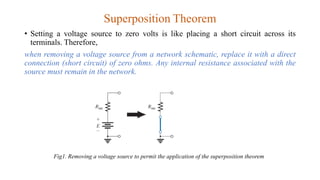
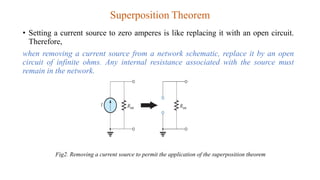
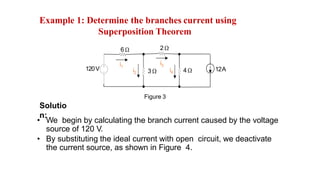
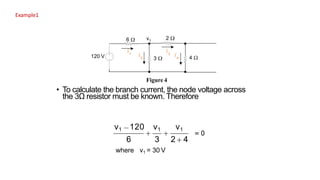
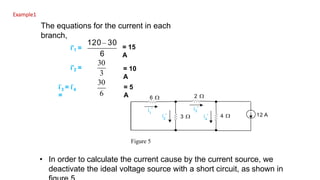
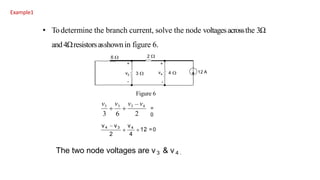
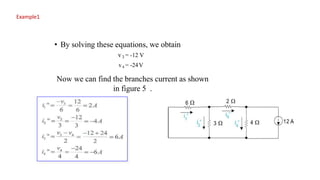
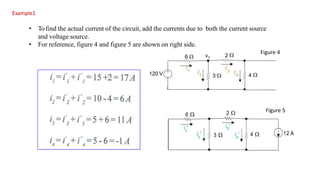
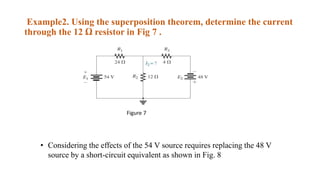
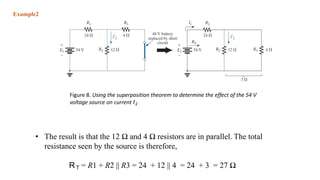
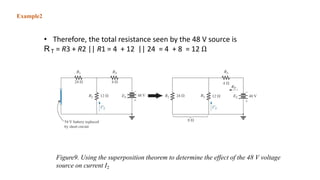
The superposition theorem allows engineers to solve for unknown voltages and currents in circuits with multiple sources. It states that the total response of a linear system to excitations is the sum of the responses that would occur due to each excitation individually. To use the theorem, each source is solved for separately while replacing other sources with their open or short circuit equivalents. The individual solutions are then combined through algebraic addition or subtraction to obtain the total solution. The document provides examples demonstrating how to use the superposition theorem to solve for branch currents in circuits with both voltage and current sources.