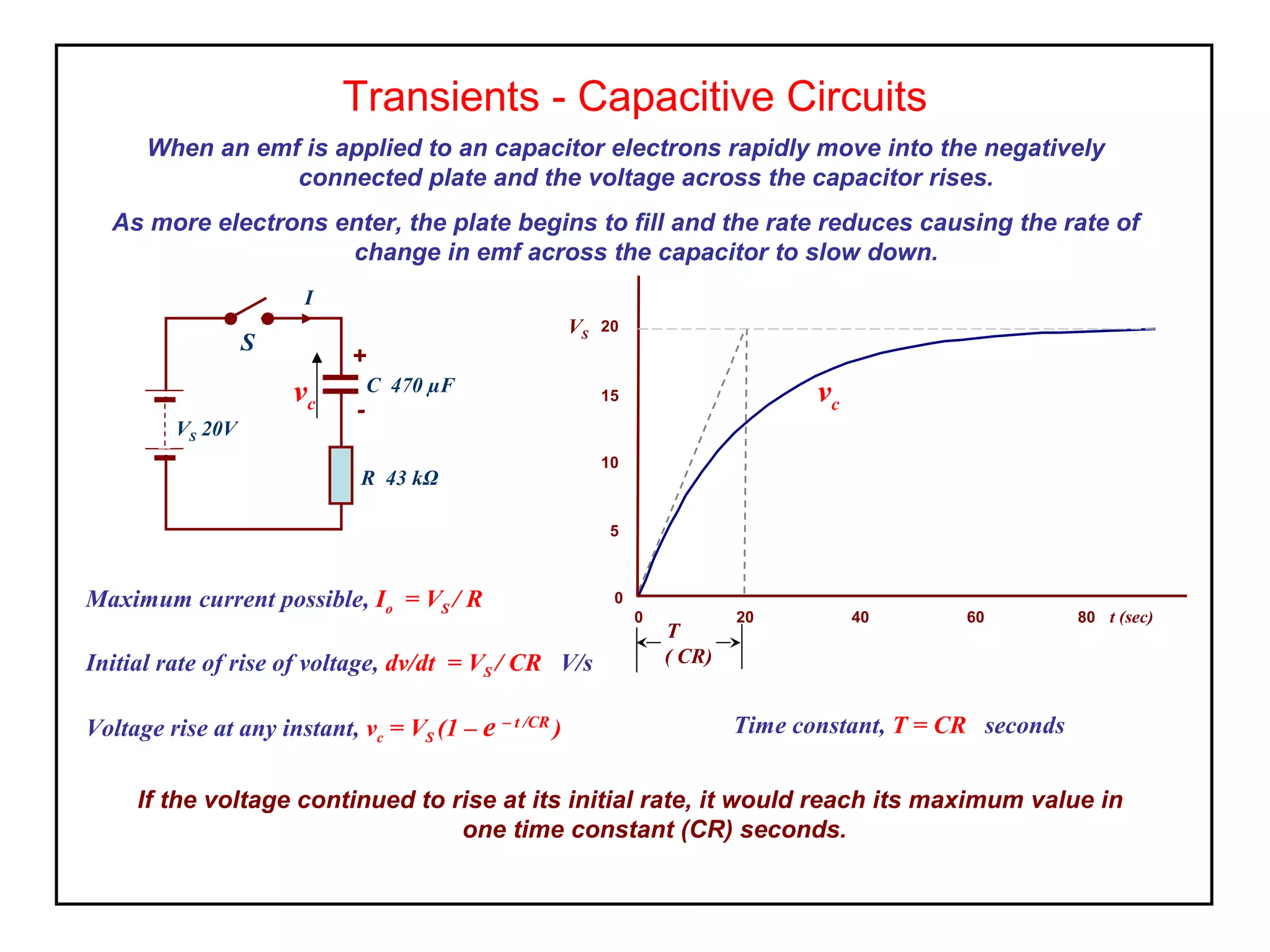
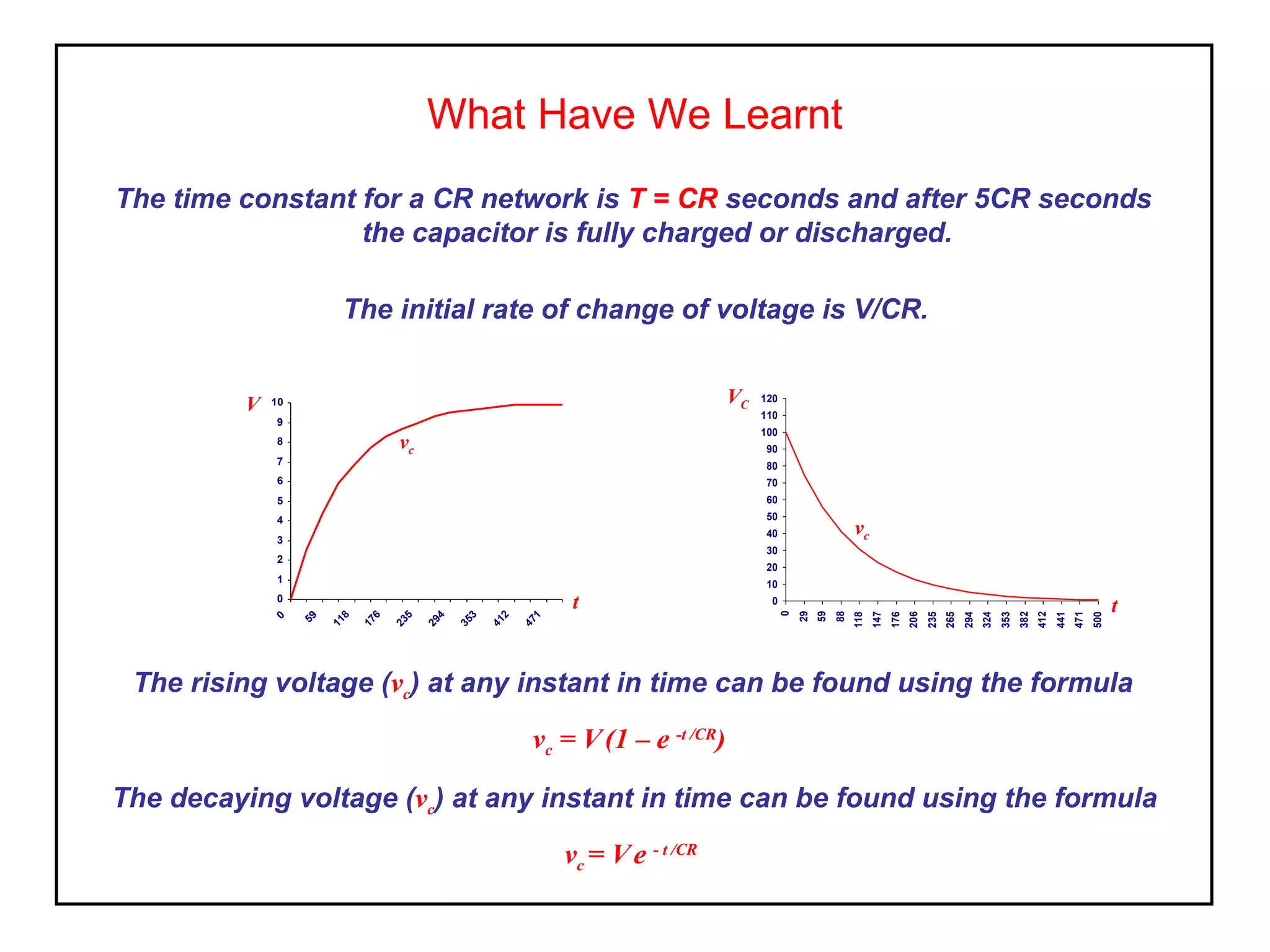
1. When a capacitor is charged by a voltage source through a resistor, the voltage across the capacitor rises exponentially as electrons move into the capacitor plates. The time it takes for the voltage to reach 63% of its final value is called the time constant and equals the product of the capacitor's capacitance and the resistor's resistance.
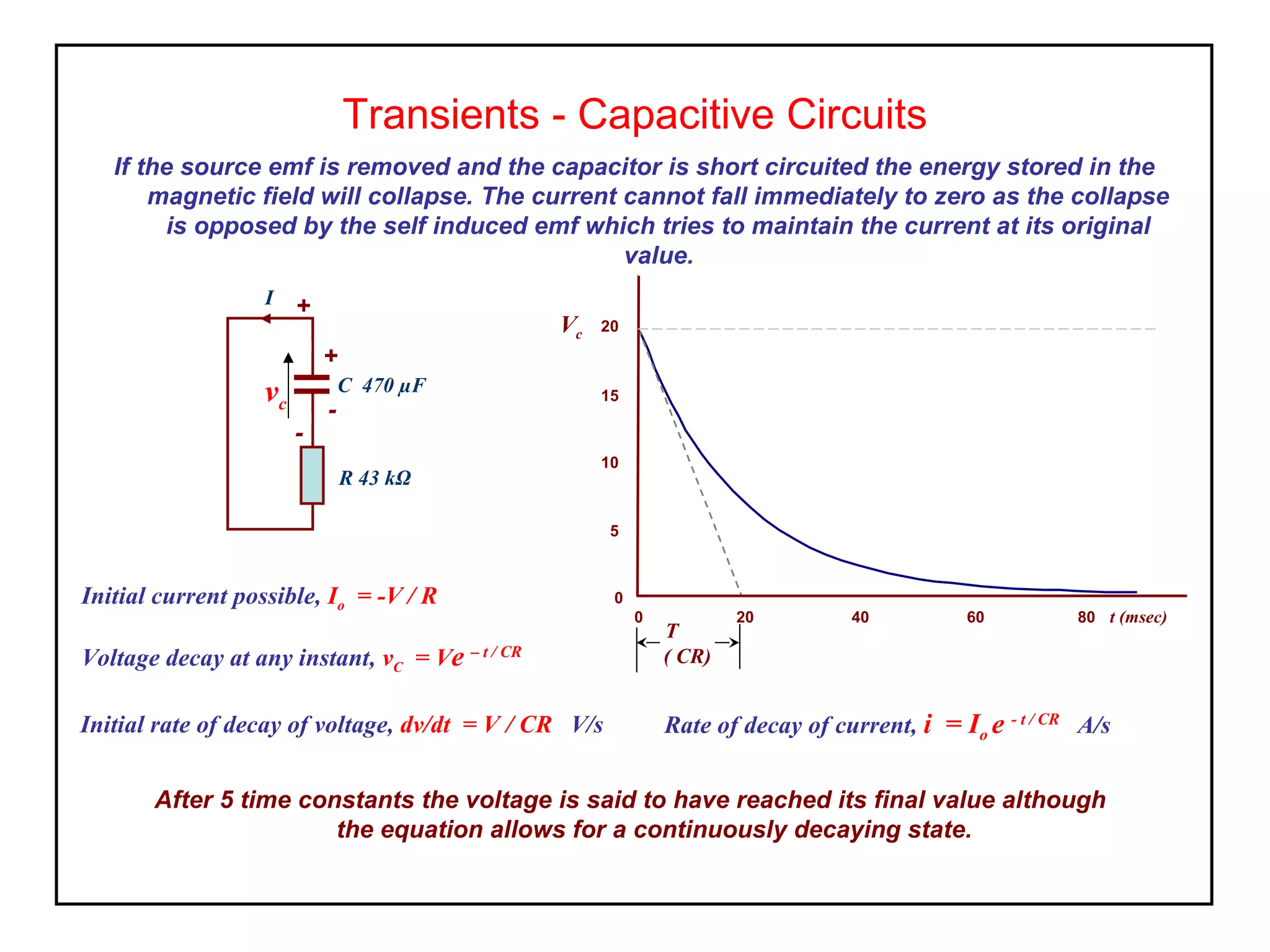
2. After being charged, if the voltage source is removed and the capacitor discharged through a short circuit, the stored energy will cause a current to flow which decays exponentially over the time constant as the electrons drain from the capacitor plates.
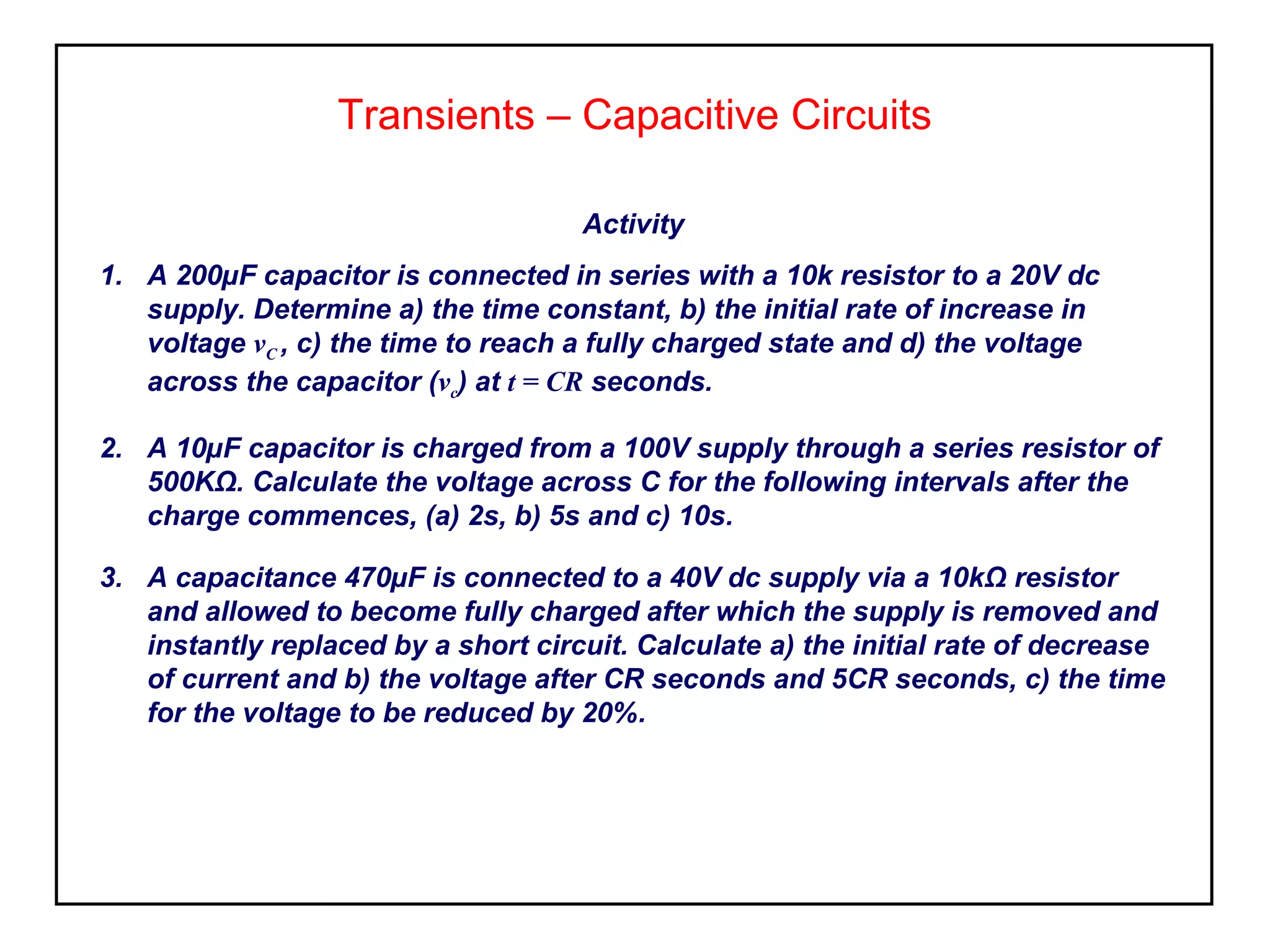
3. The voltage and current values at any time during the charging or discharging process can be calculated using equations that involve the time constant,