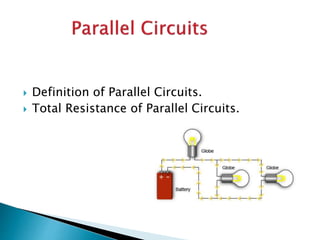
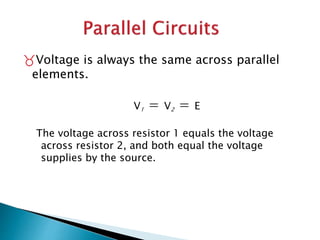
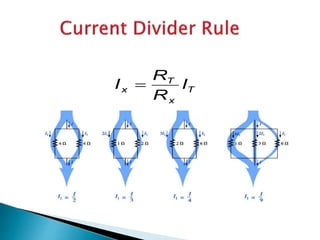
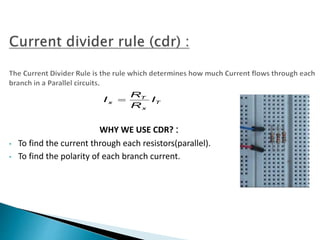
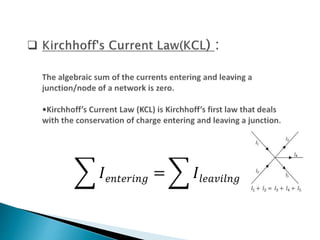
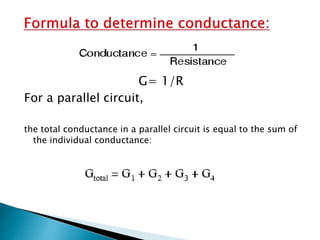
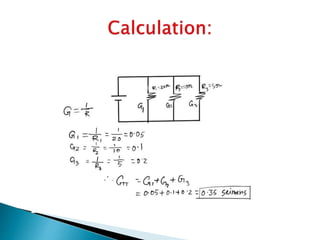
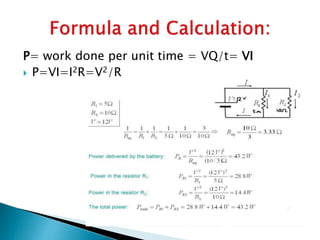
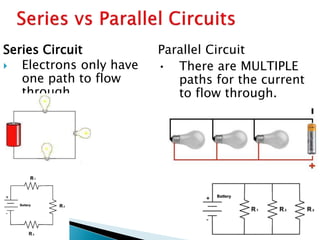
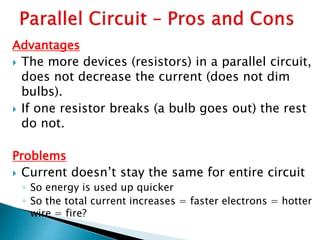
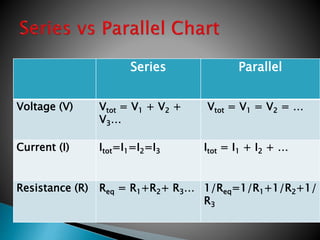
This document discusses parallel circuits. It defines parallel circuits as having multiple paths for current to flow and that the voltage is the same across each component. The total resistance of a parallel circuit is smaller than its branches because the overall conductance is the sum of the individual conductances. The current divider rule is used to calculate the current through each resistor in a parallel circuit.