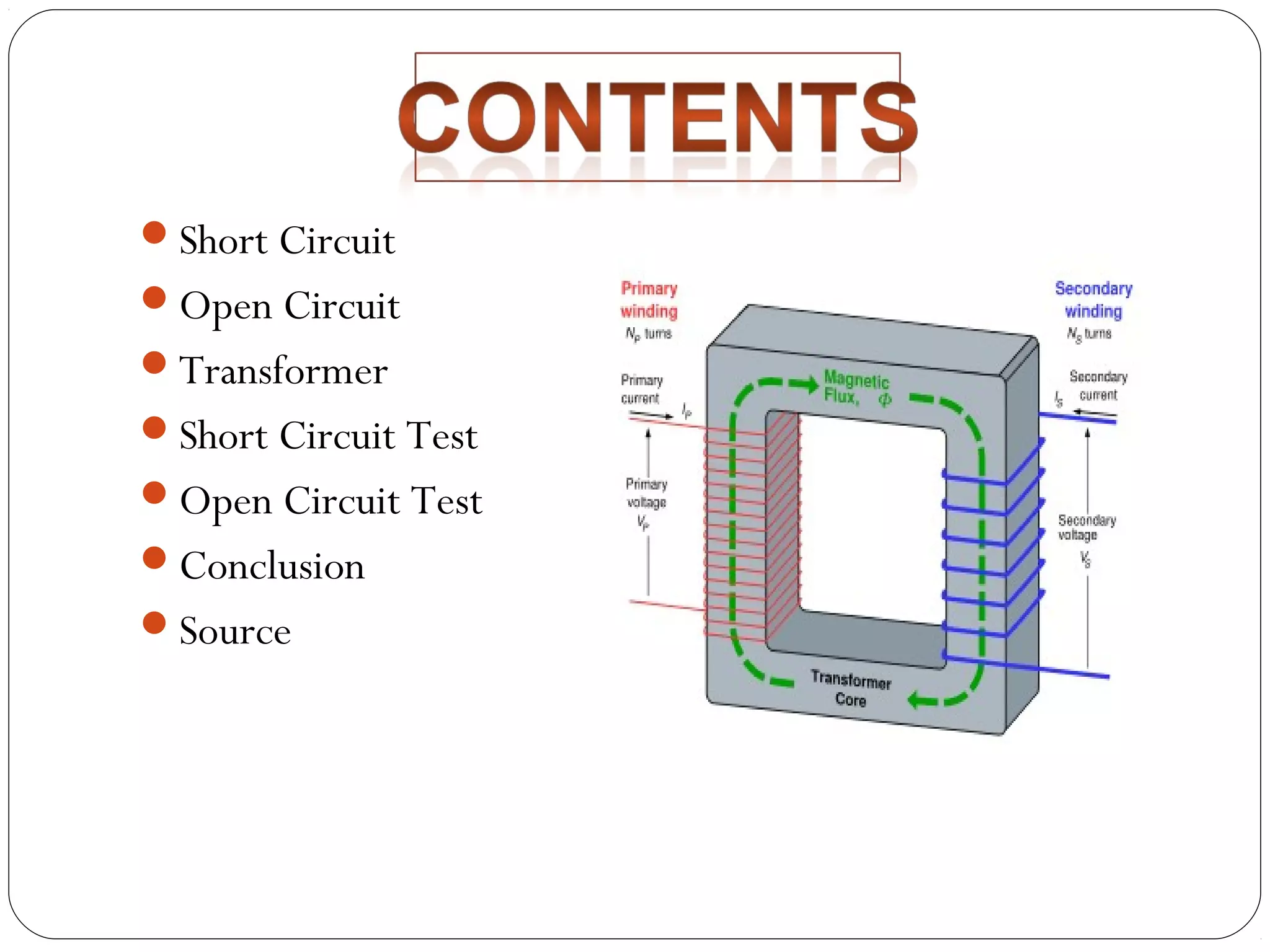
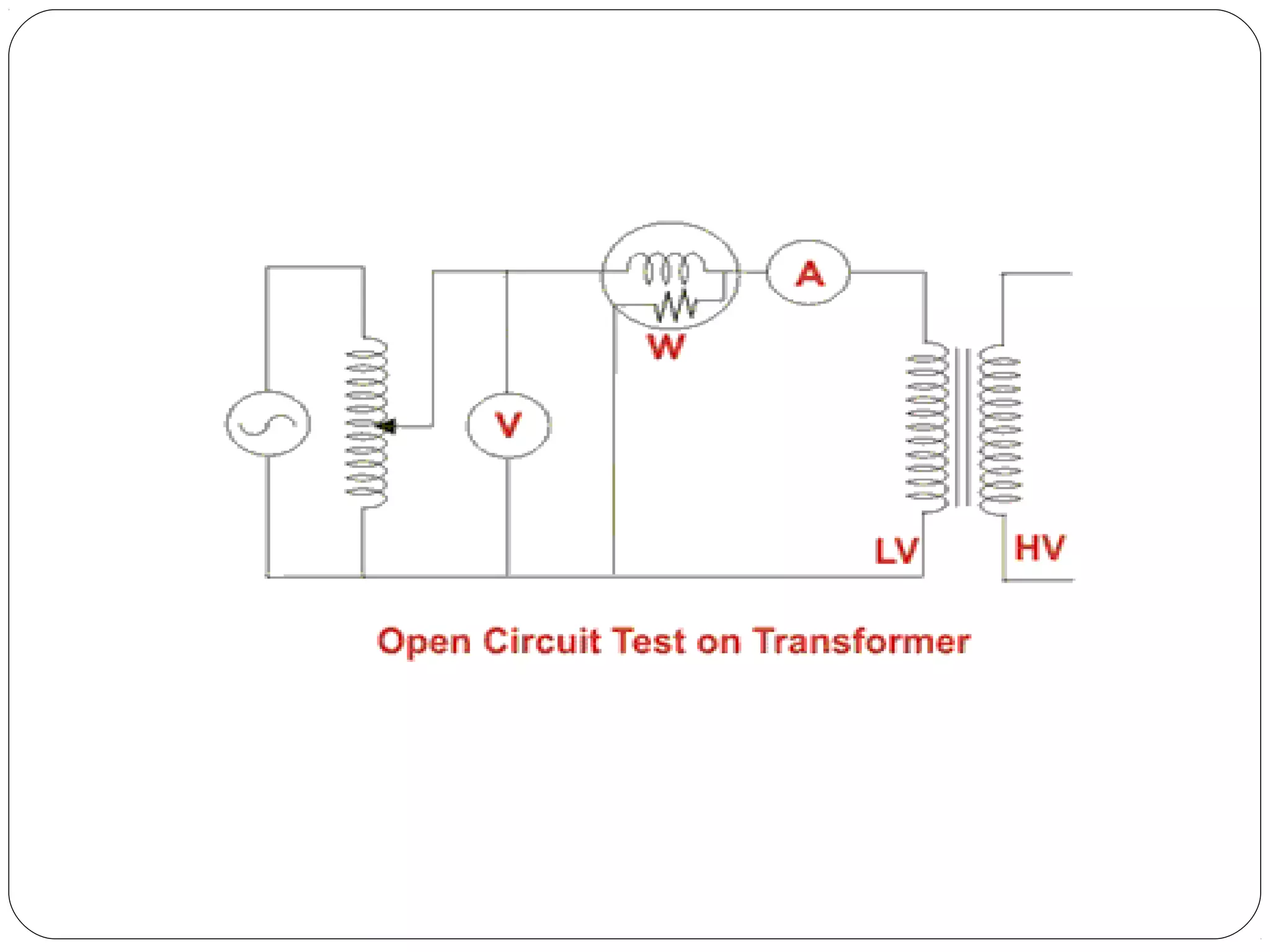
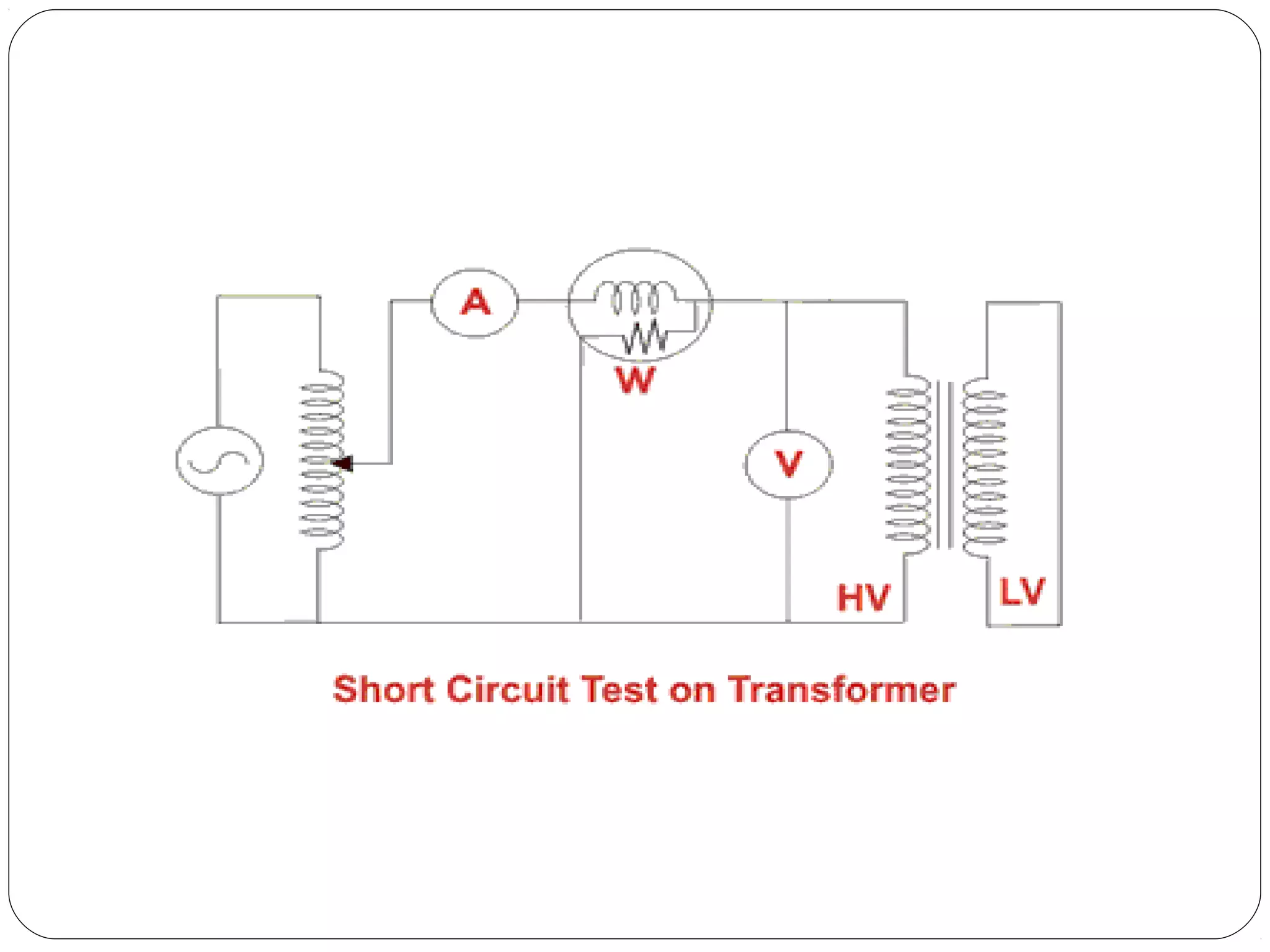
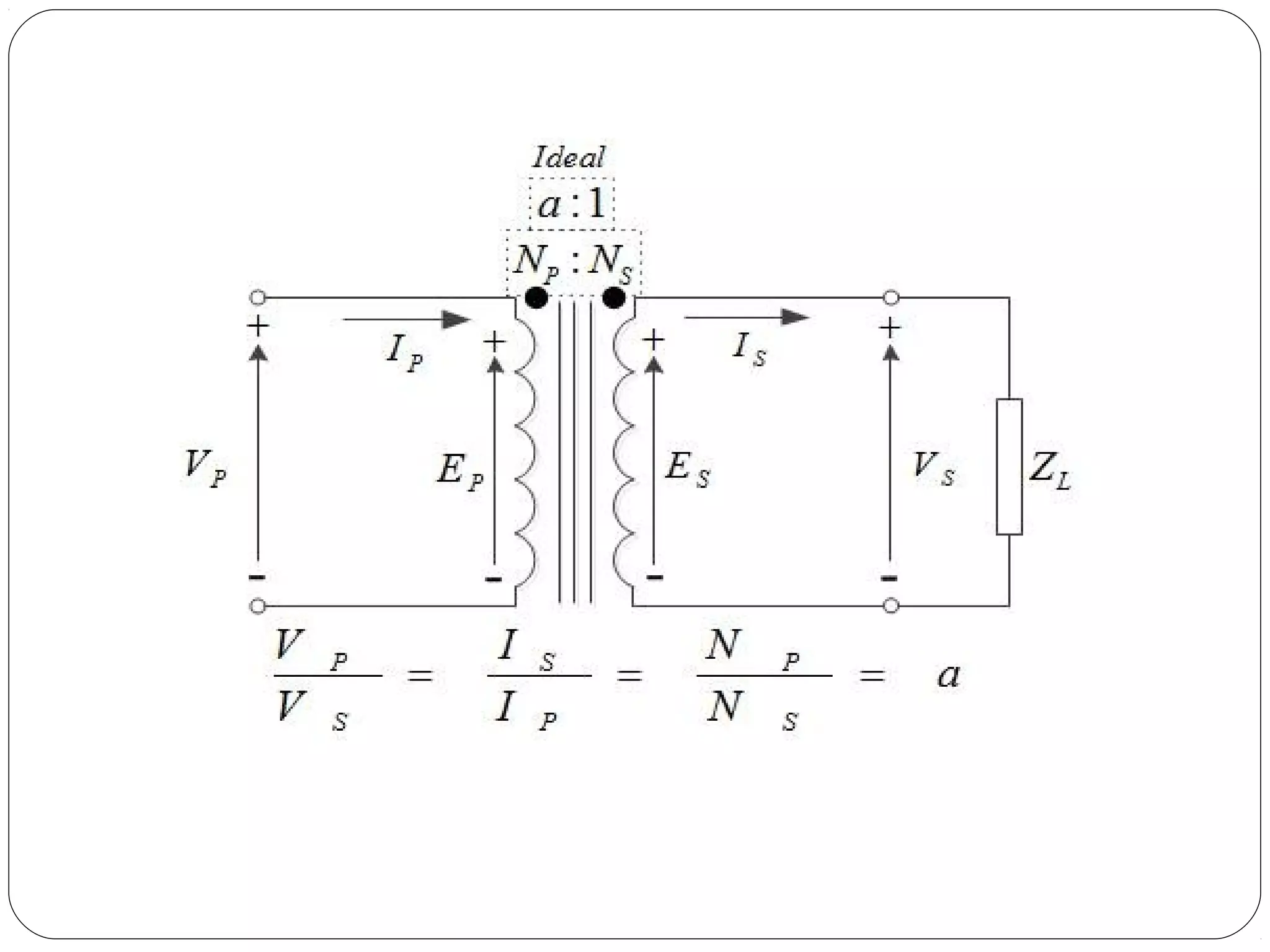
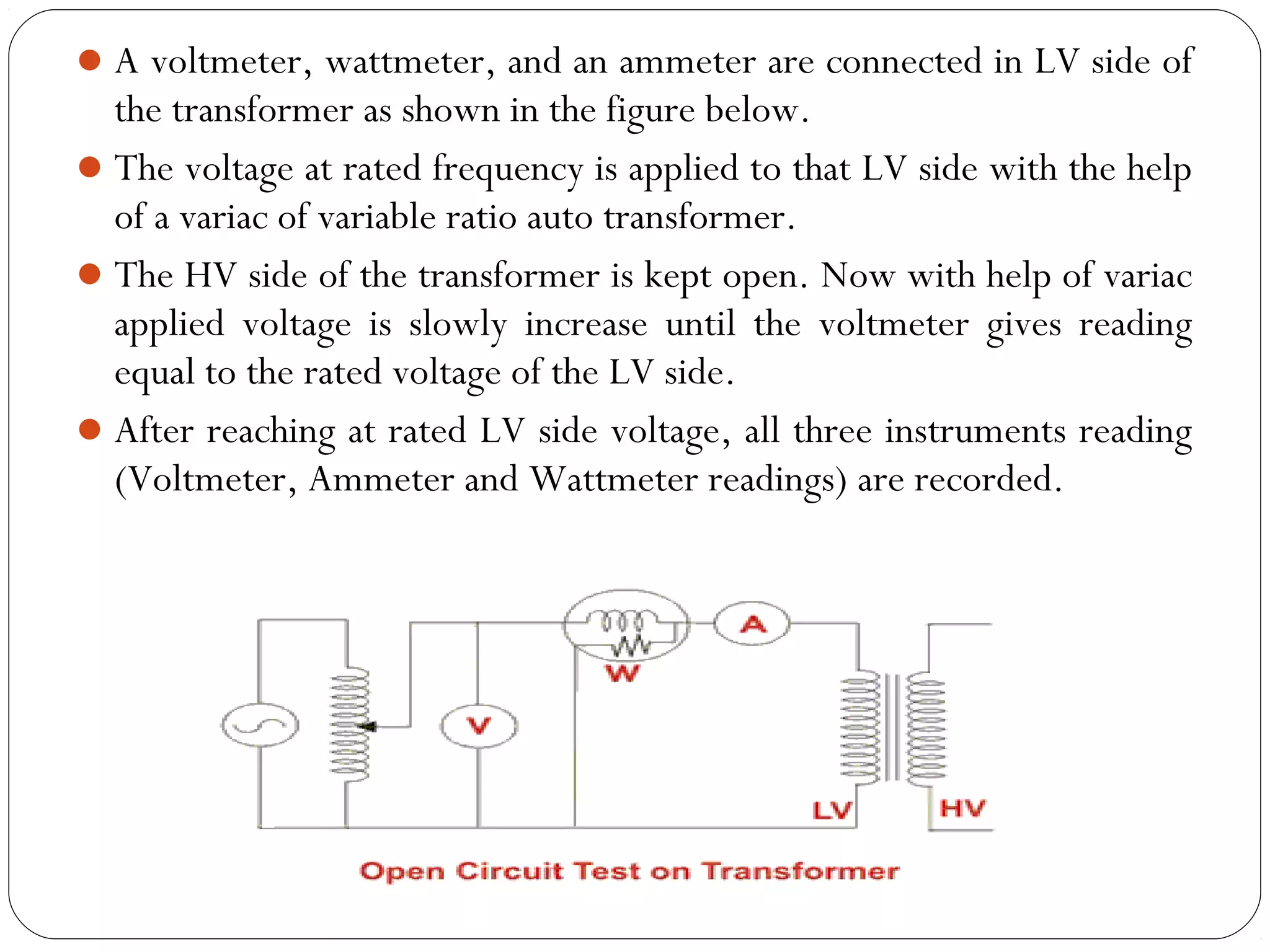
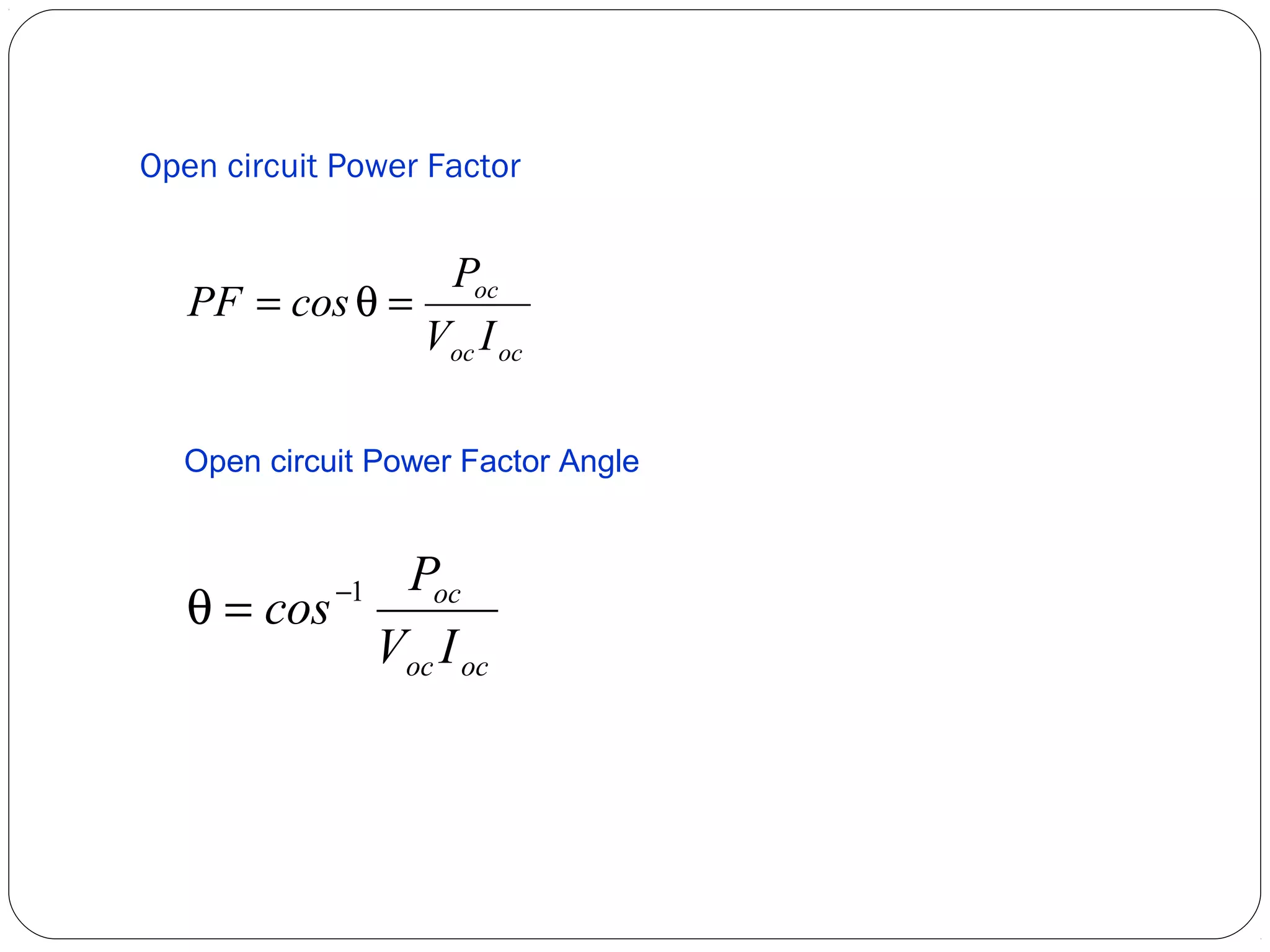
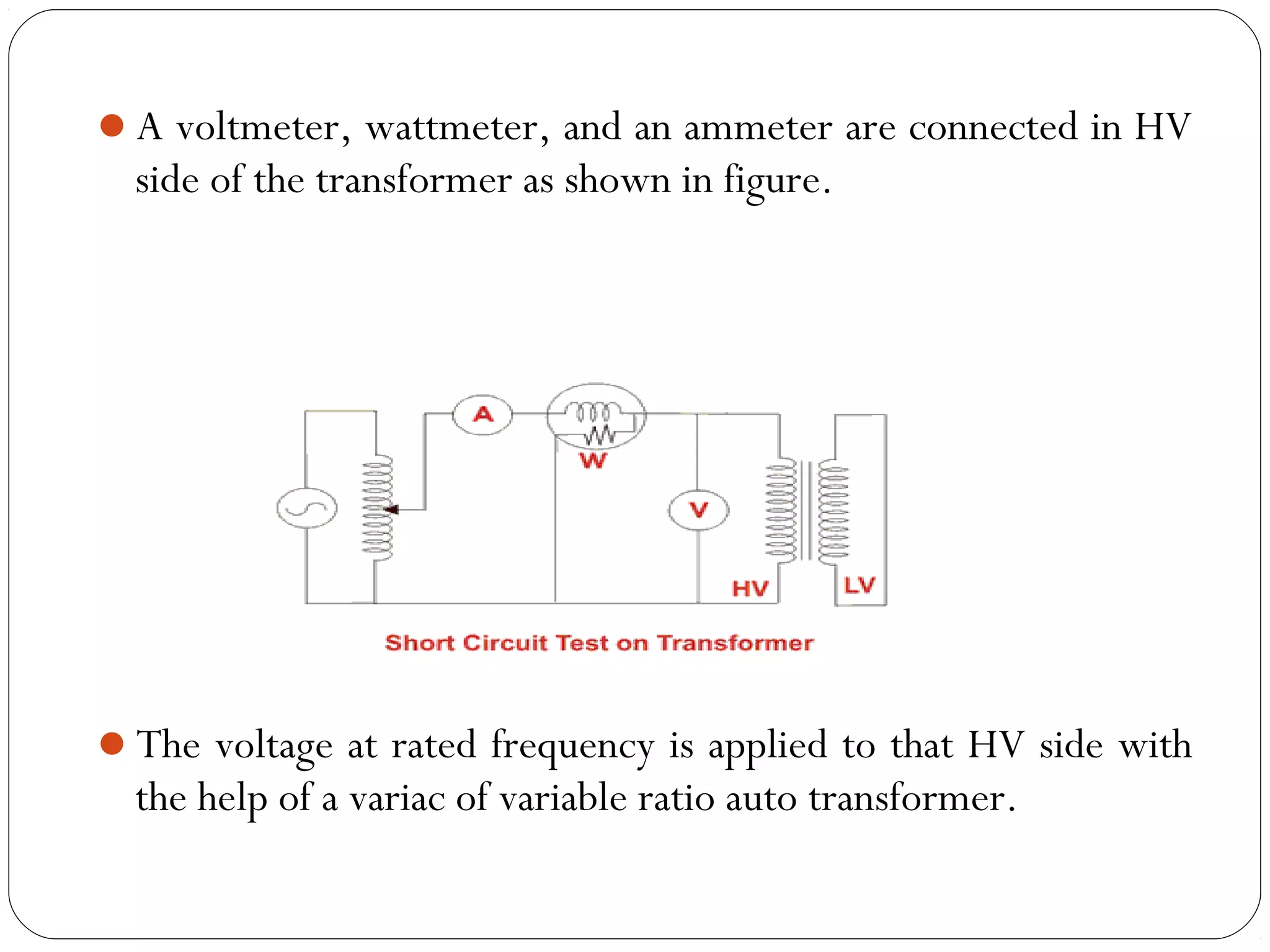
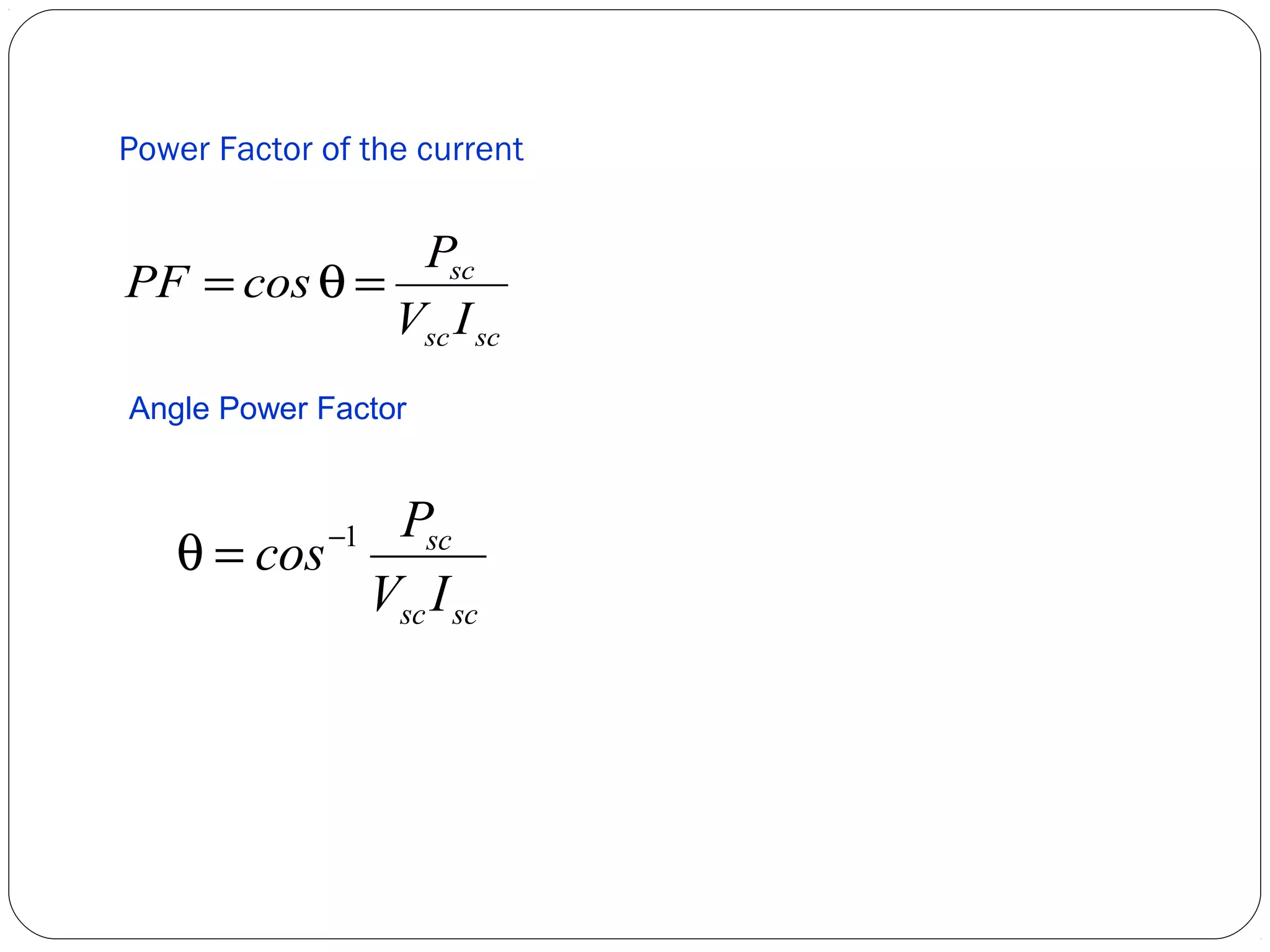
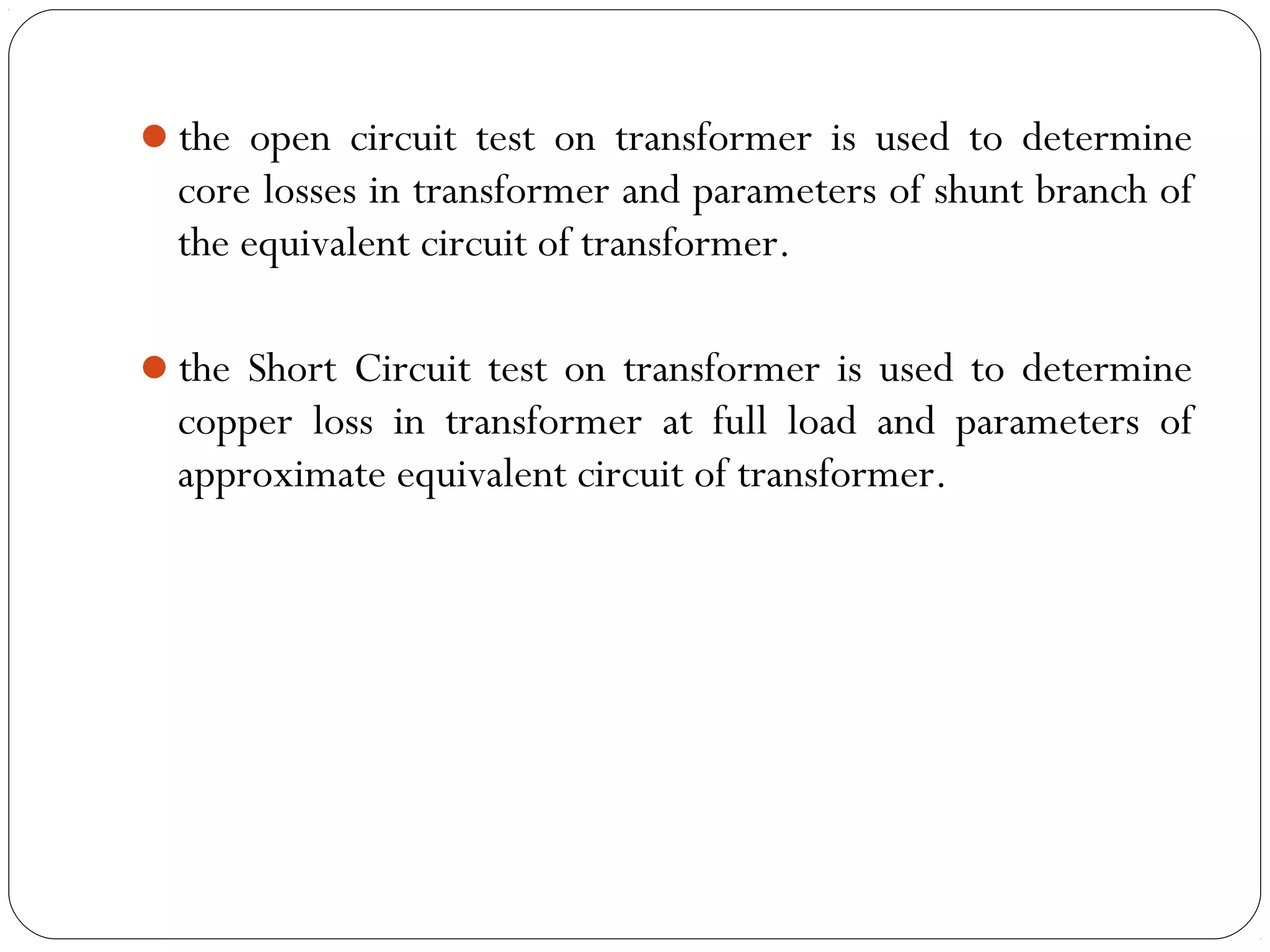
This document discusses short circuits, open circuits, and transformer tests. It explains that a short circuit allows current along an unintended path with little resistance, while an open circuit lacks a complete path for current flow. Transformer tests include open circuit and short circuit tests. The open circuit test determines core losses and shunt branch parameters, while the short circuit test determines copper losses and approximate circuit parameters. Instruments are connected and measurements recorded to evaluate losses and parameters from the tests.