Embed presentation
Downloaded 85 times
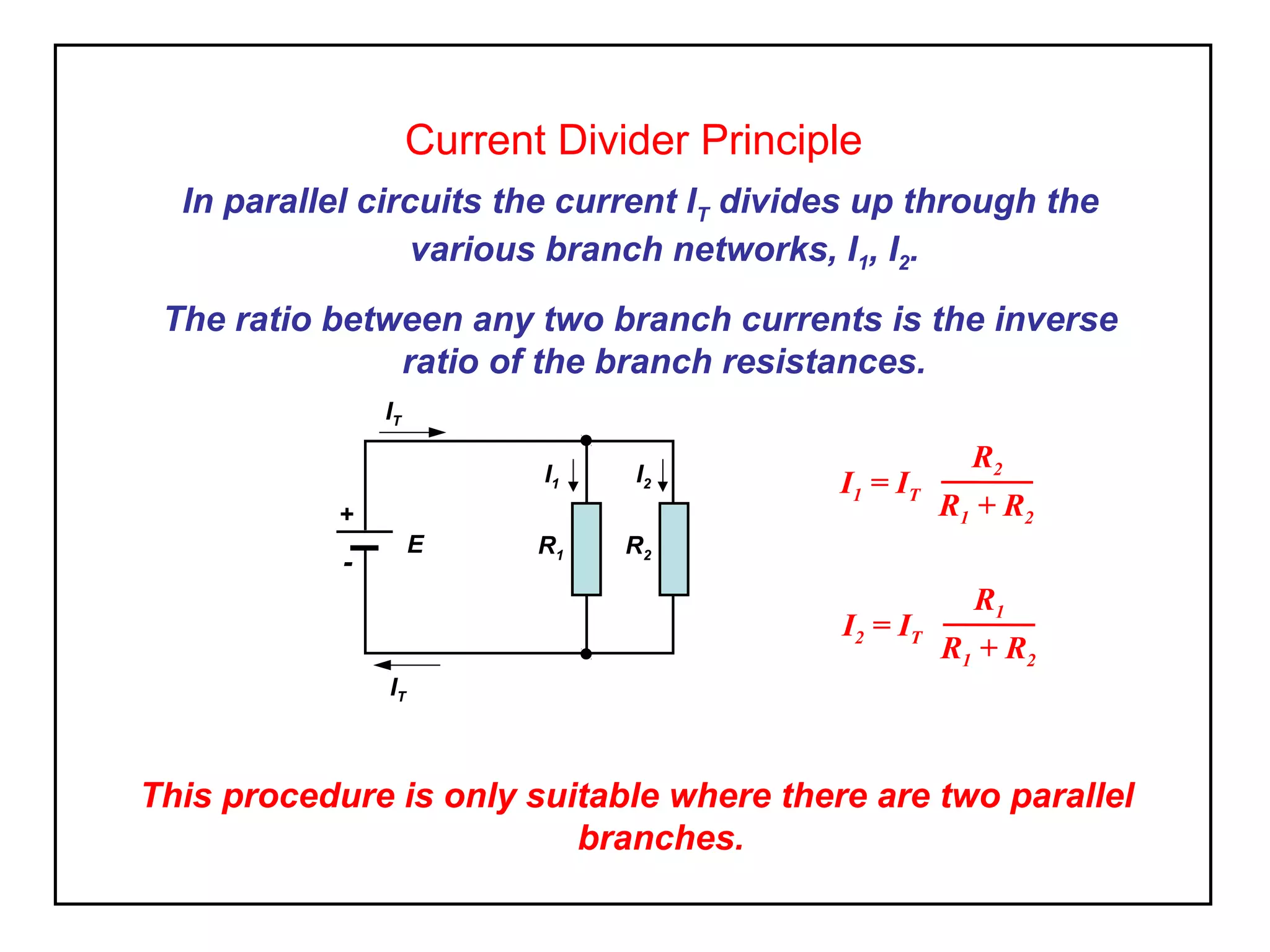
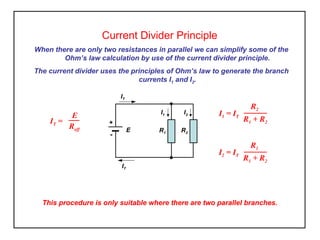
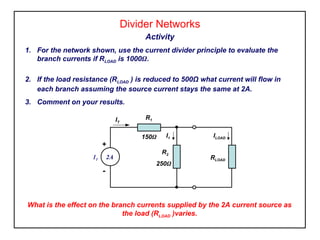
The current divider principle states that in a parallel circuit, the total current divides up among the branches proportionally to the resistances of each branch. Specifically: I1 = IT * R2 / (R1 + R2) I2 = IT * R1 / (R1 + R2) Where IT is the total current, I1 and I2 are the currents in each branch, and R1 and R2 are the resistances of each branch. This allows simplifying some Ohm's law calculations for parallel circuits with two branches. The principle is only applicable when there are two parallel branches.


