Report
Share
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Introduction to electric power transmission and distribution

Introduction to electric power transmission and distribution
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (20)
Similar to Elect principles 2 current divider
Pb2012.01 an application of utilizing the system efficient-esd-design (seed) ...

Pb2012.01 an application of utilizing the system efficient-esd-design (seed) ...ESDEMC Technology LLC
Similar to Elect principles 2 current divider (20)
11.[49 61]optimizing the output current for a dc-dc converter![11.[49 61]optimizing the output current for a dc-dc converter](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![11.[49 61]optimizing the output current for a dc-dc converter](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
11.[49 61]optimizing the output current for a dc-dc converter
Emotional Stress Indicator and Digital Thermometer-Project-8thsem

Emotional Stress Indicator and Digital Thermometer-Project-8thsem
Pb2012.01 an application of utilizing the system efficient-esd-design (seed) ...

Pb2012.01 an application of utilizing the system efficient-esd-design (seed) ...
More from sdacey
More from sdacey (20)
Elect principles 2 current divider
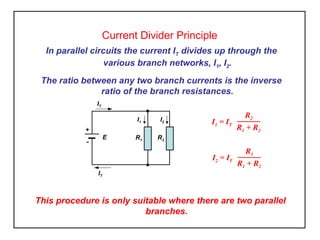
- 1. Current Divider Principle In parallel circuits the current IT divides up through the various branch networks, I1, I2. The ratio between any two branch currents is the inverse ratio of the branch resistances. I1 = IT R2 R1 + R2 E + - IT R2R1 I1 I2 IT I2 = IT R1 R1 + R2 This procedure is only suitable where there are two parallel branches.
- 2. Current Divider Principle When there are only two resistances in parallel we can simplify some of the Ohm’s law calculation by use of the current divider principle. The current divider uses the principles of Ohm’s law to generate the branch currents I1 and I2. This procedure is only suitable where there are two parallel branches. E + - IT R2R1 I1 I2 IT I1 = IT R2 R1 + R2 Reff E IT = I2 = IT R1 R1 + R2
- 3. Divider Networks Activity 1. For the network shown, use the current divider principle to evaluate the branch currents if RLOAD is 1000Ω. 2. If the load resistance (RLOAD ) is reduced to 500Ω what current will flow in each branch assuming the source current stays the same at 2A. 3. Comment on your results. What is the effect on the branch currents supplied by the 2A current source as the load (RLOAD )varies. IT RLOAD ILOADI1 R1 150Ω R2 250Ω + - 2AIT