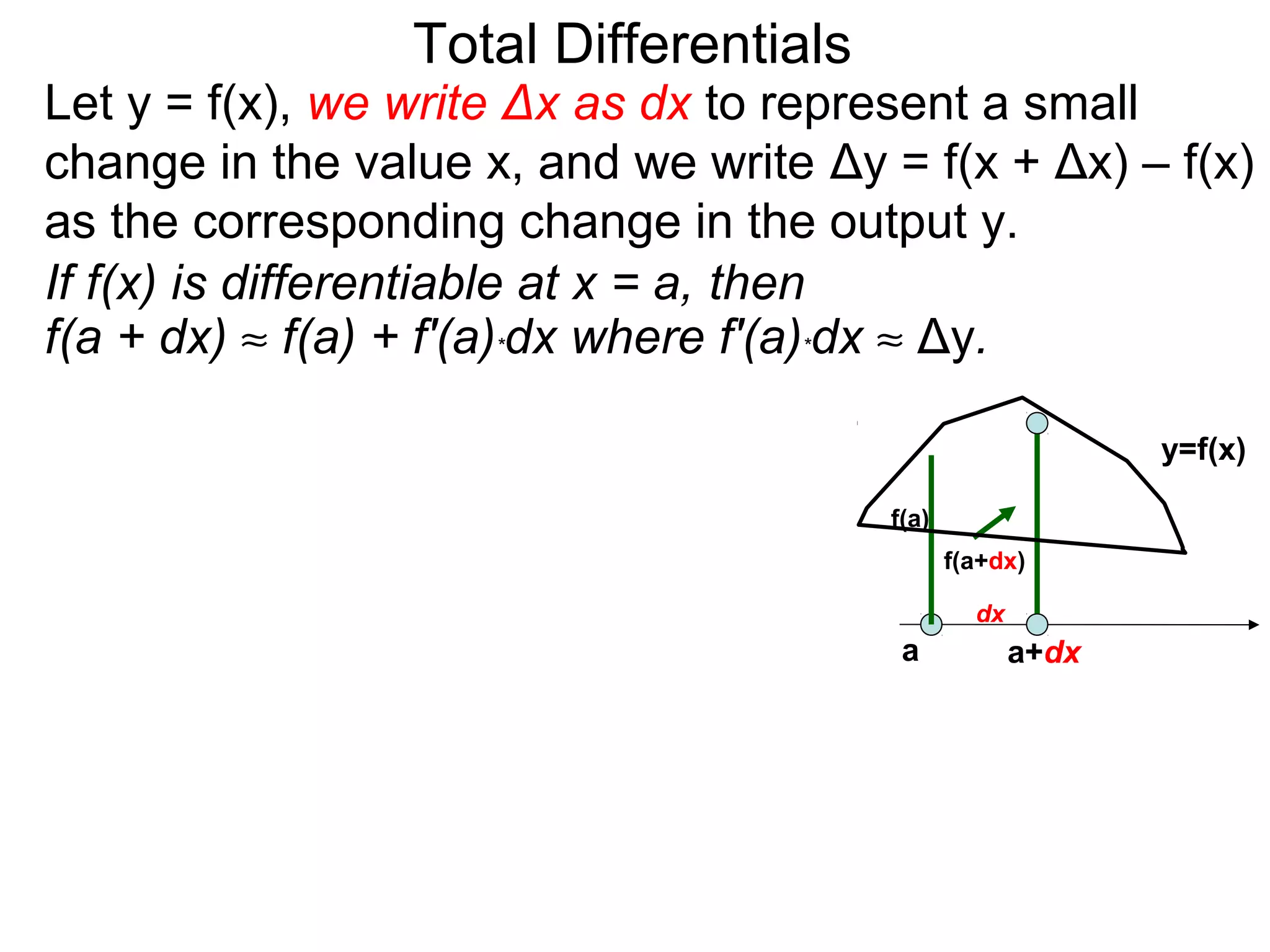
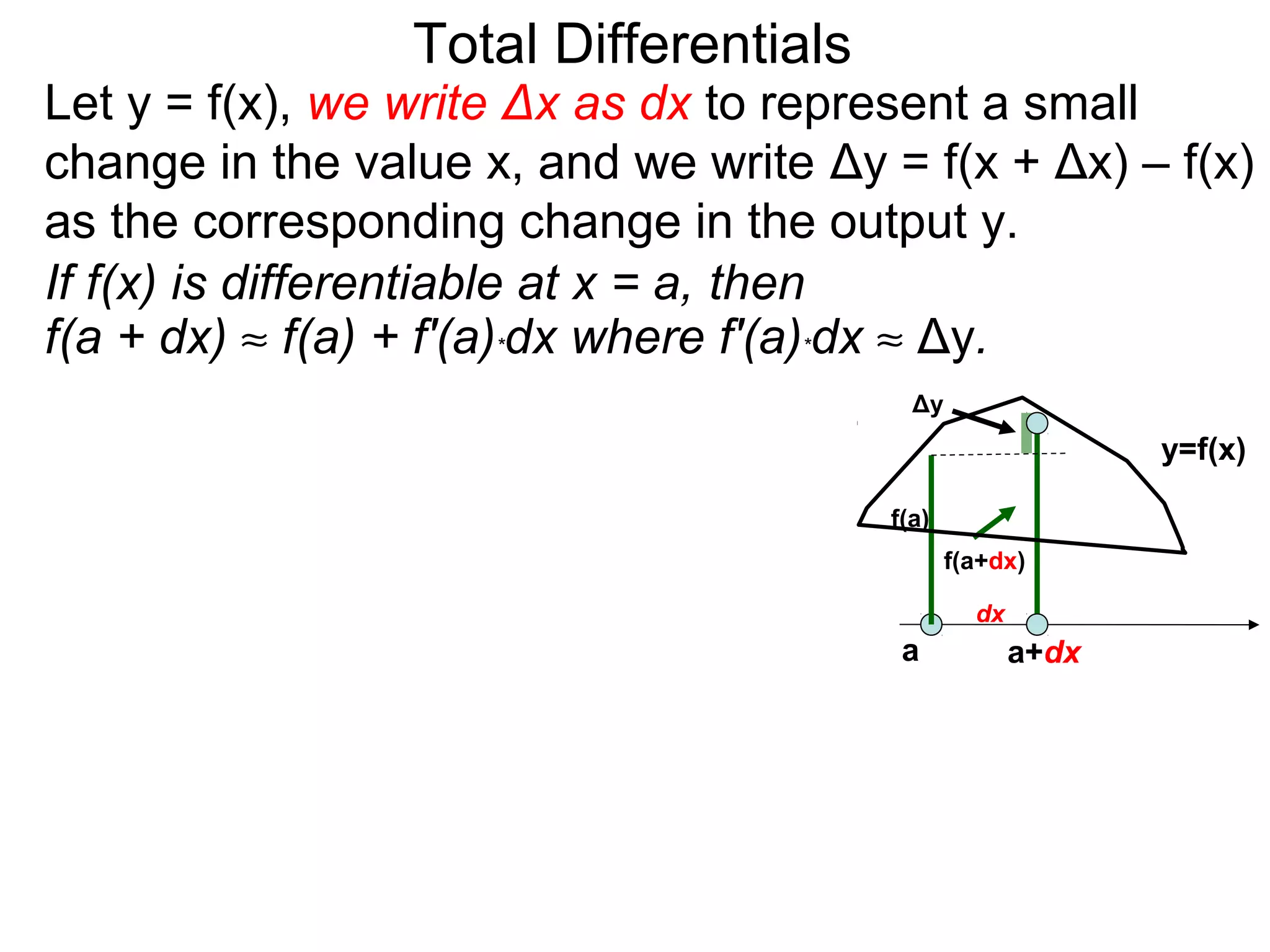
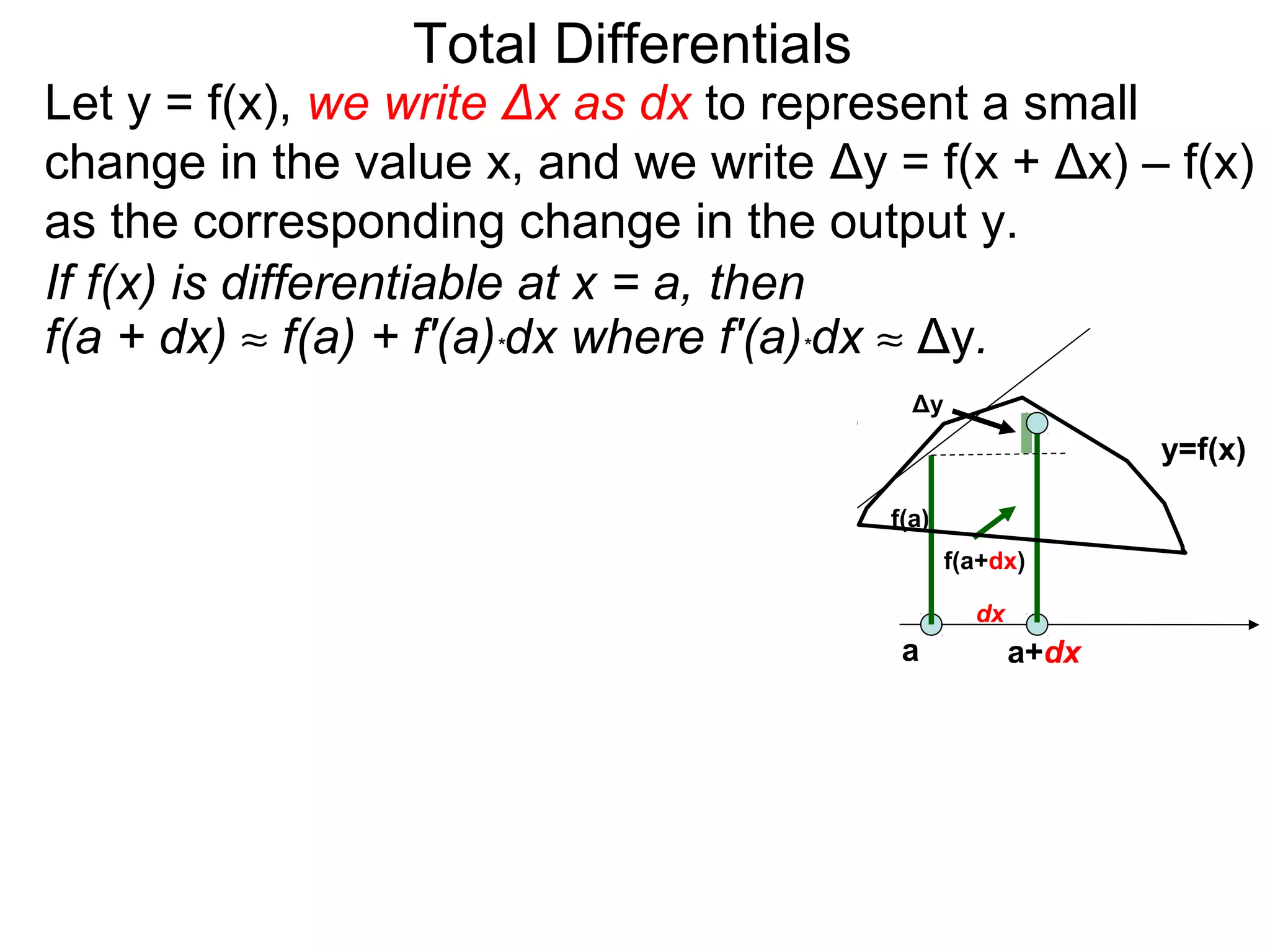
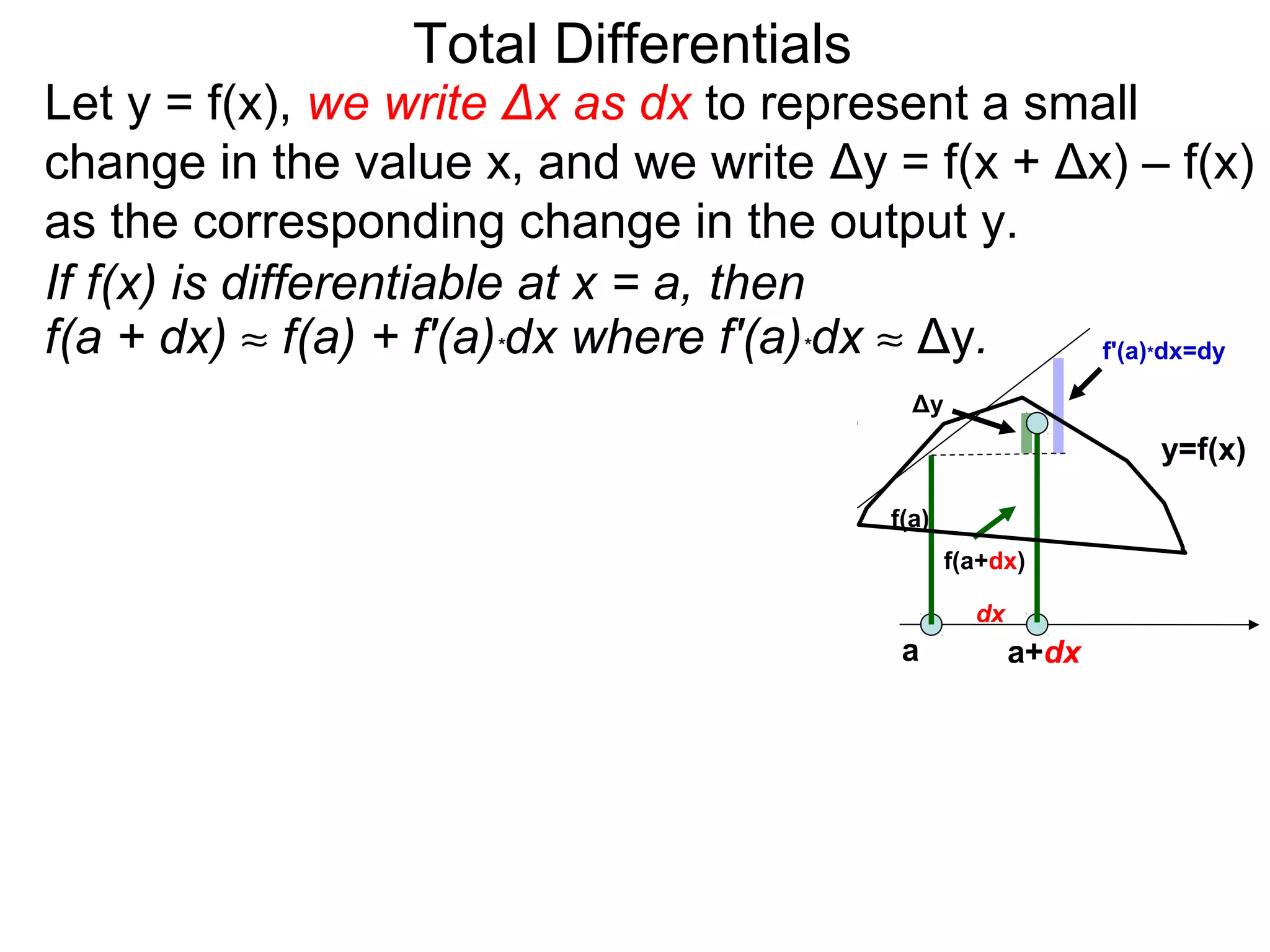
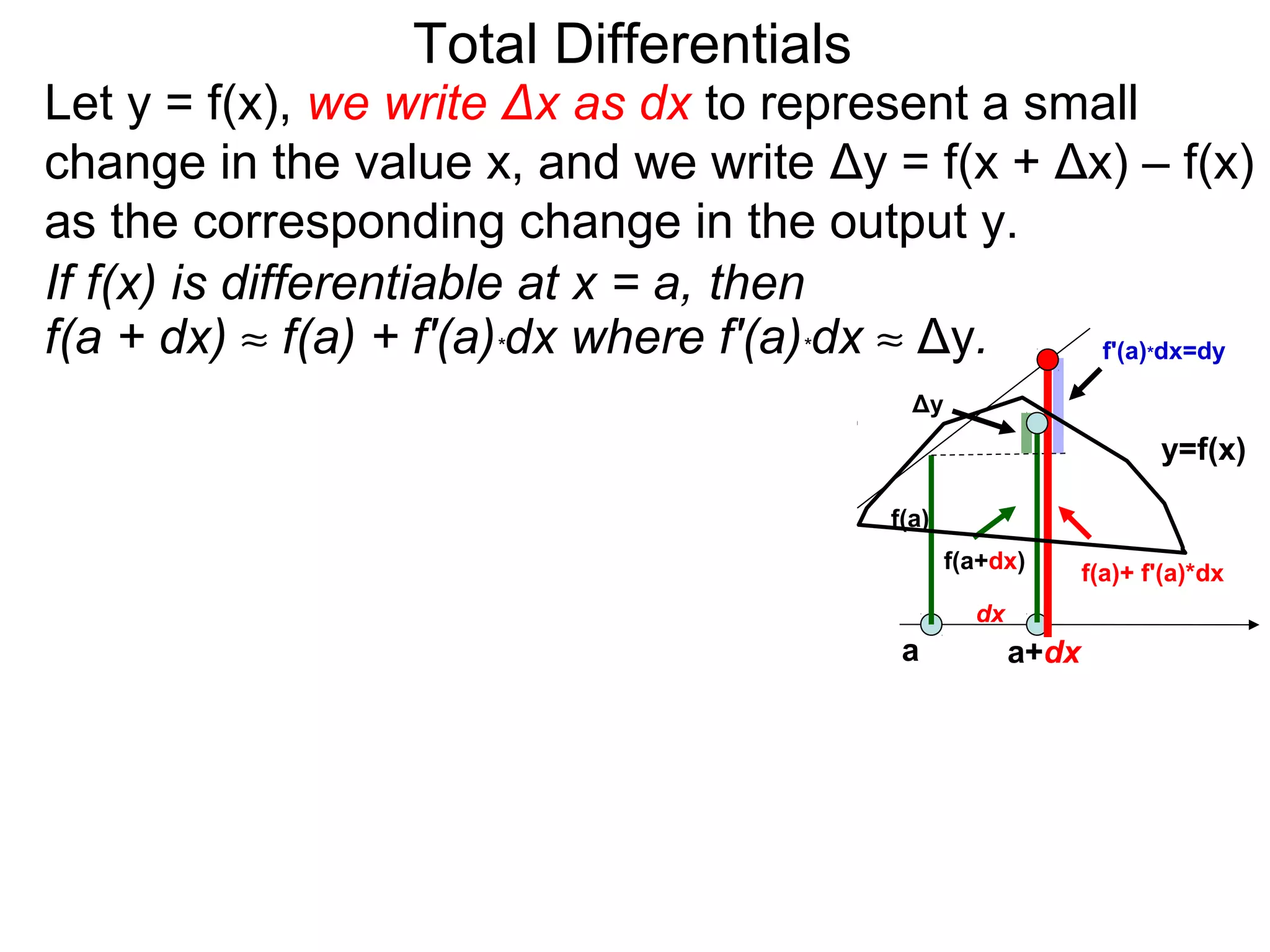
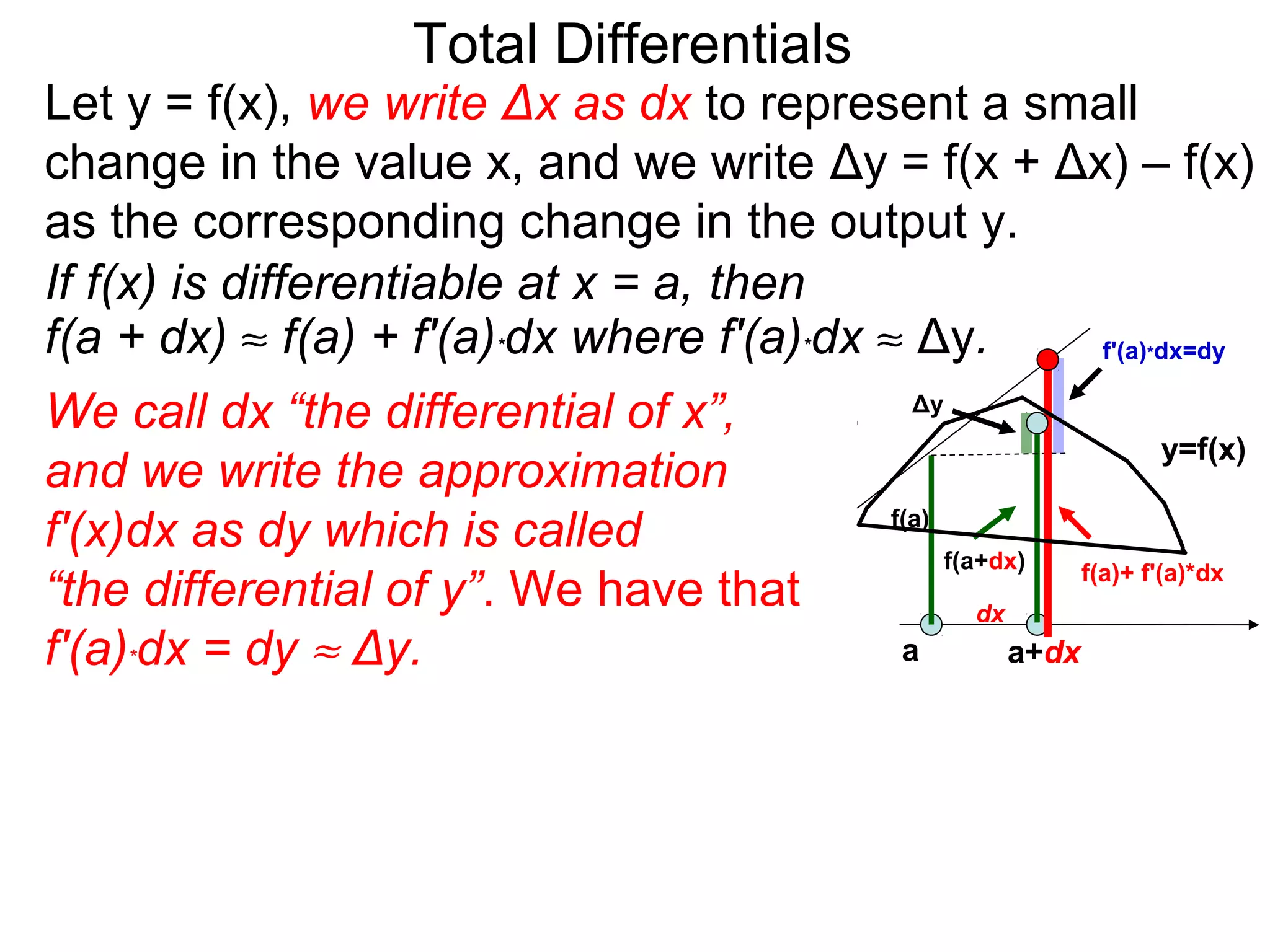
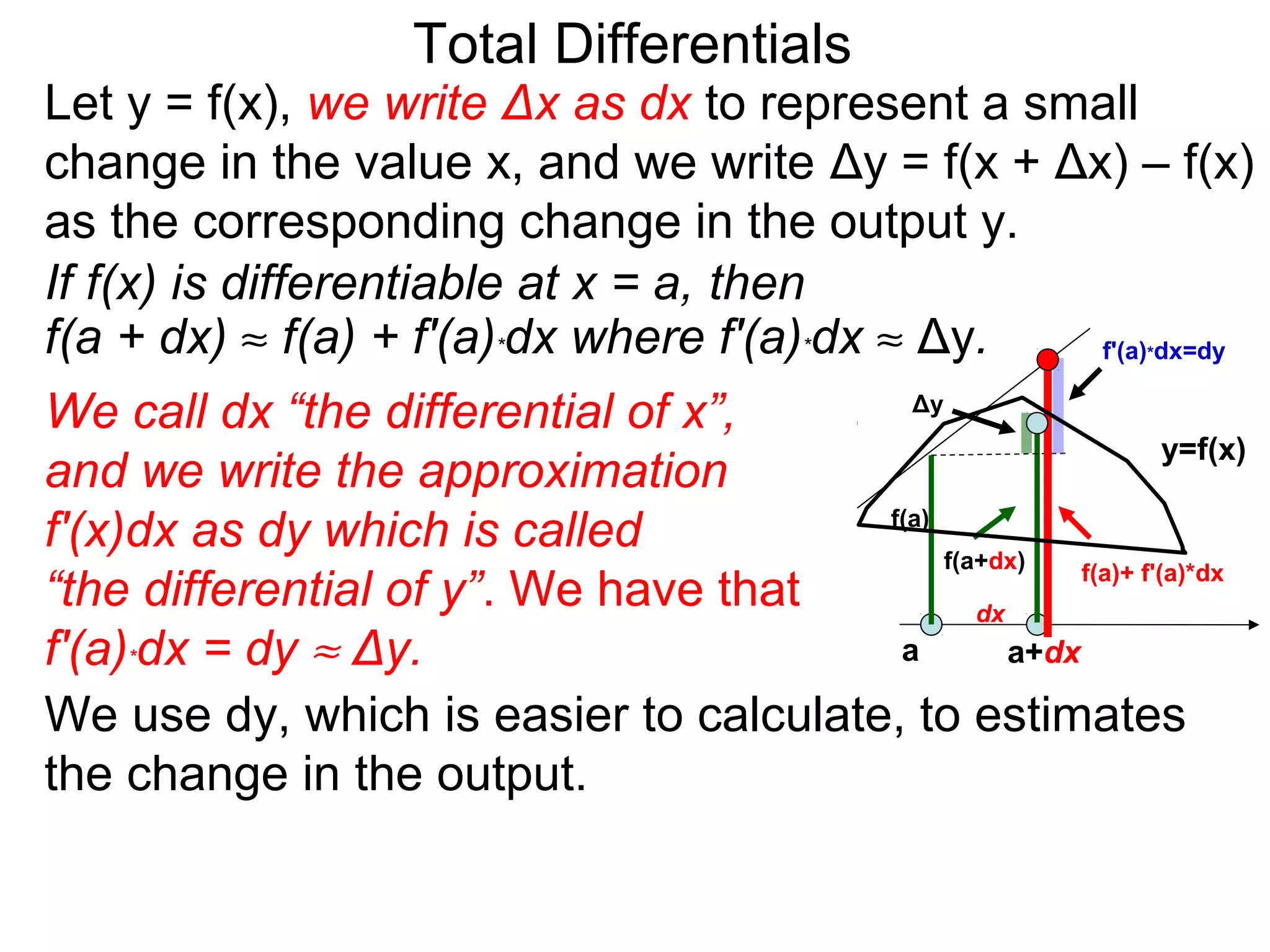
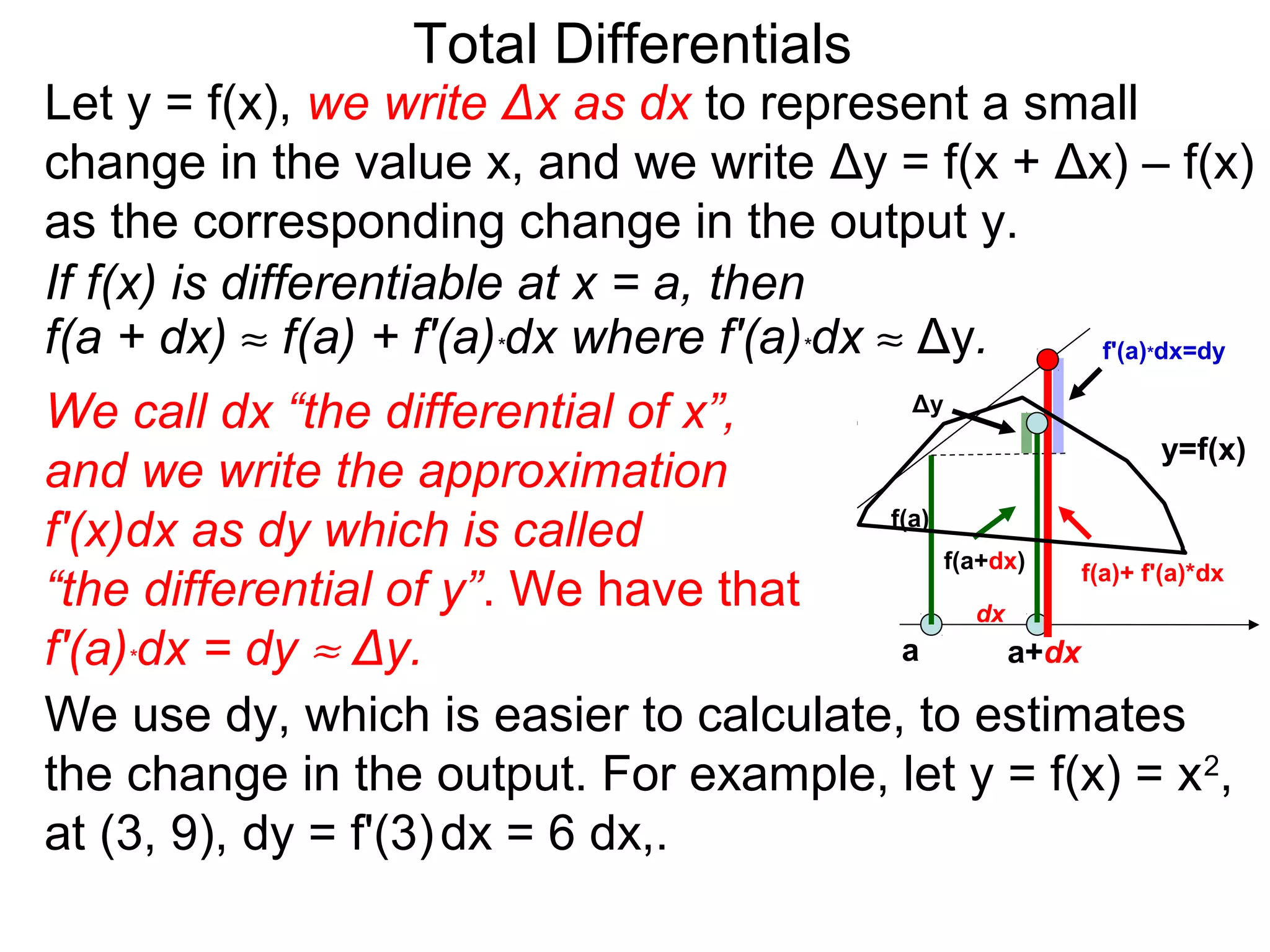
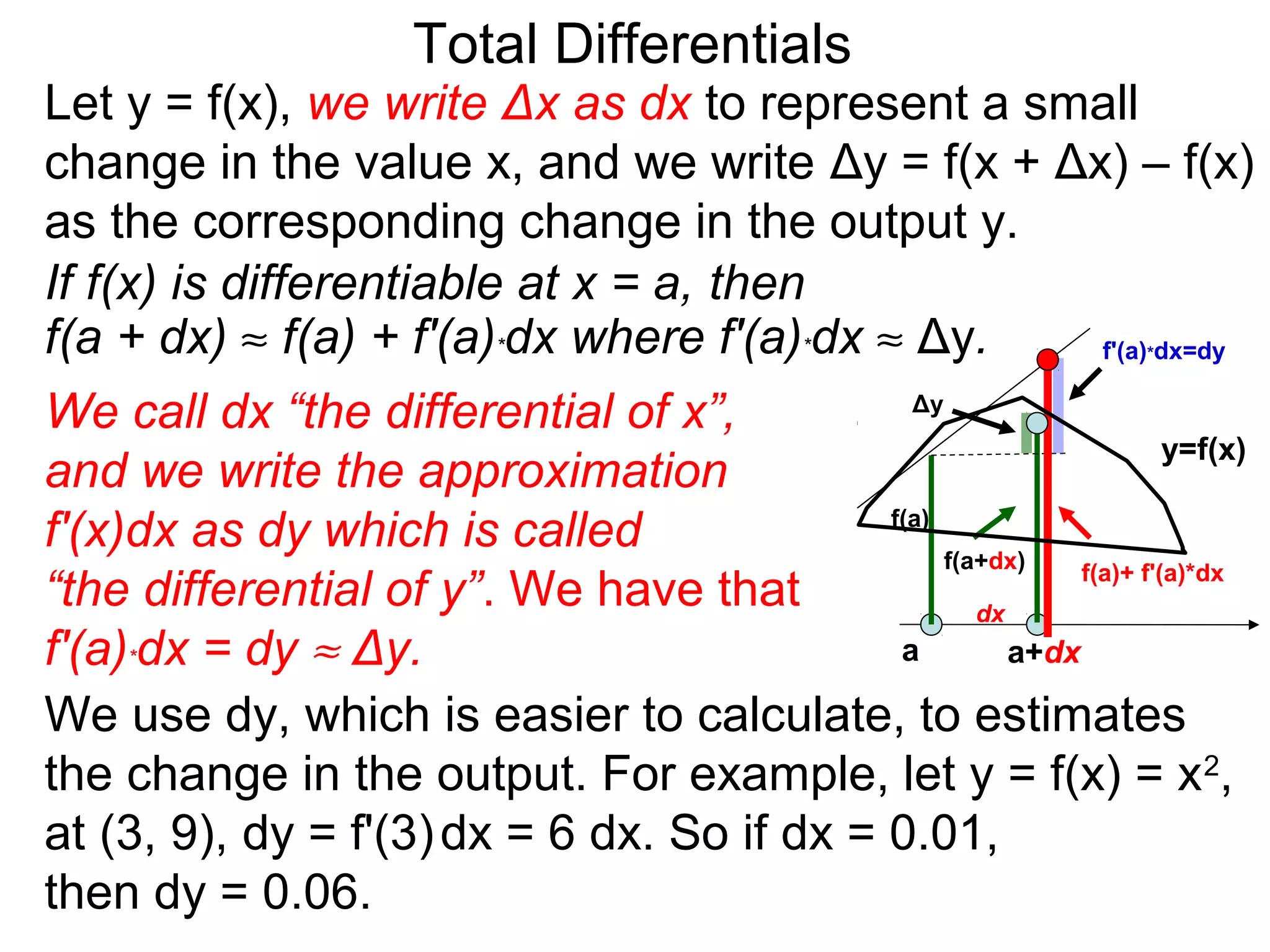
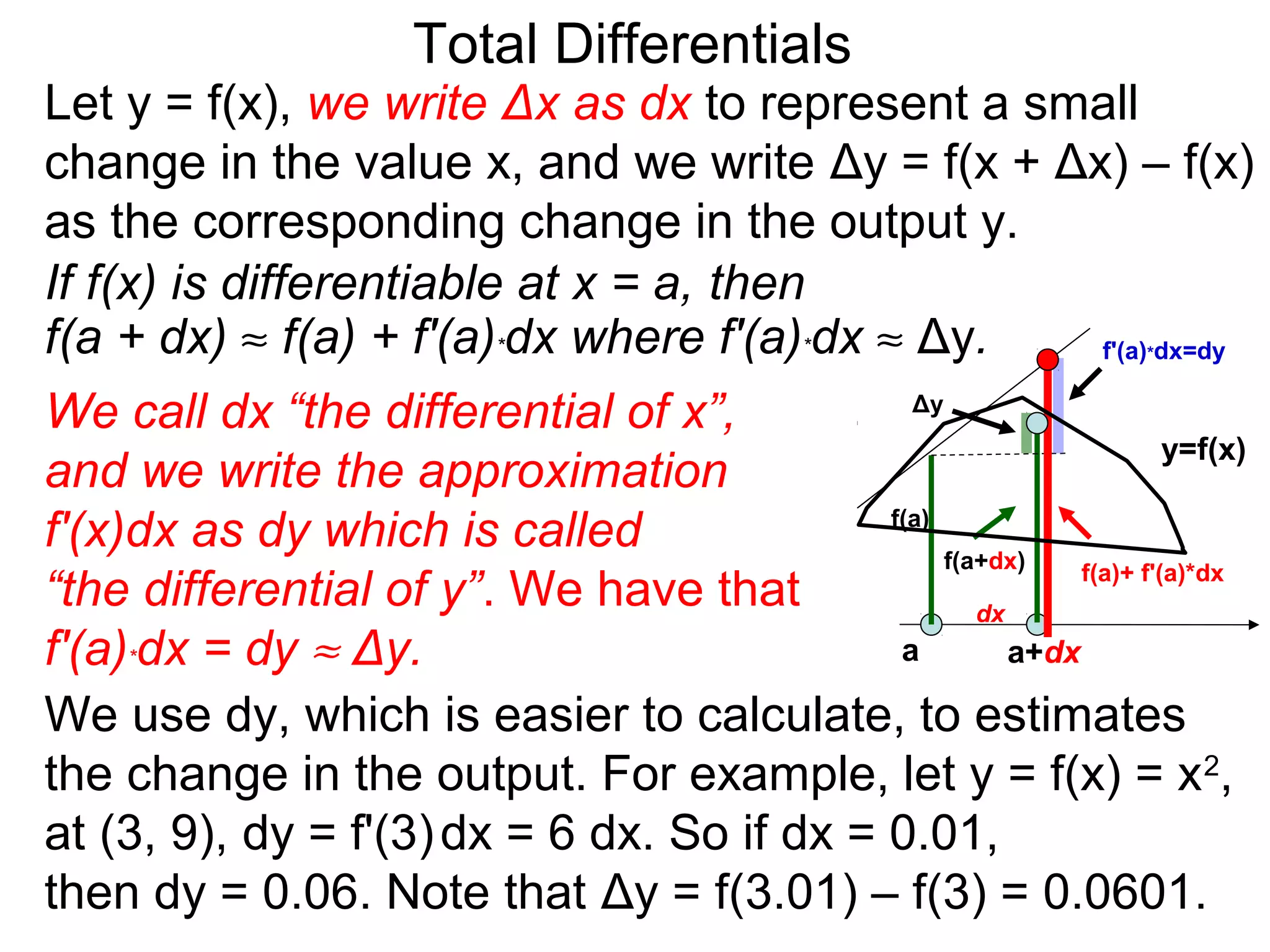
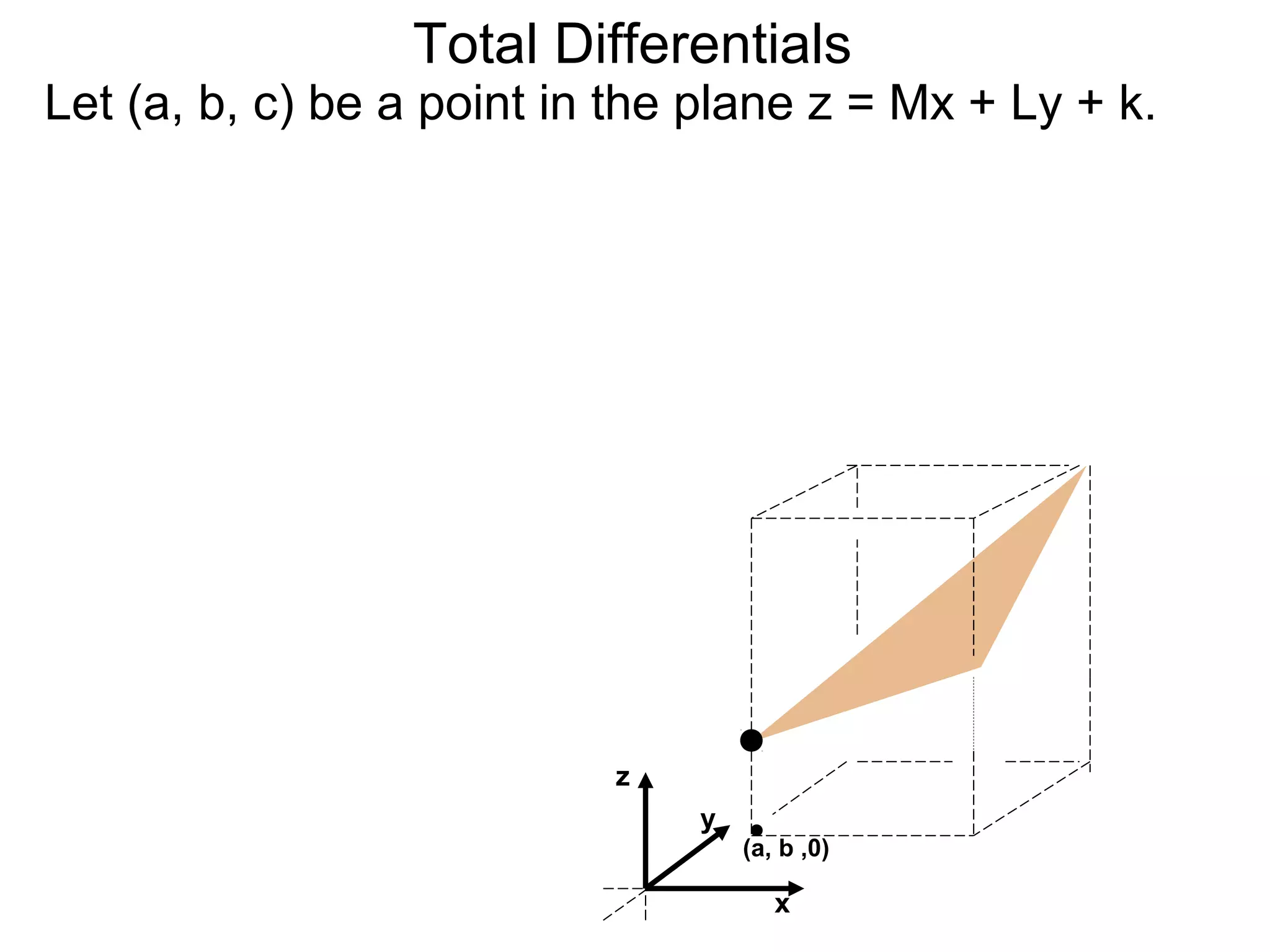
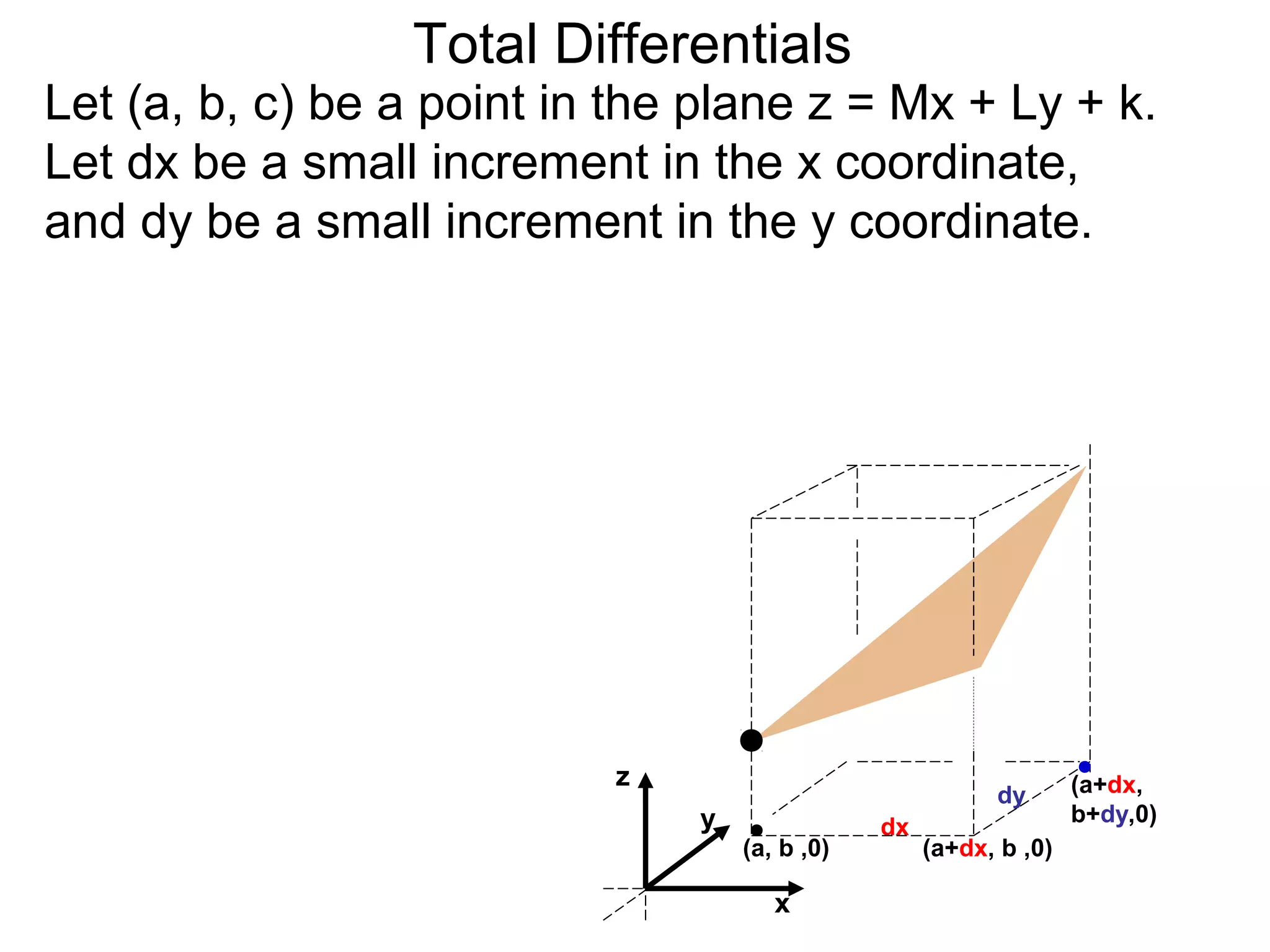
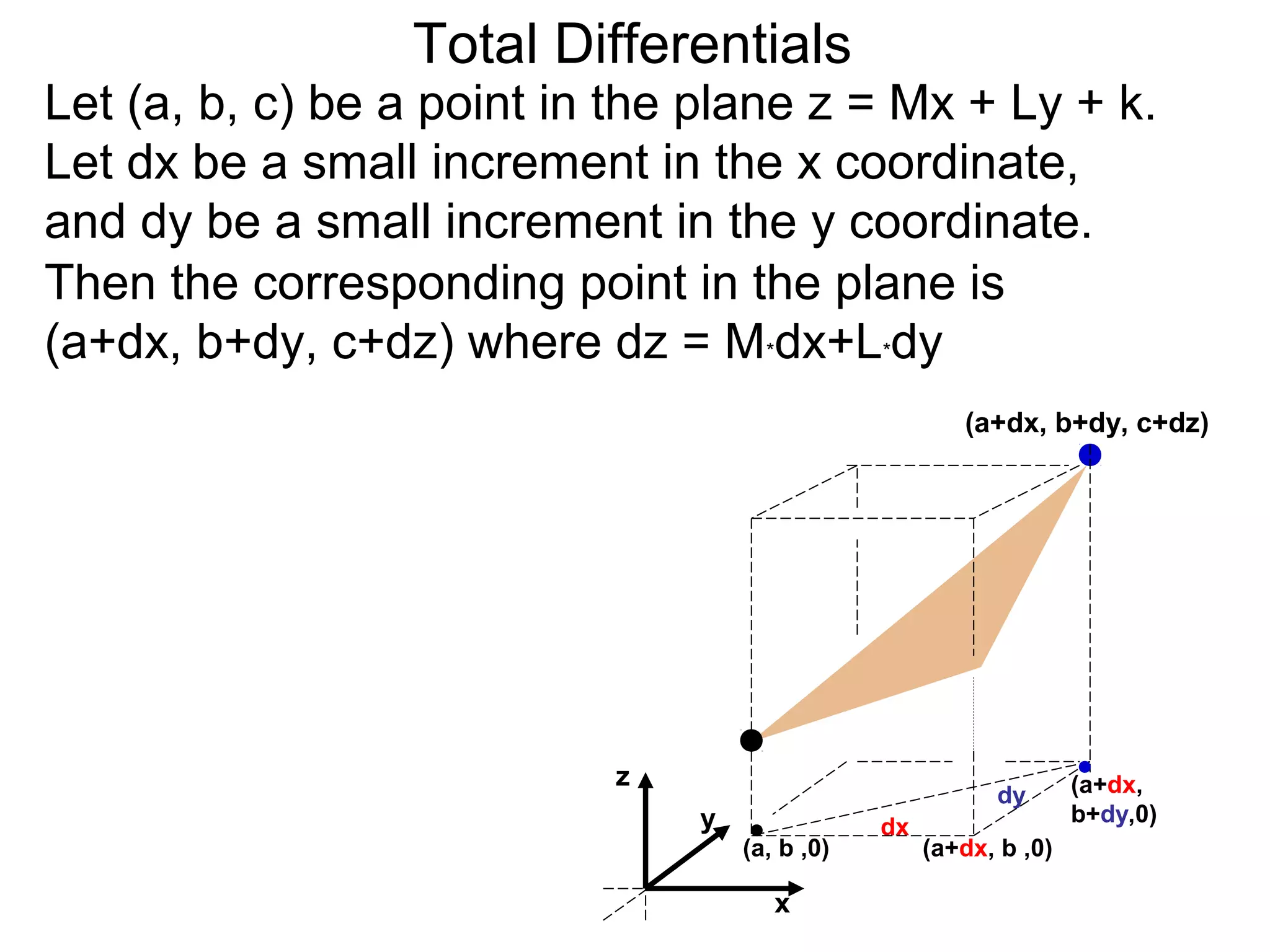
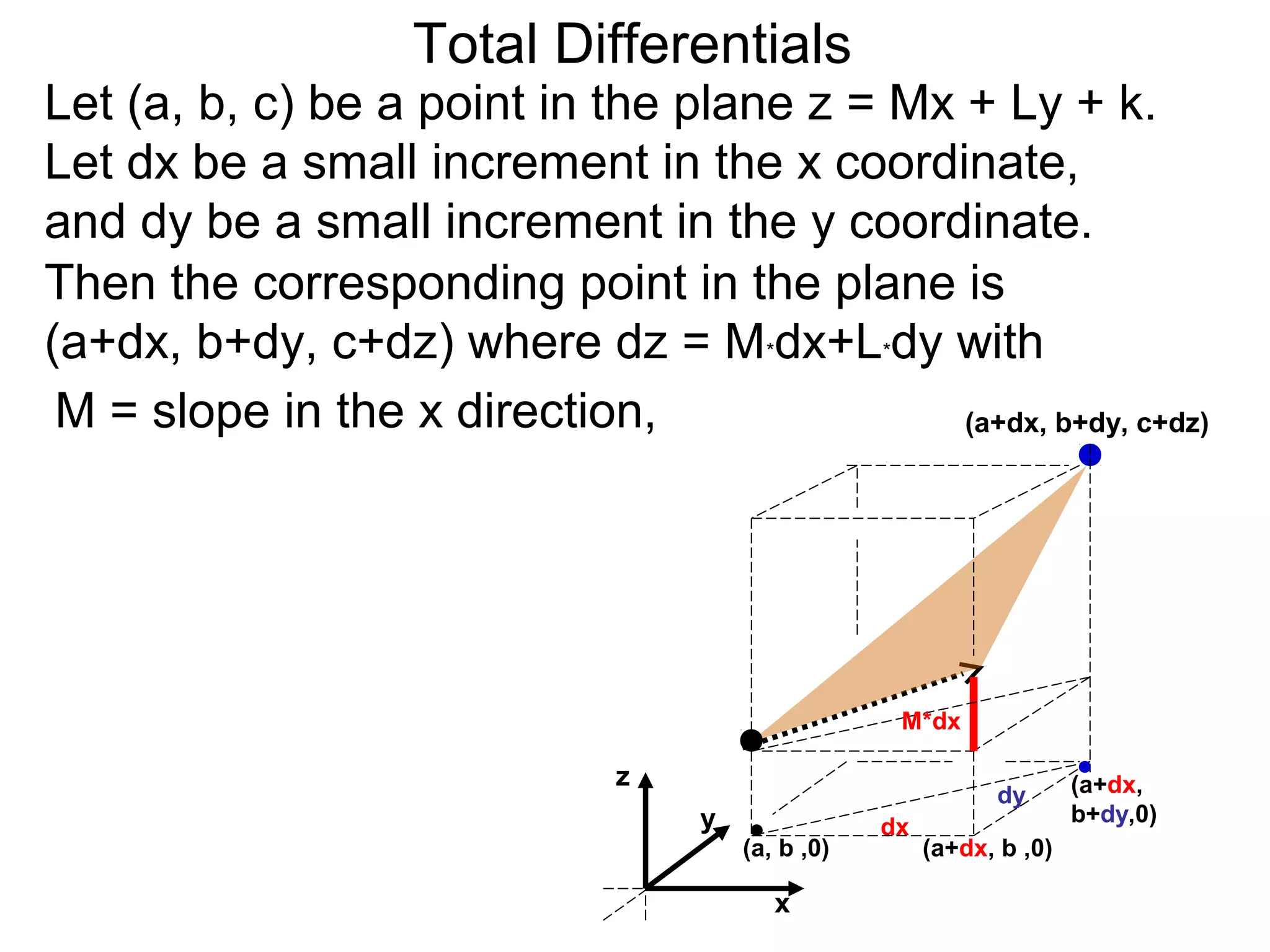
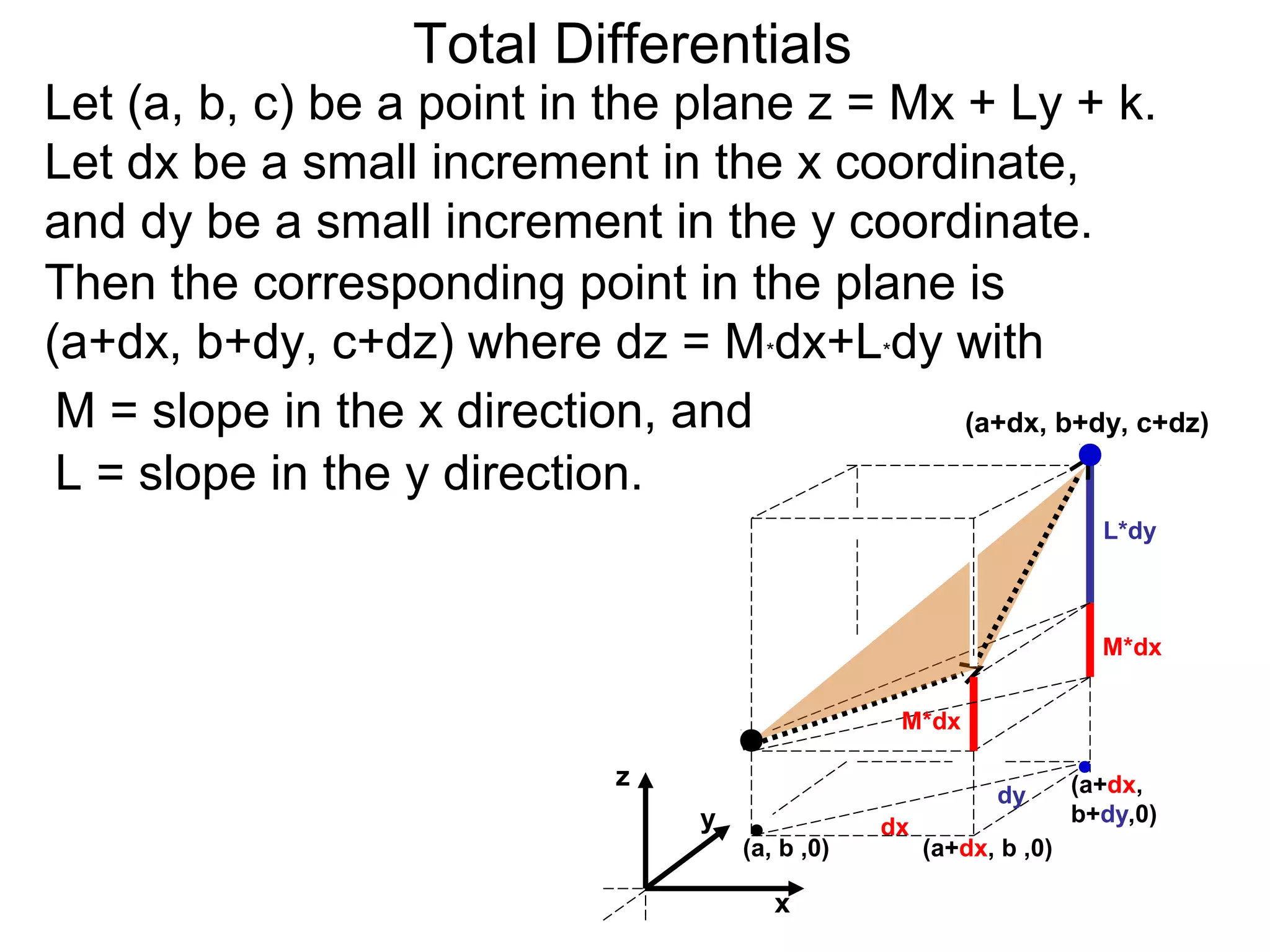
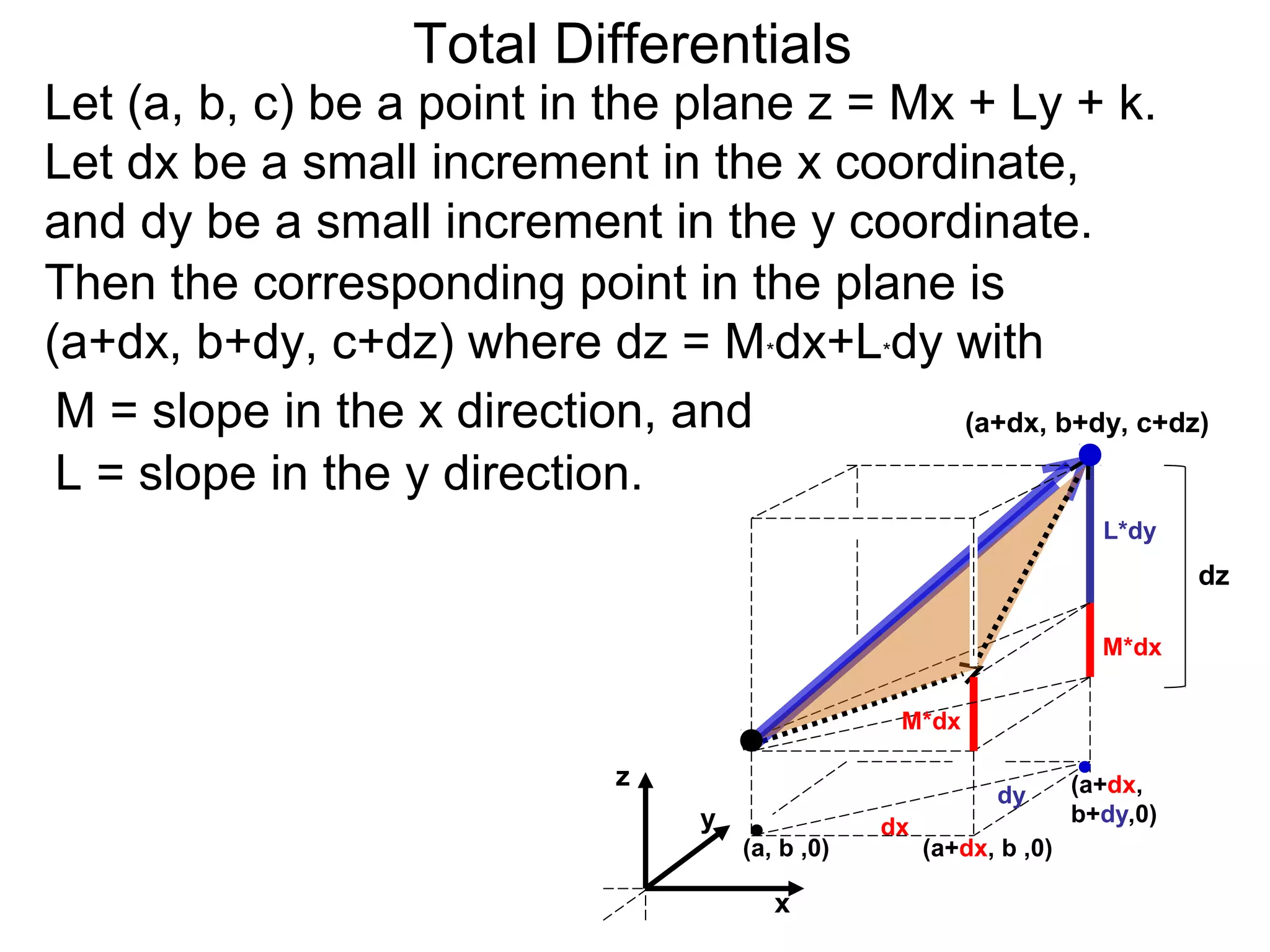
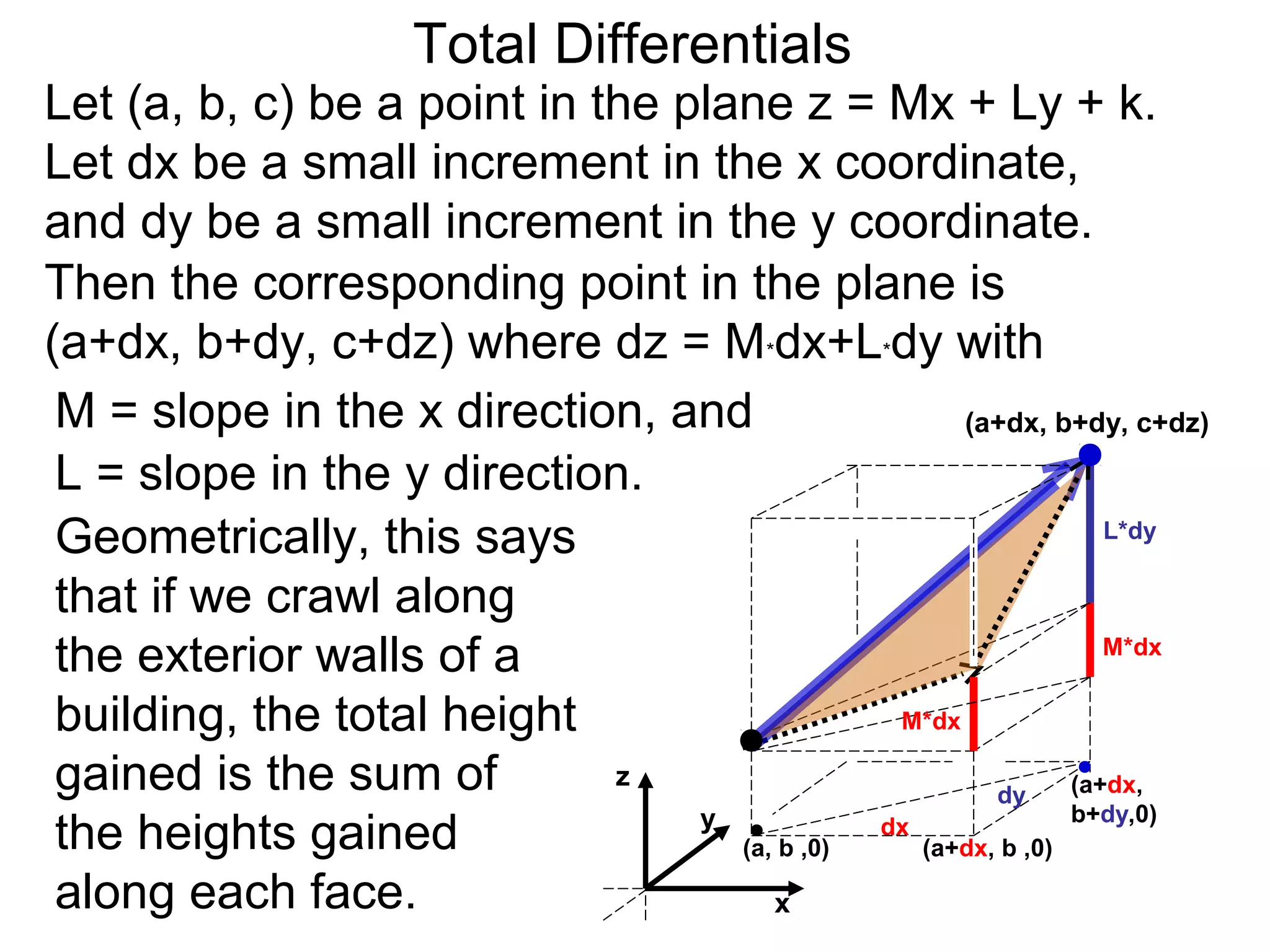
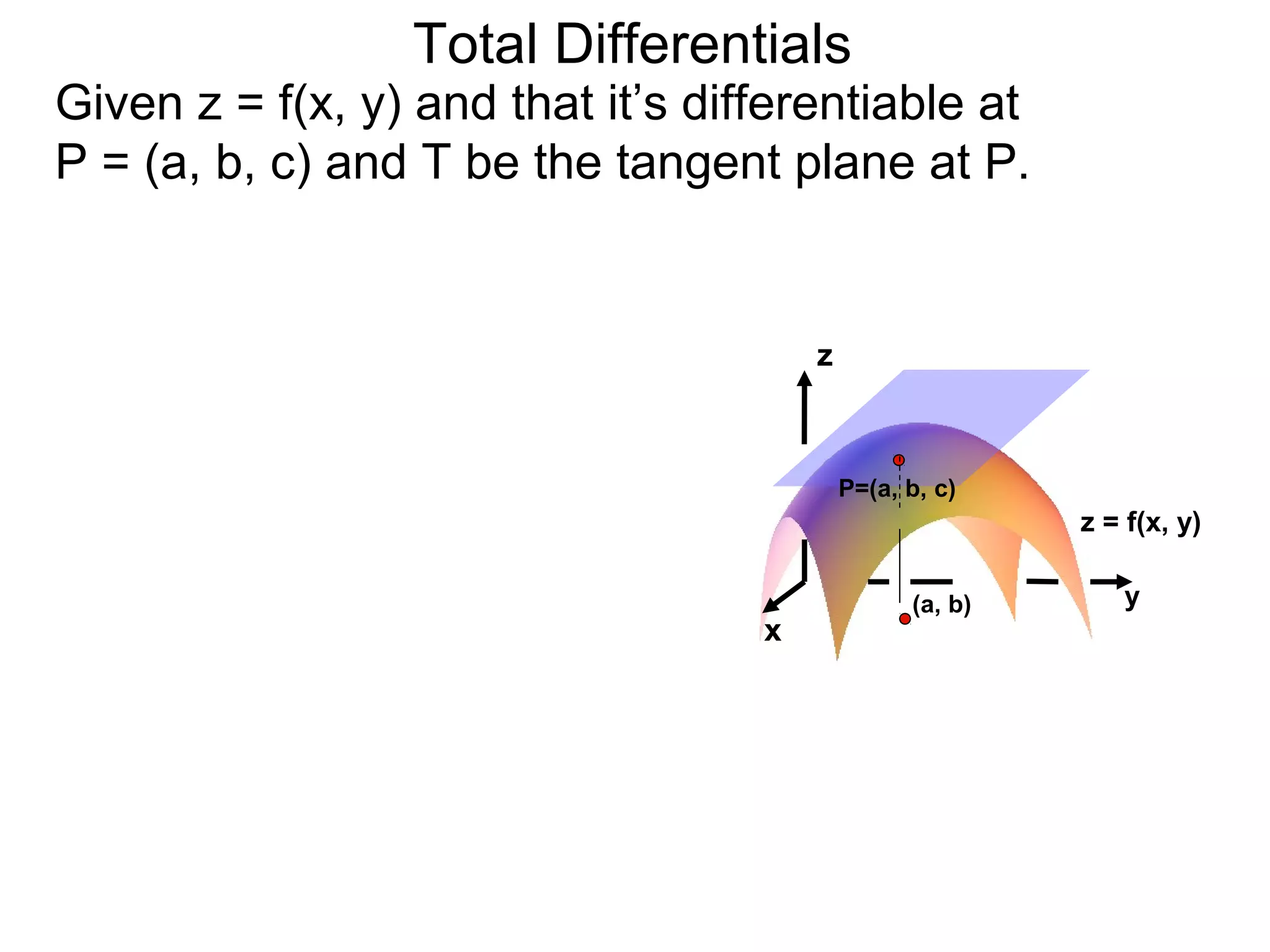
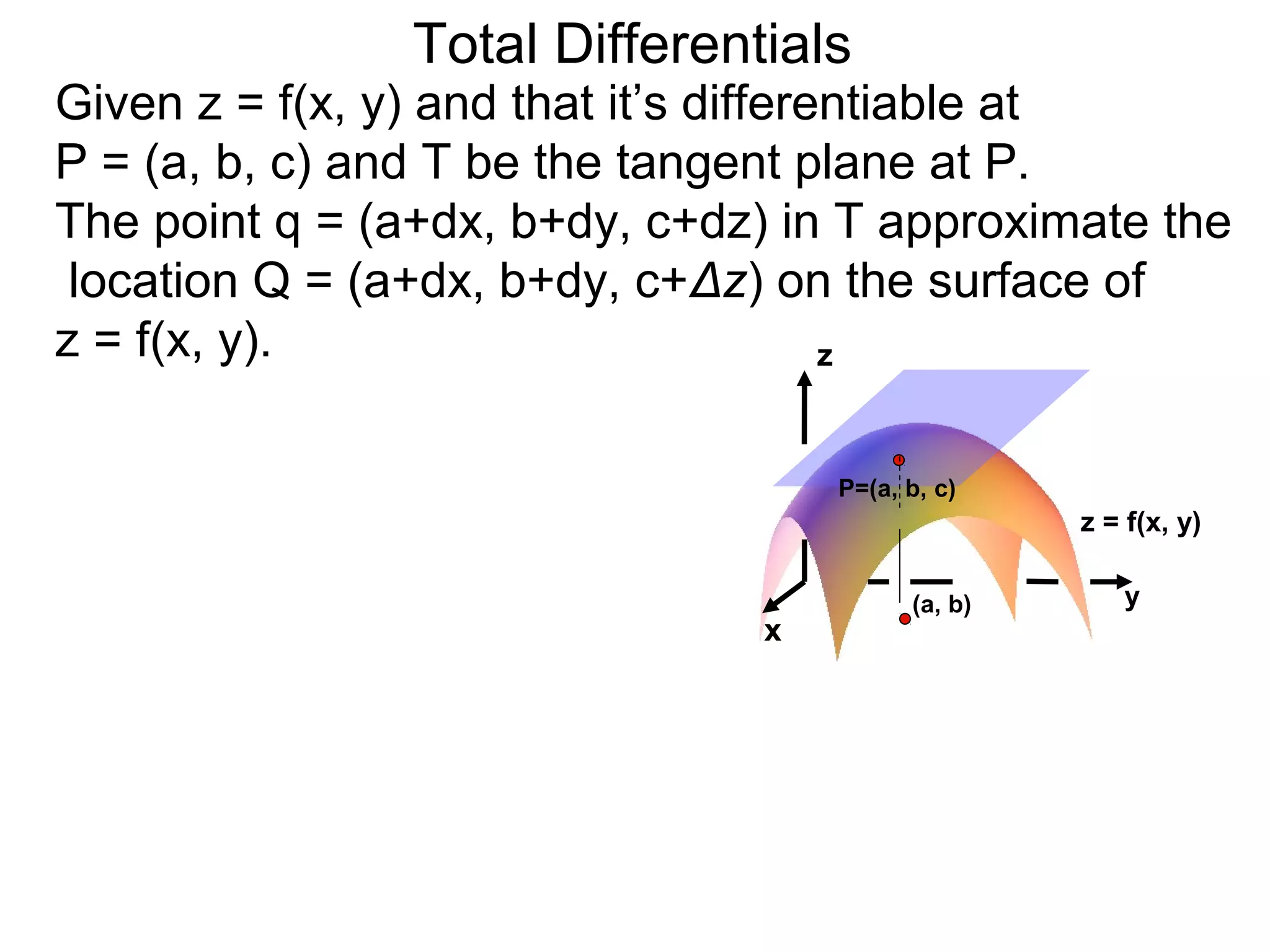
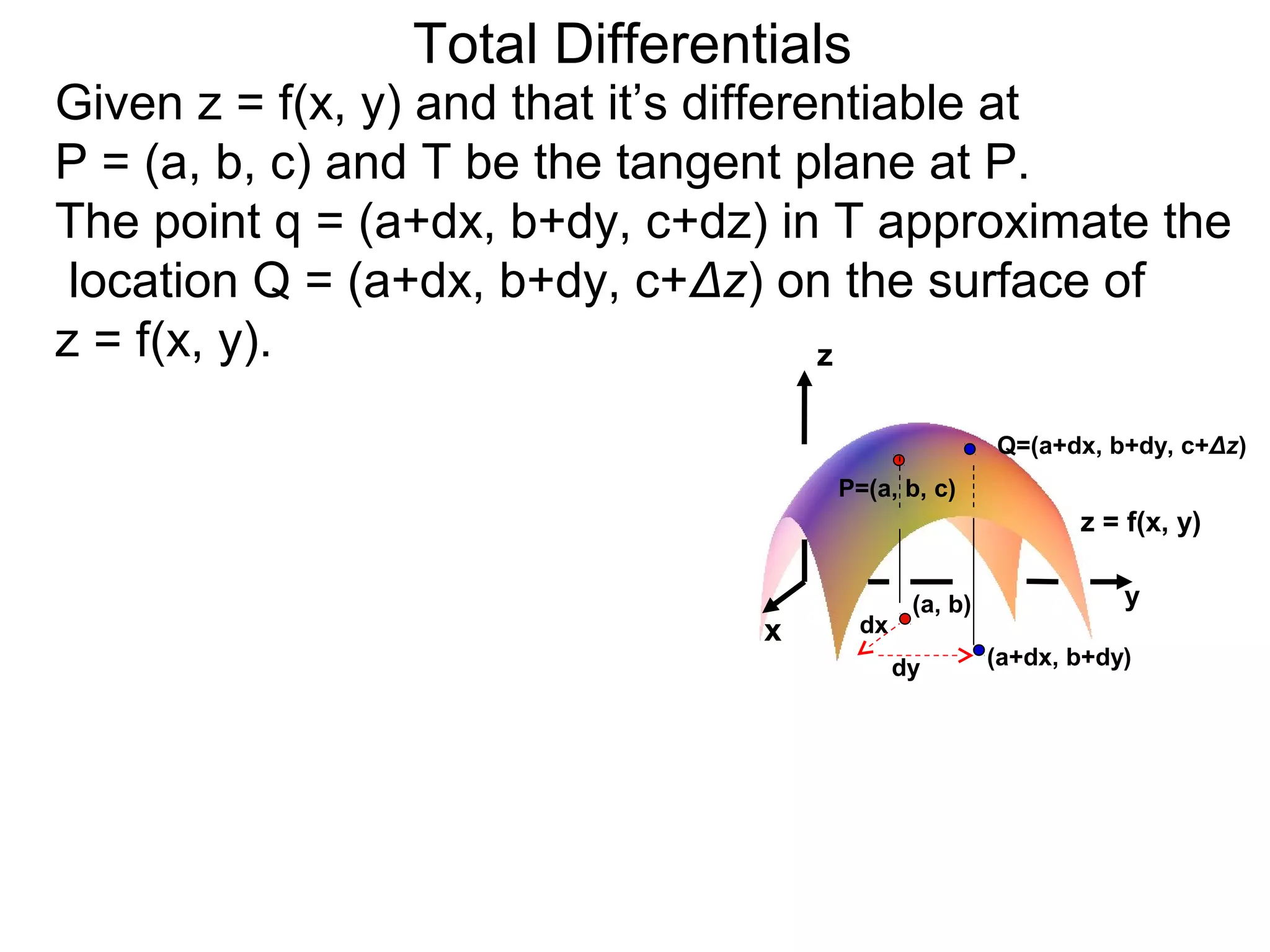
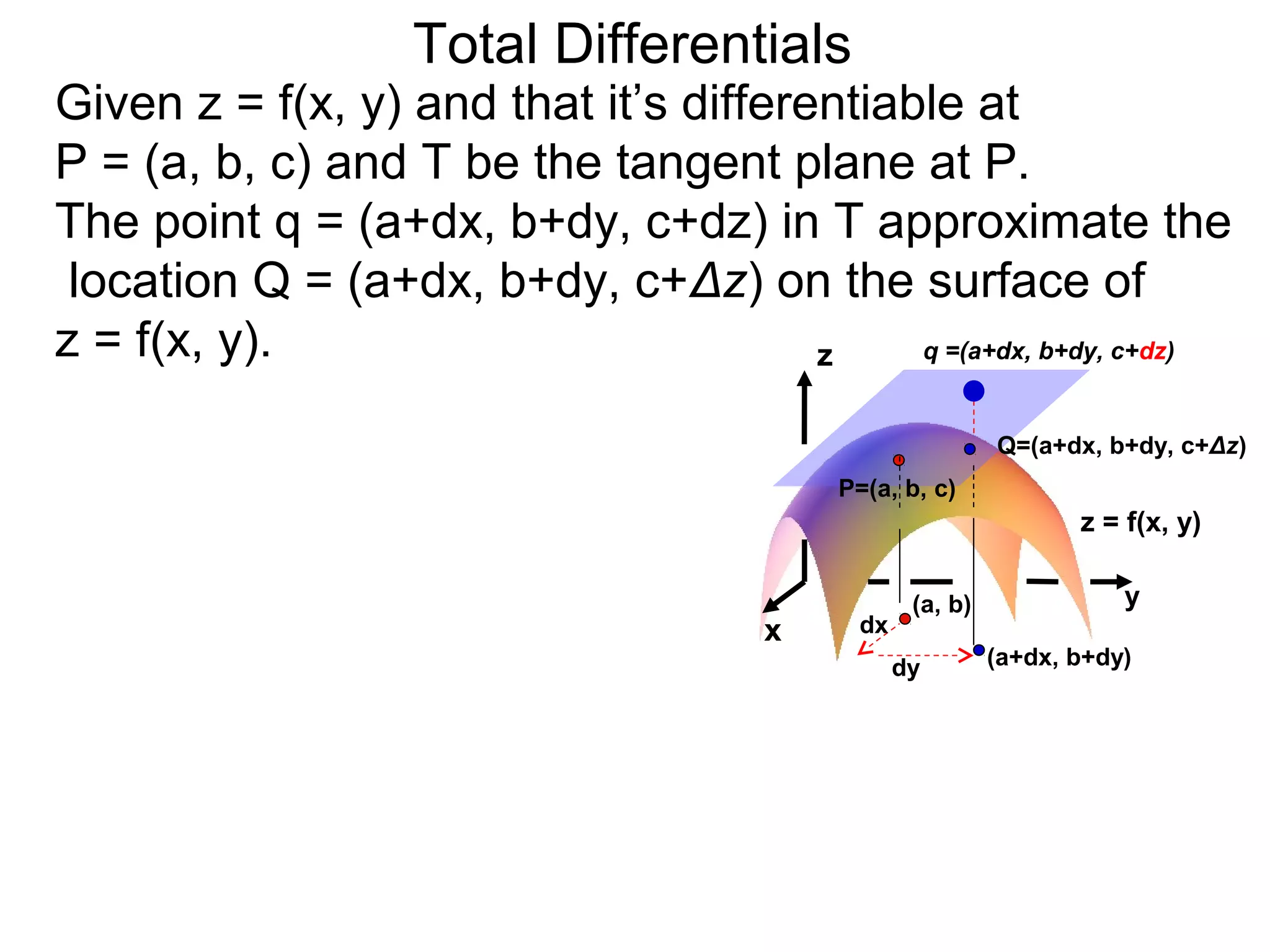
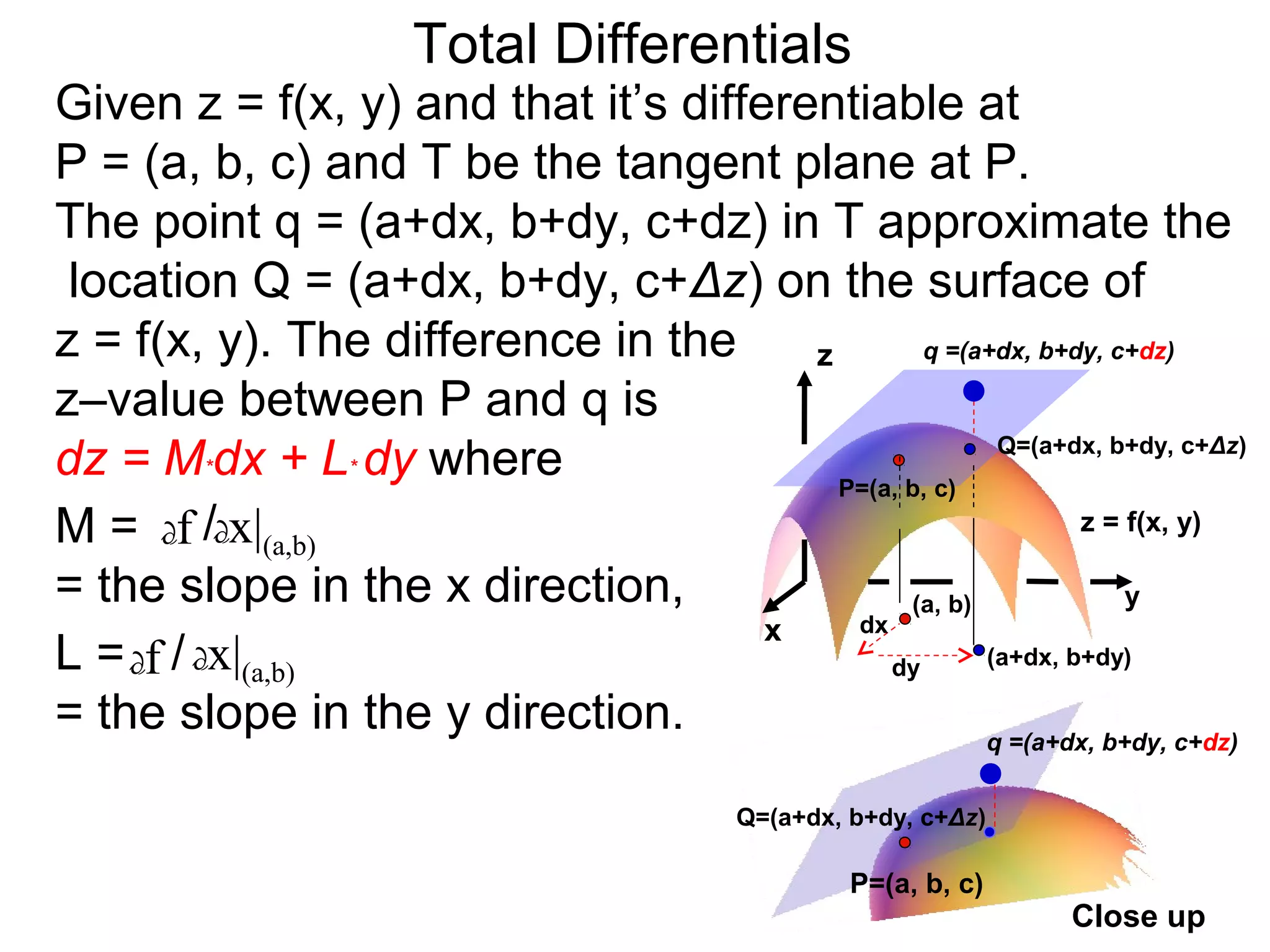
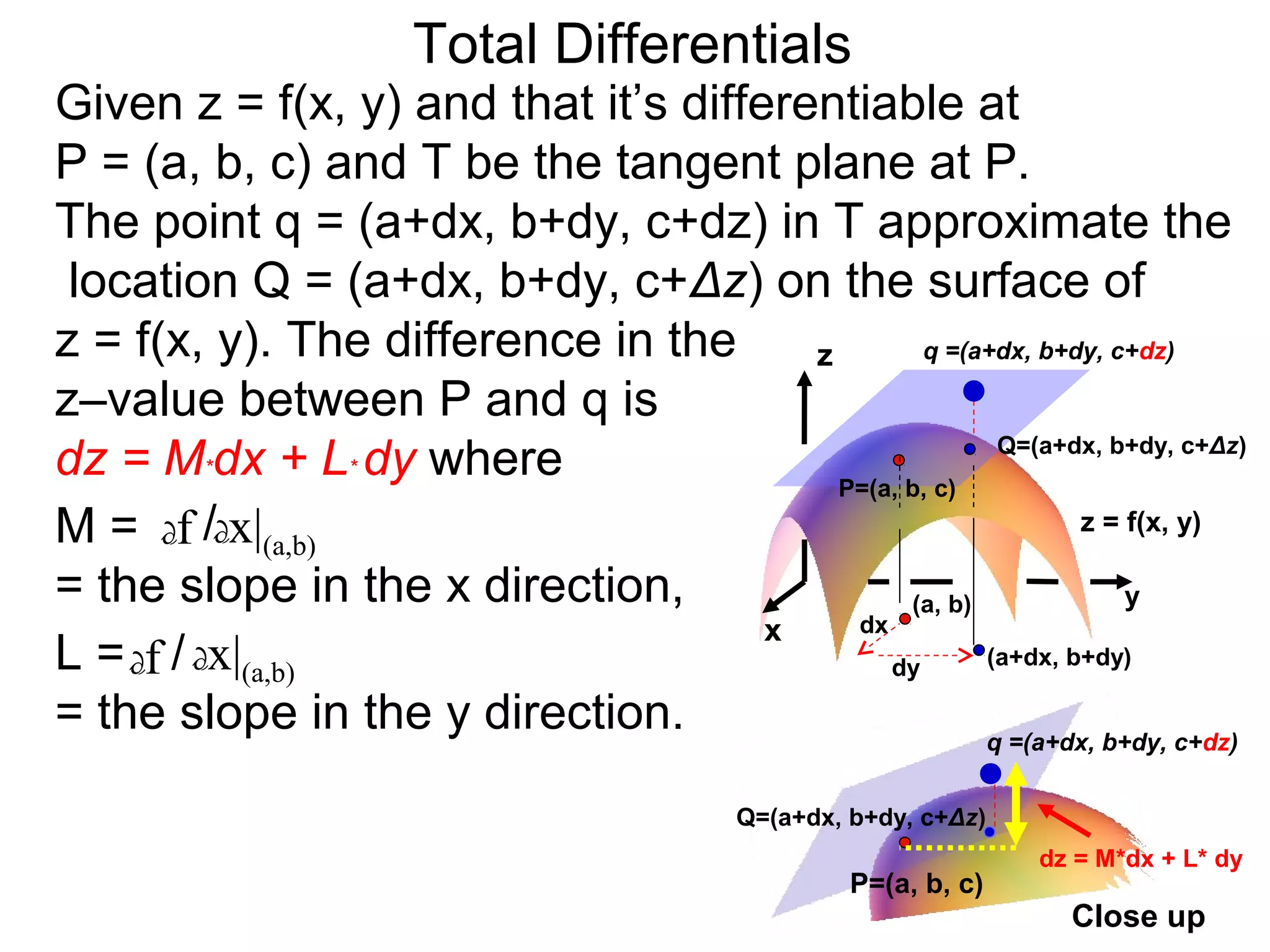
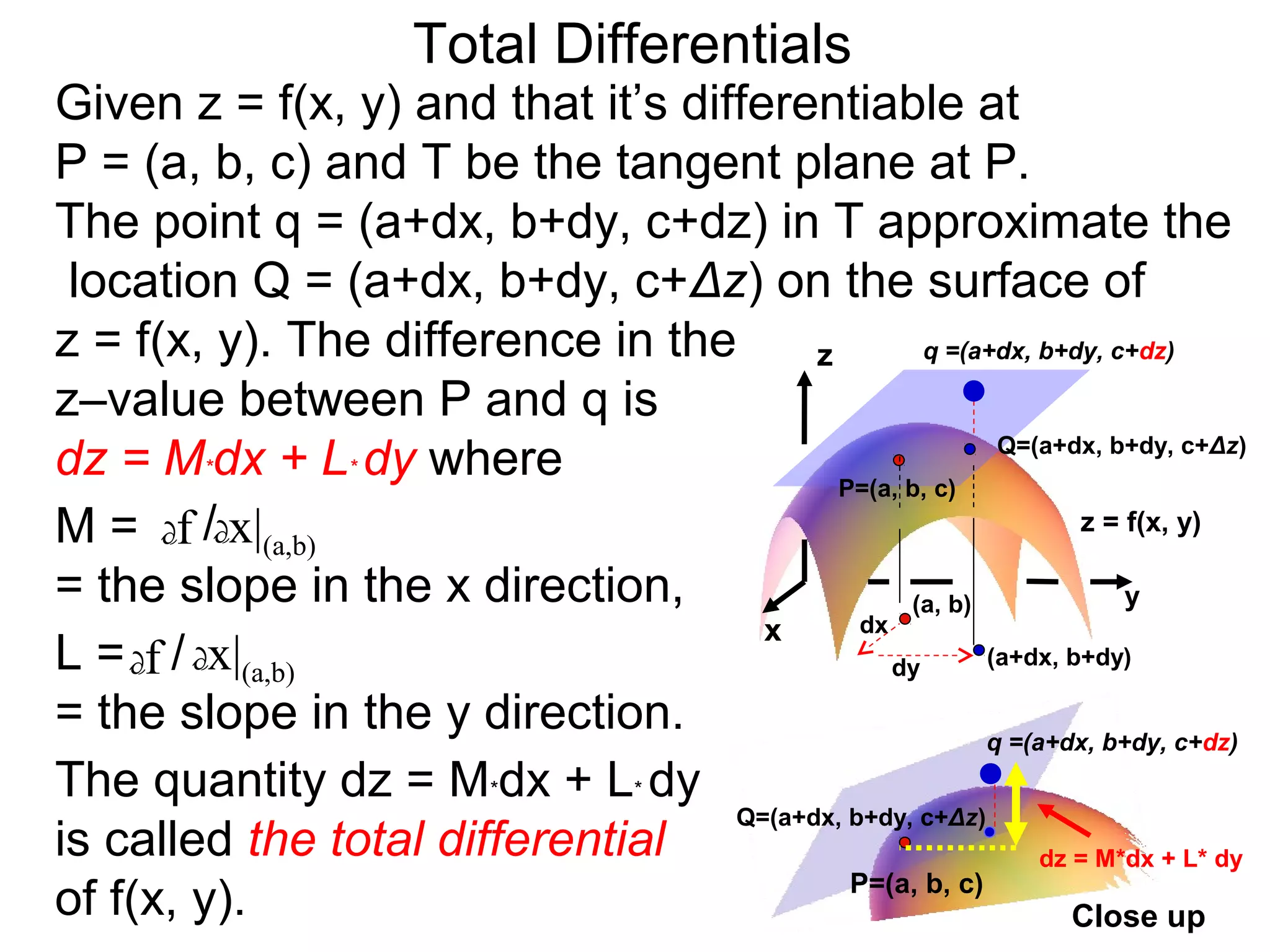
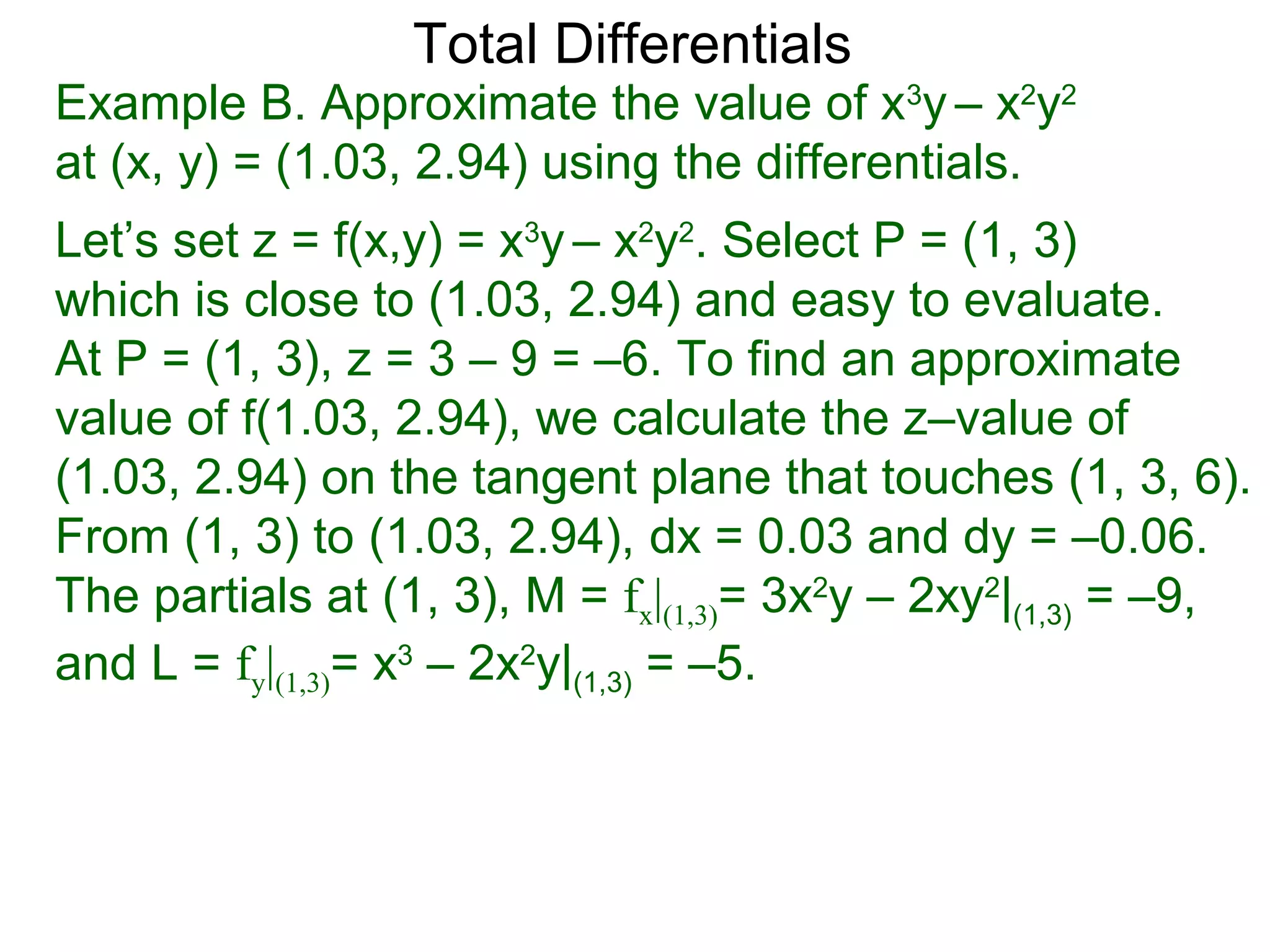
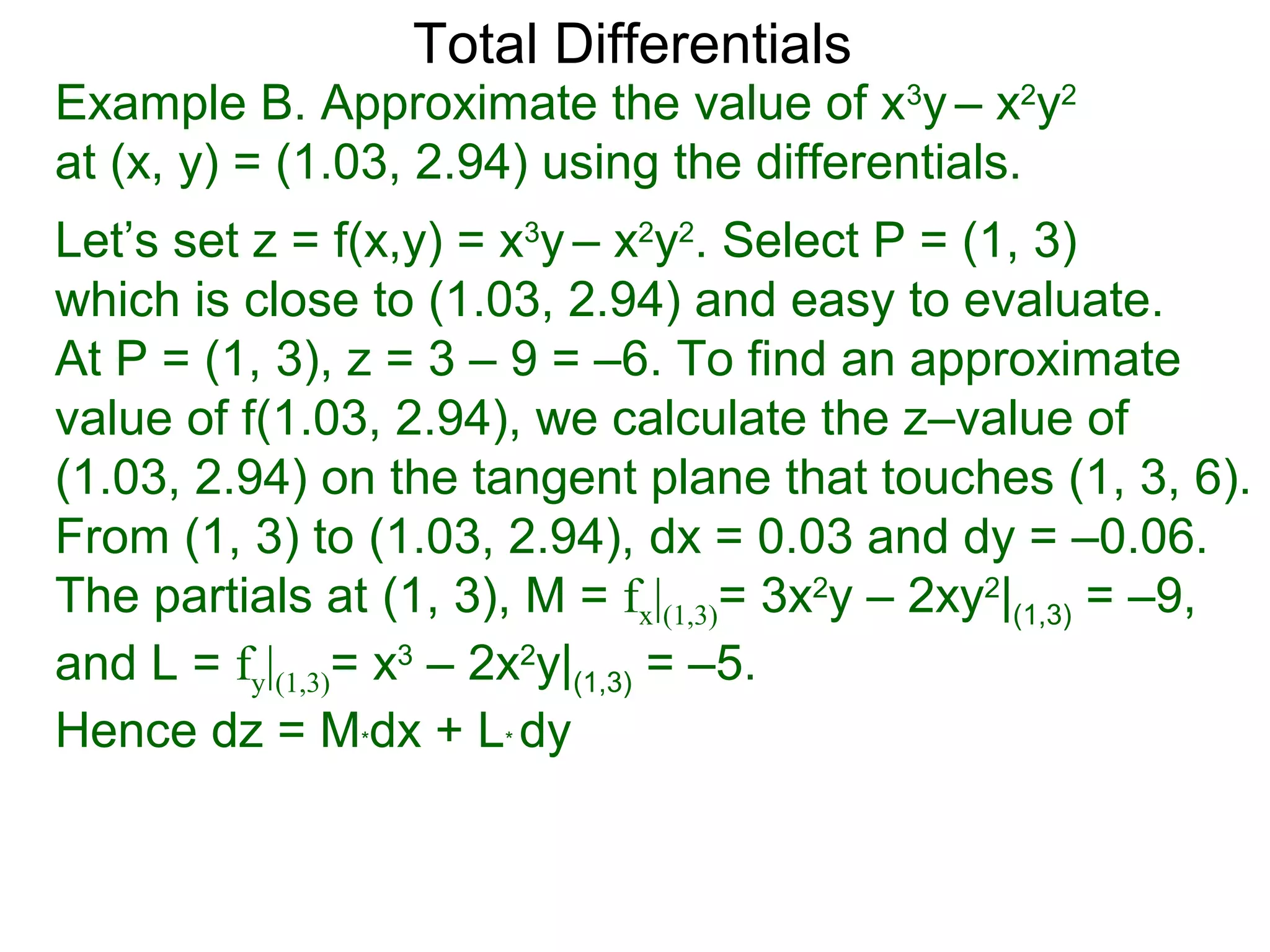
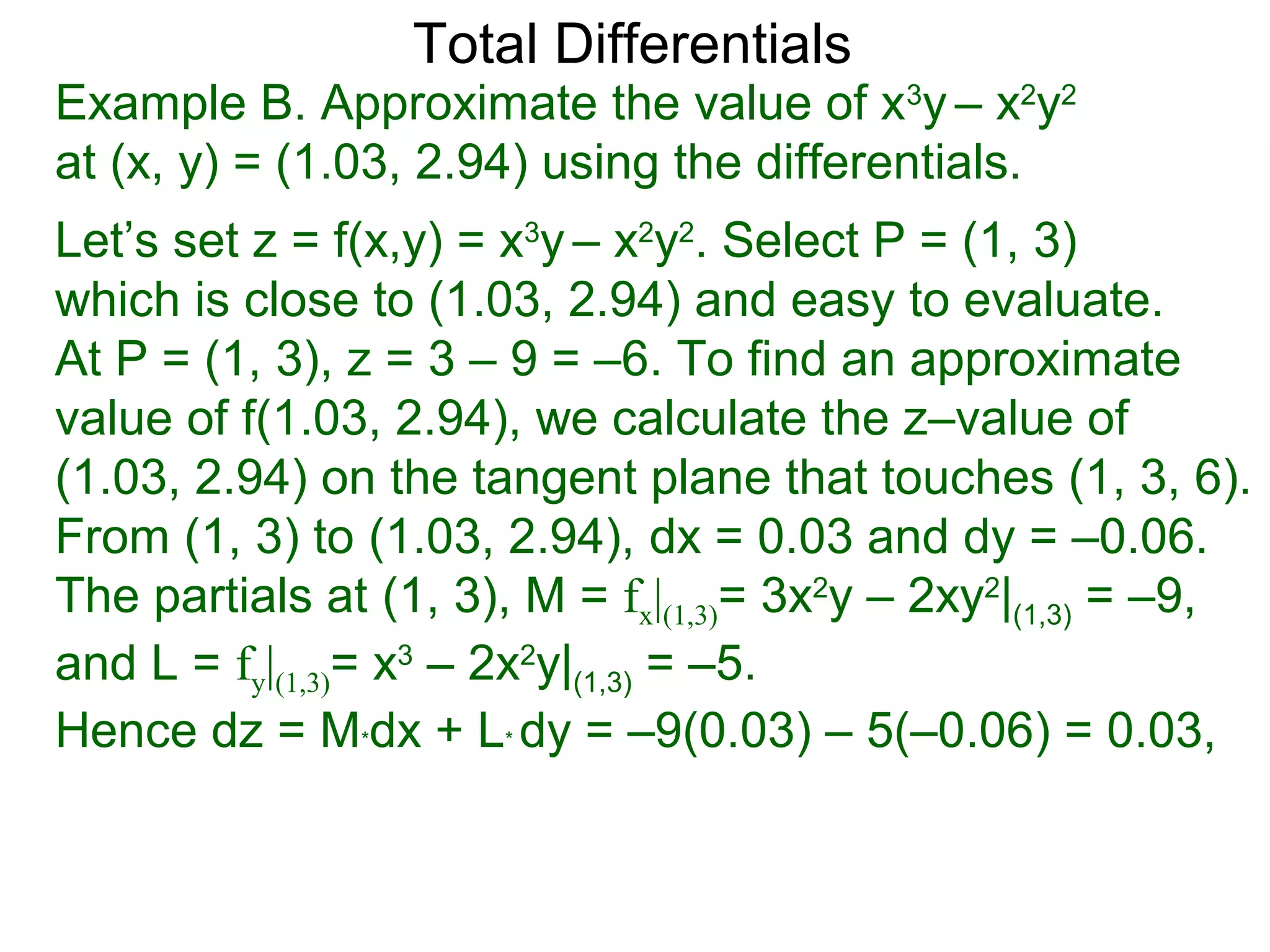
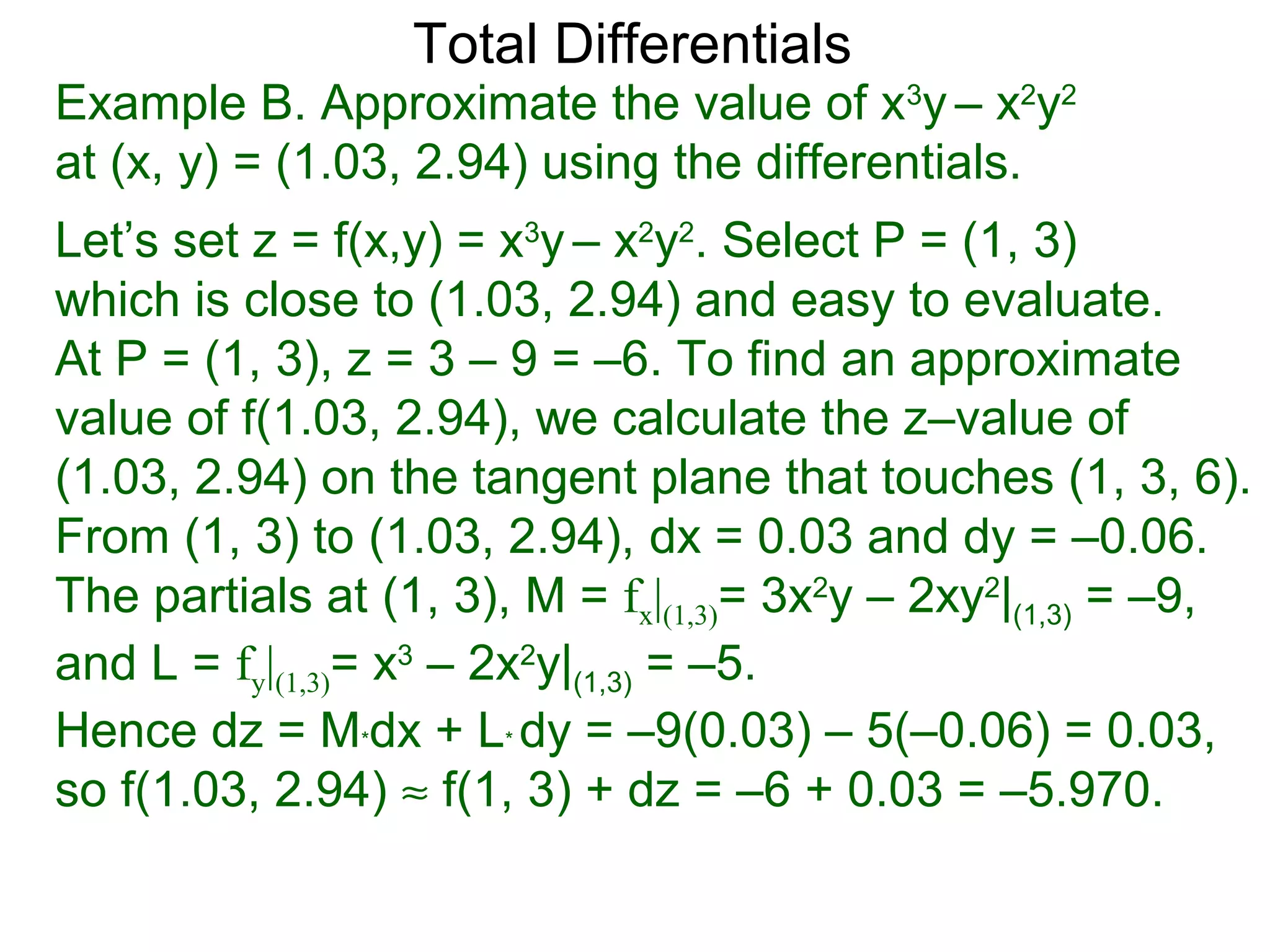
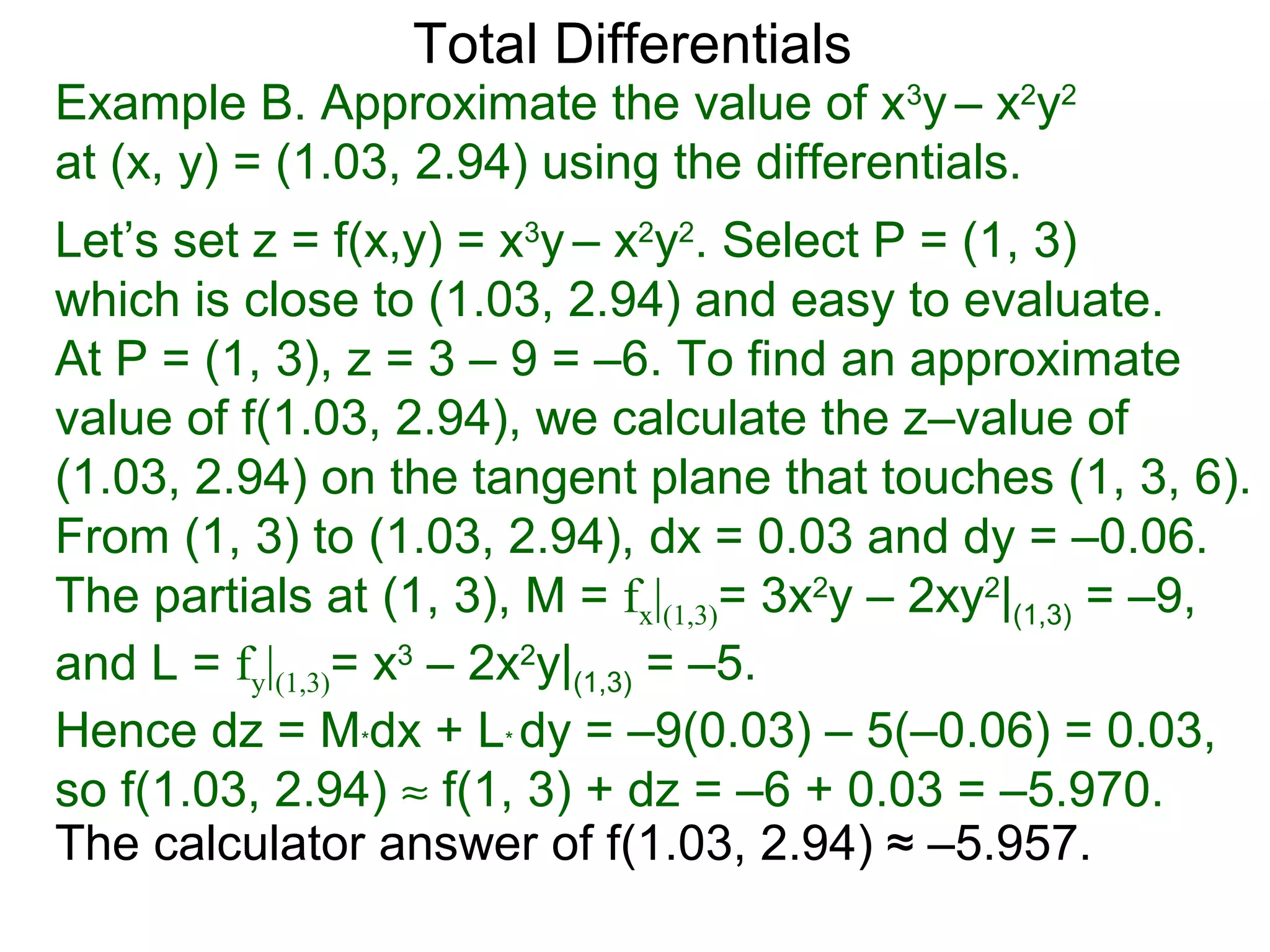
The document discusses tangent planes to surfaces. A surface is differentiable at a point if it is smooth and has a well-defined tangent plane at that point. The tangent plane approximates the surface near the point of tangency. To find the equation of the tangent plane, we calculate the partial derivatives of the surface function at the point to determine the slopes in the x- and y-directions. These slopes and the point define vectors in the tangent plane, and their cross product gives the normal vector. The equation of the tangent plane is then (z - c) = M(x - a) + L(y - b), where M and L are the partial derivatives and (a, b, c) is the