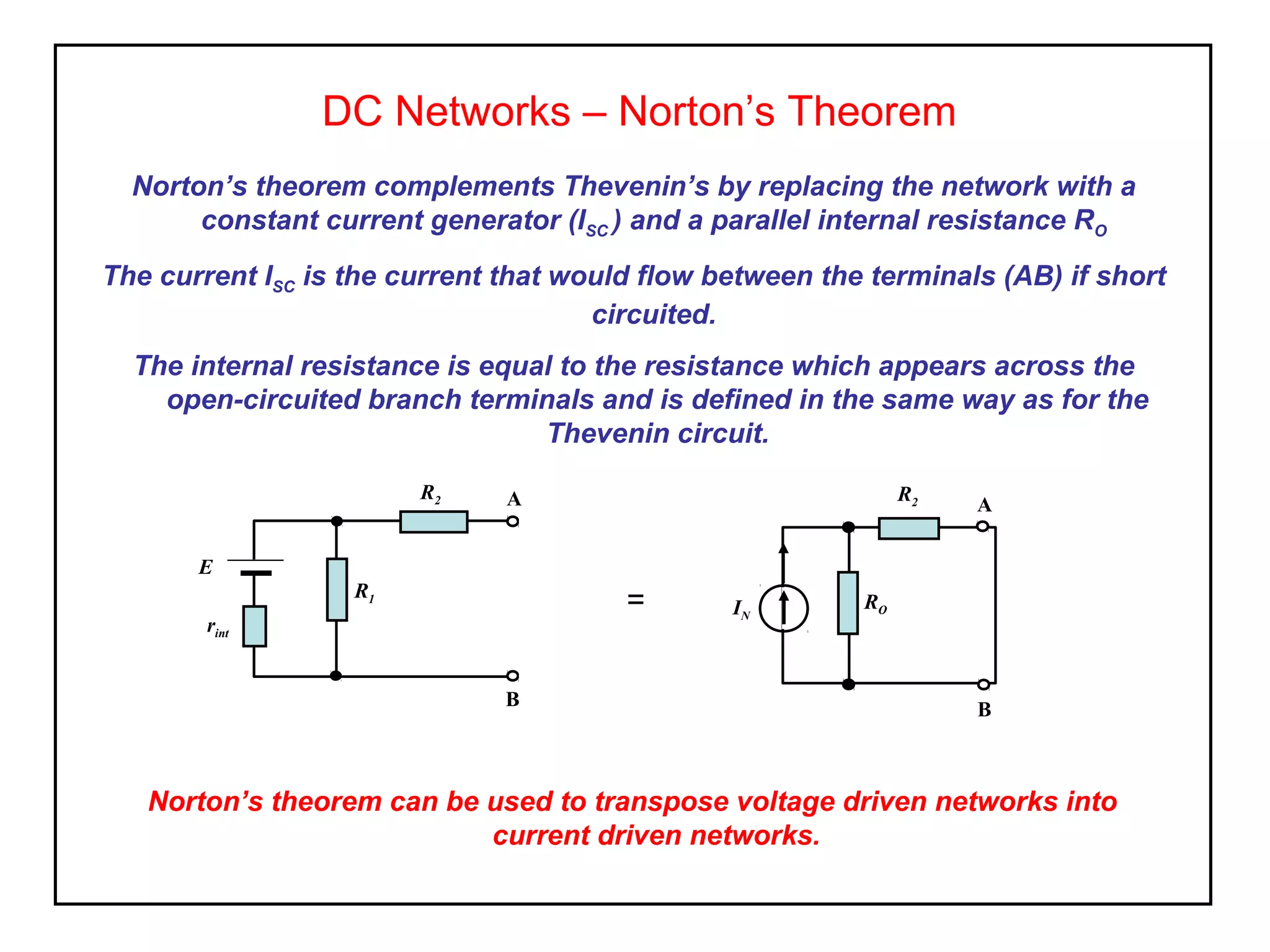
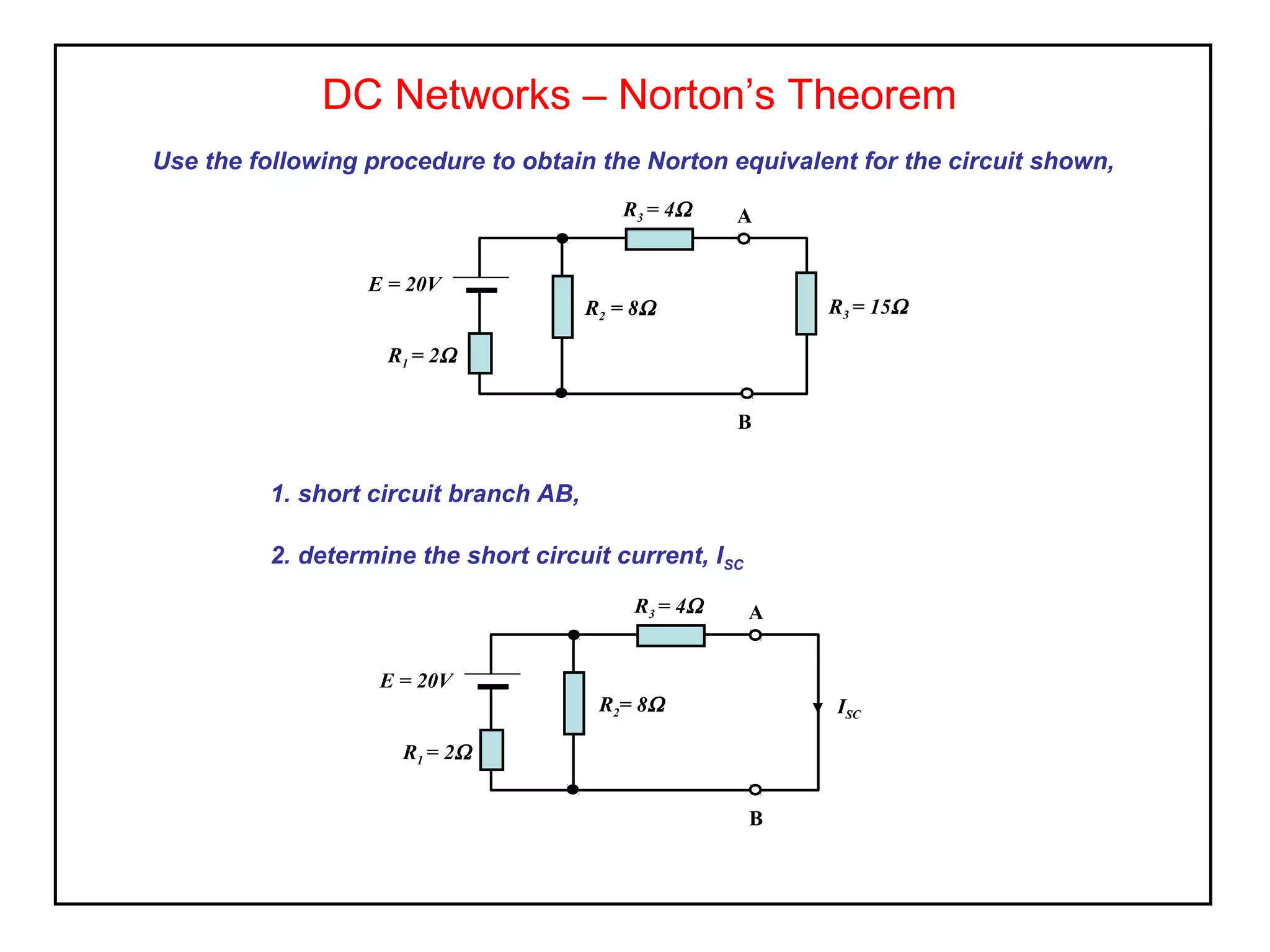
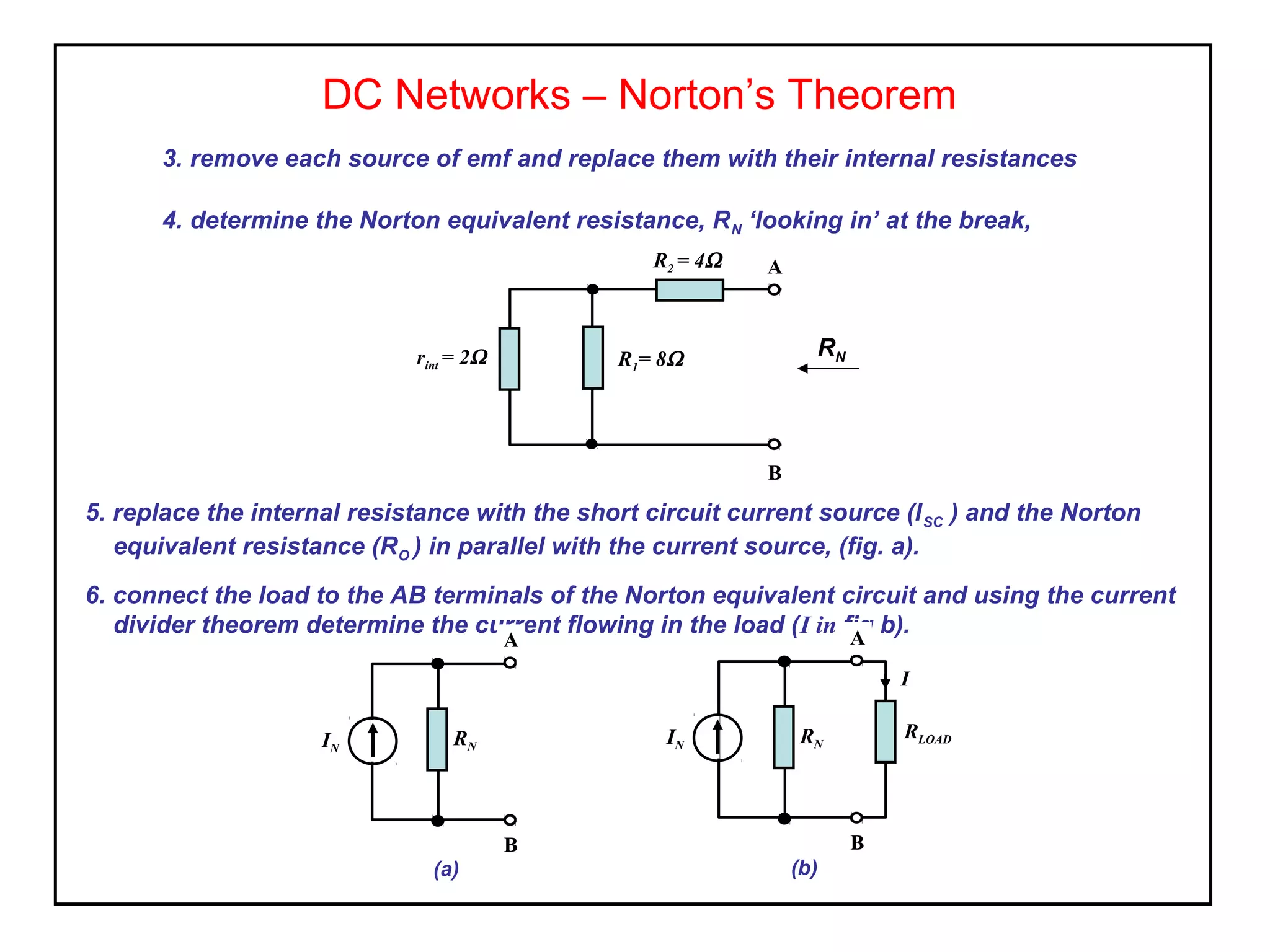
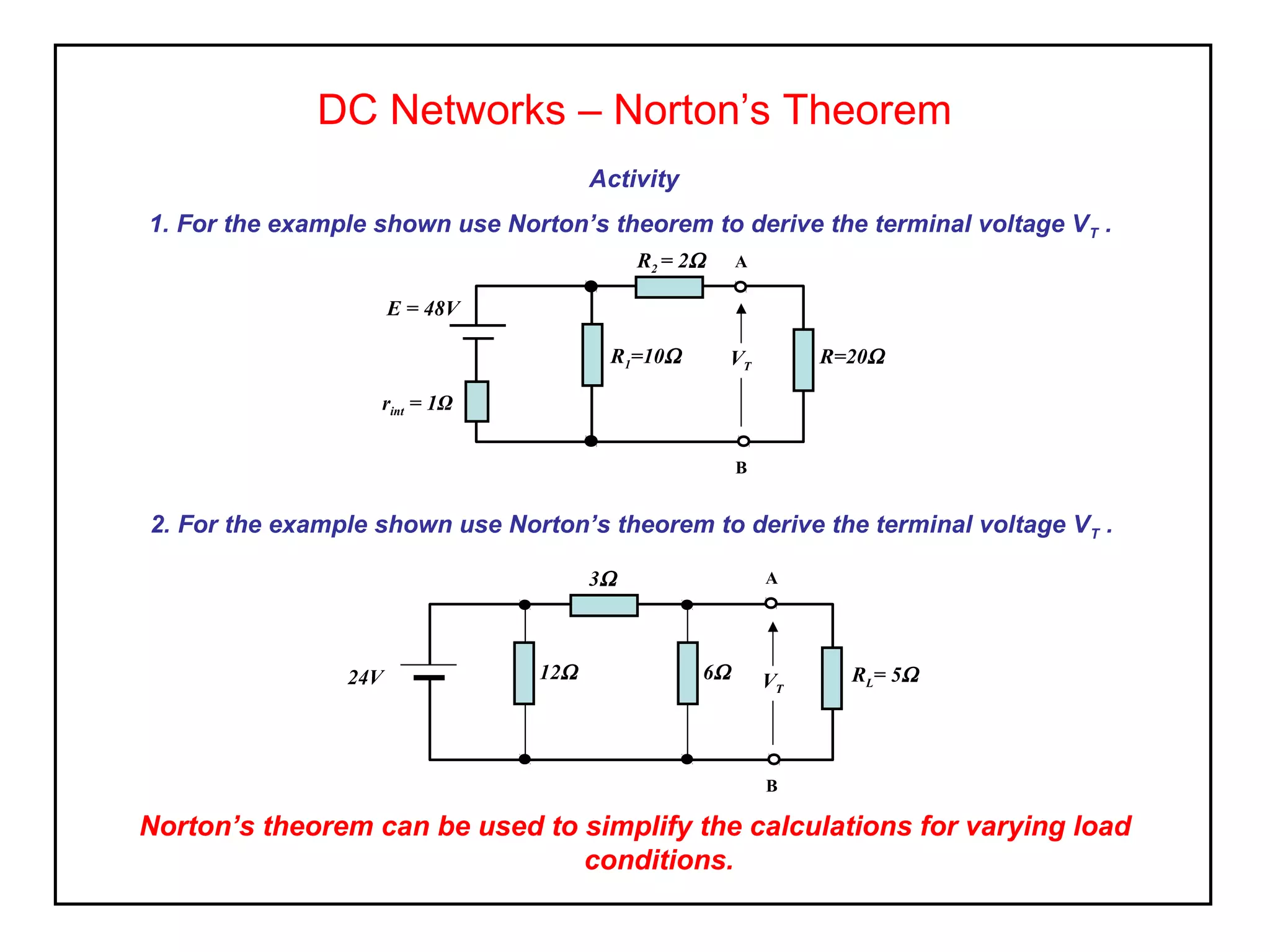
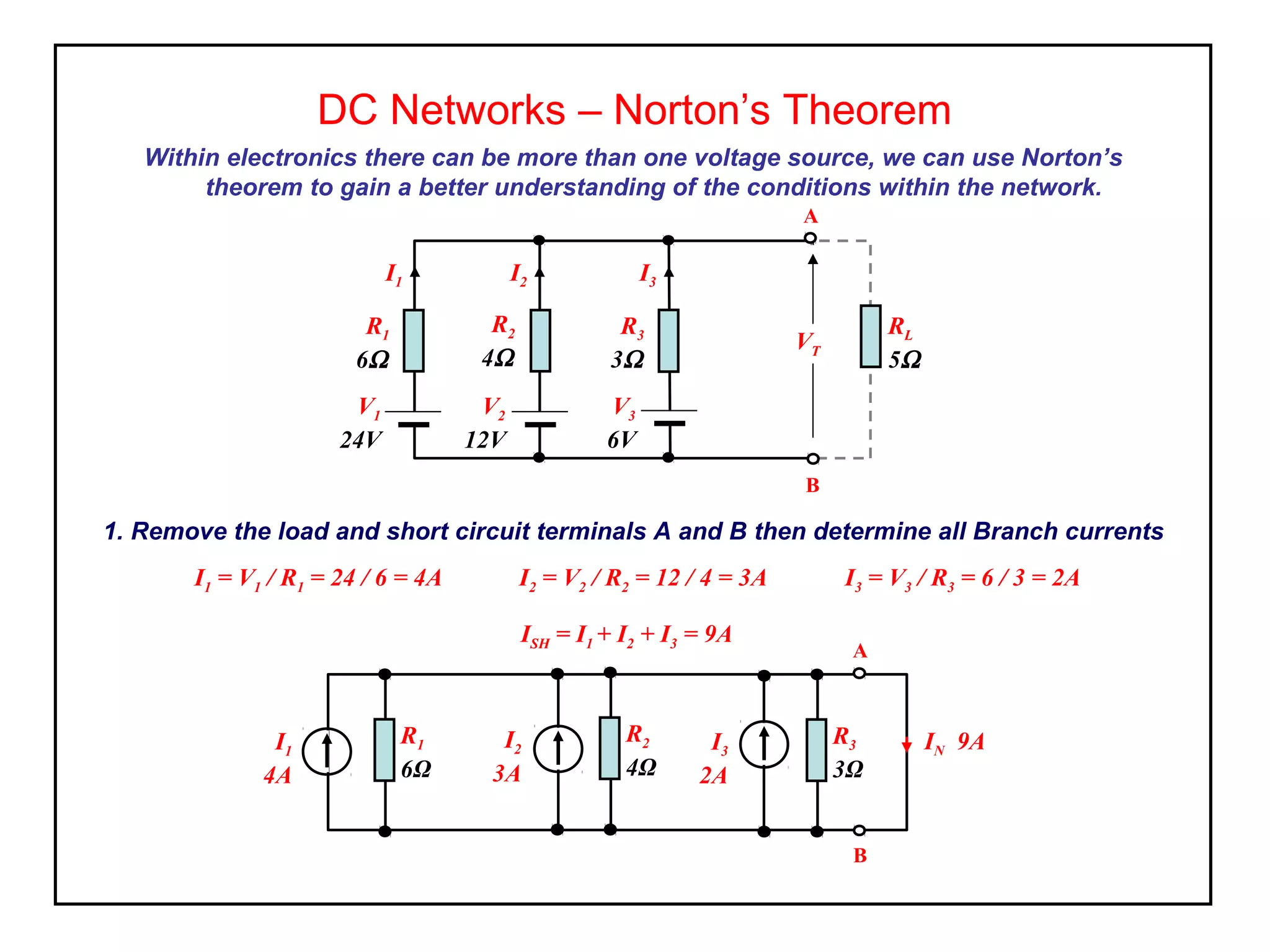
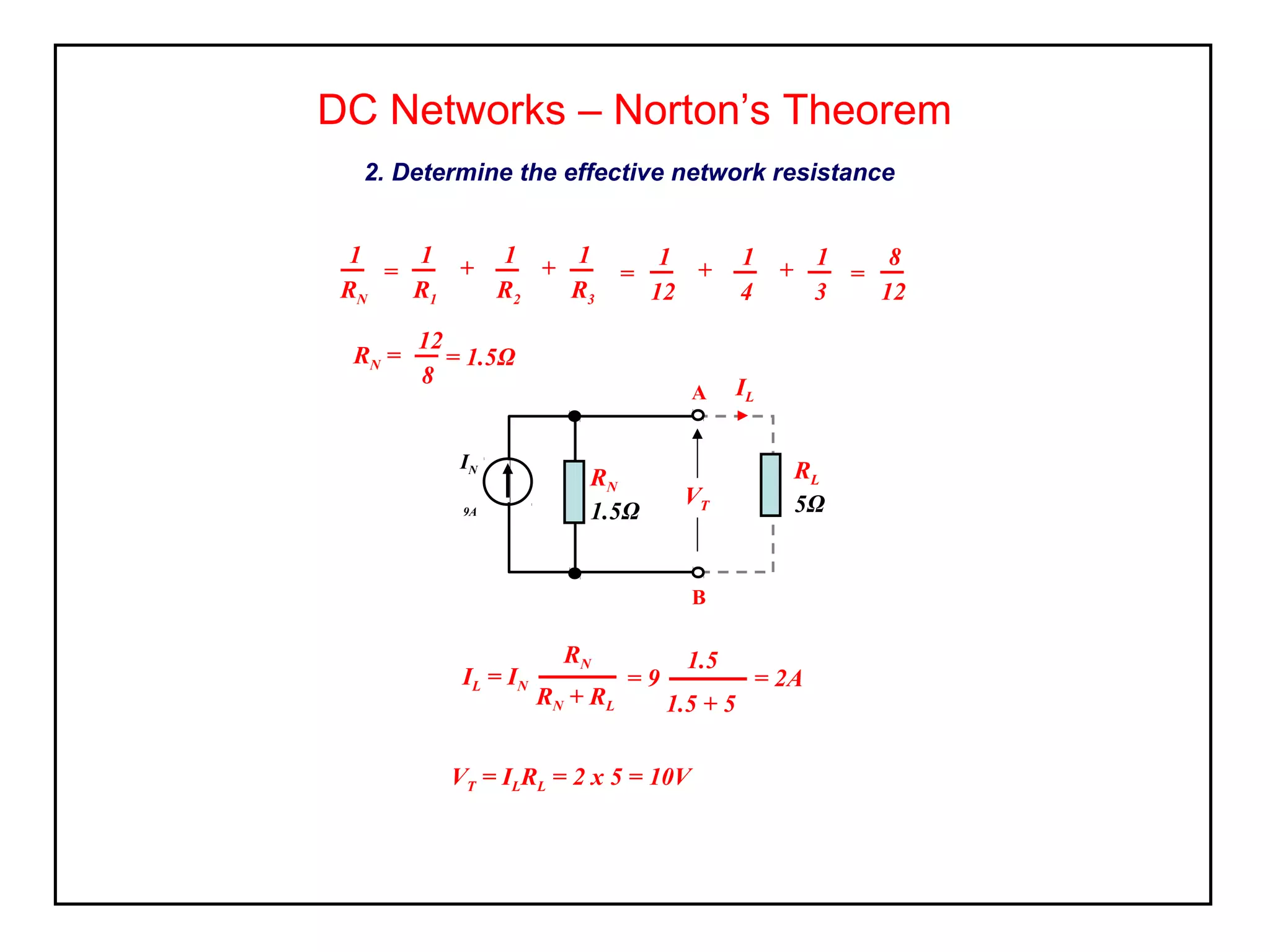
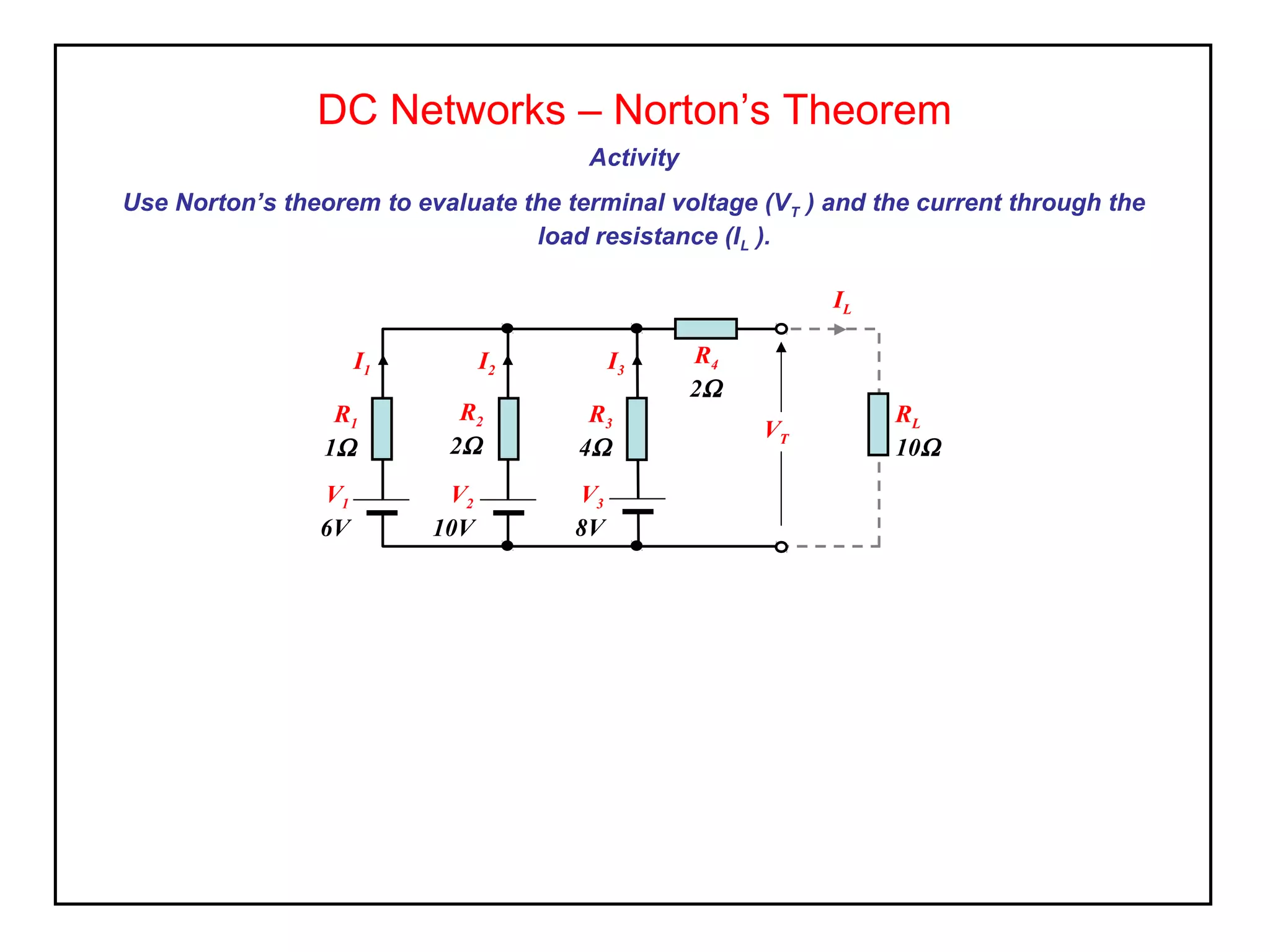
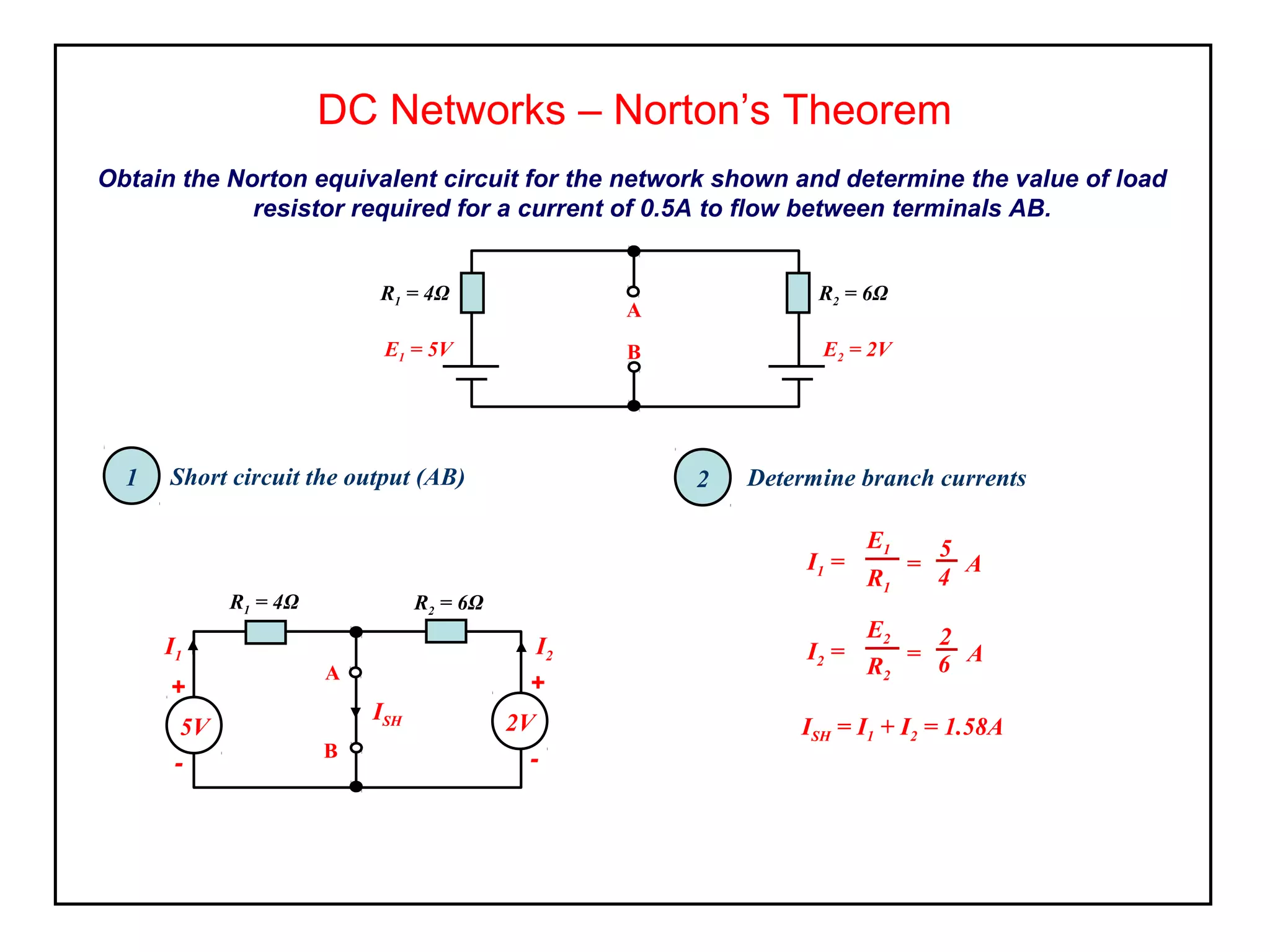
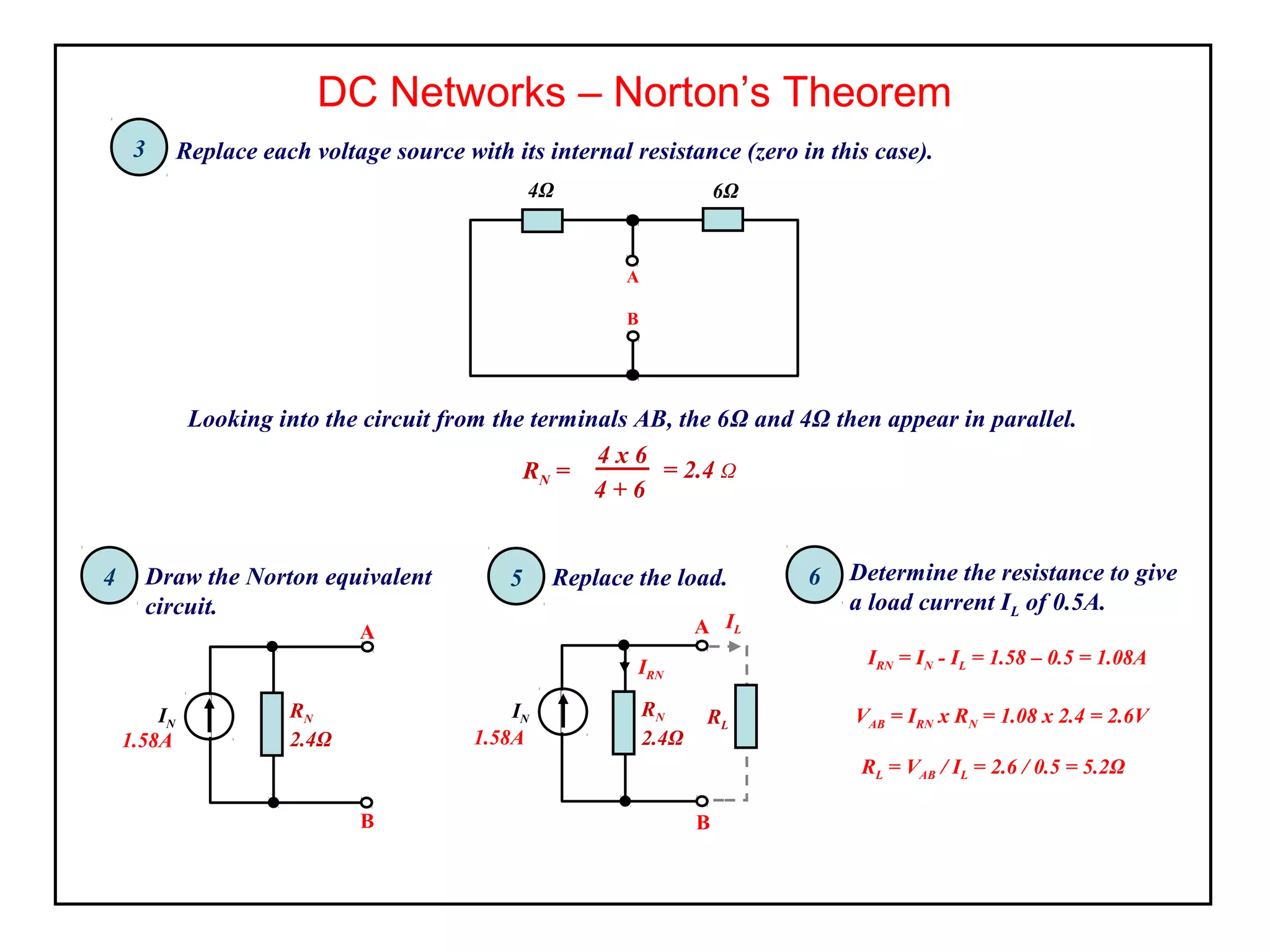
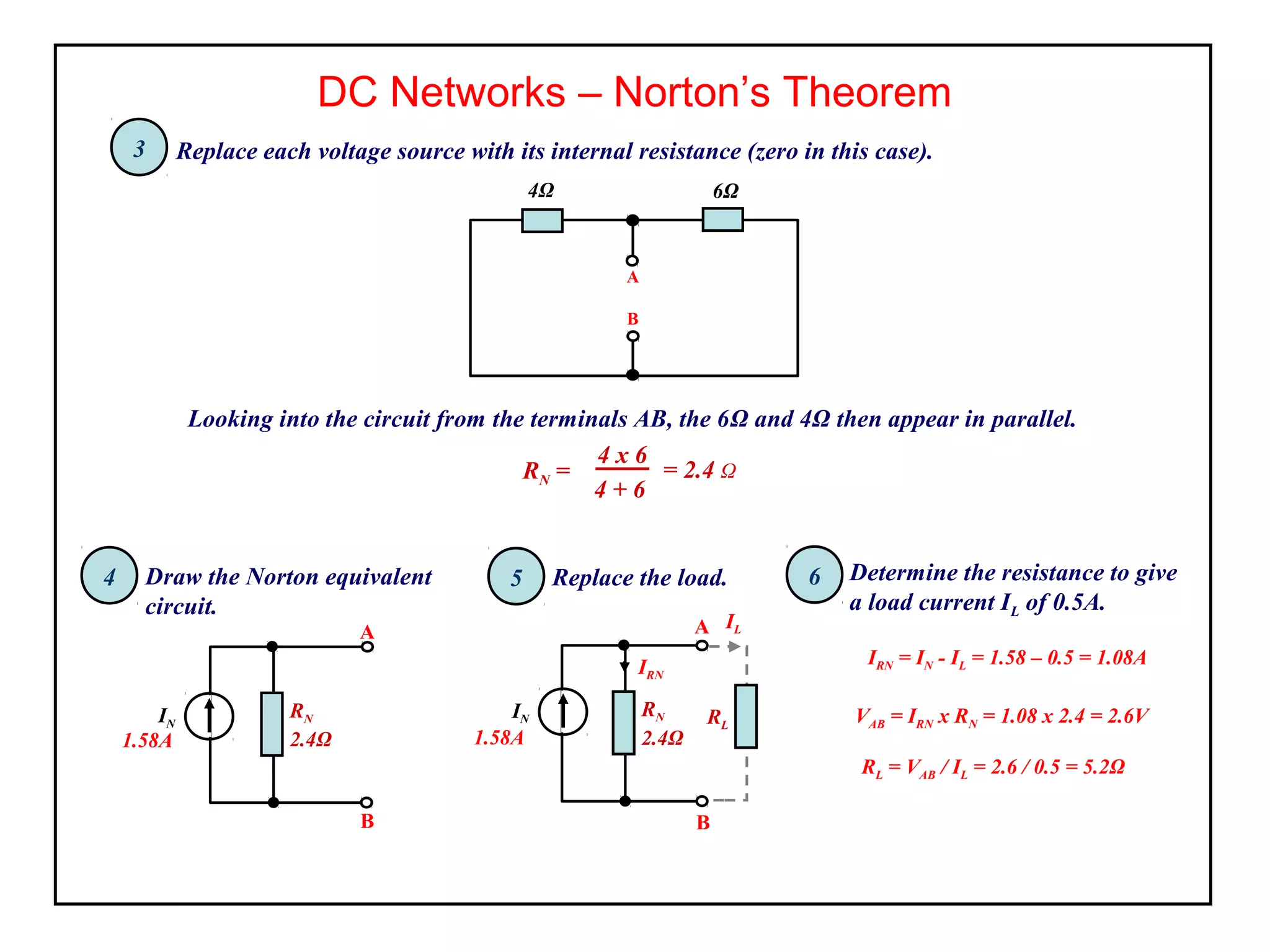
Norton's theorem allows replacing a network containing voltage sources with a current source (ISC) in parallel with an internal resistance (RN). It is derived by short-circuiting the terminals to find the short-circuit current (ISC), then calculating the equivalent resistance RN by removing the sources. The Norton equivalent circuit can then be used to analyze the network for any load conditions by applying current division.