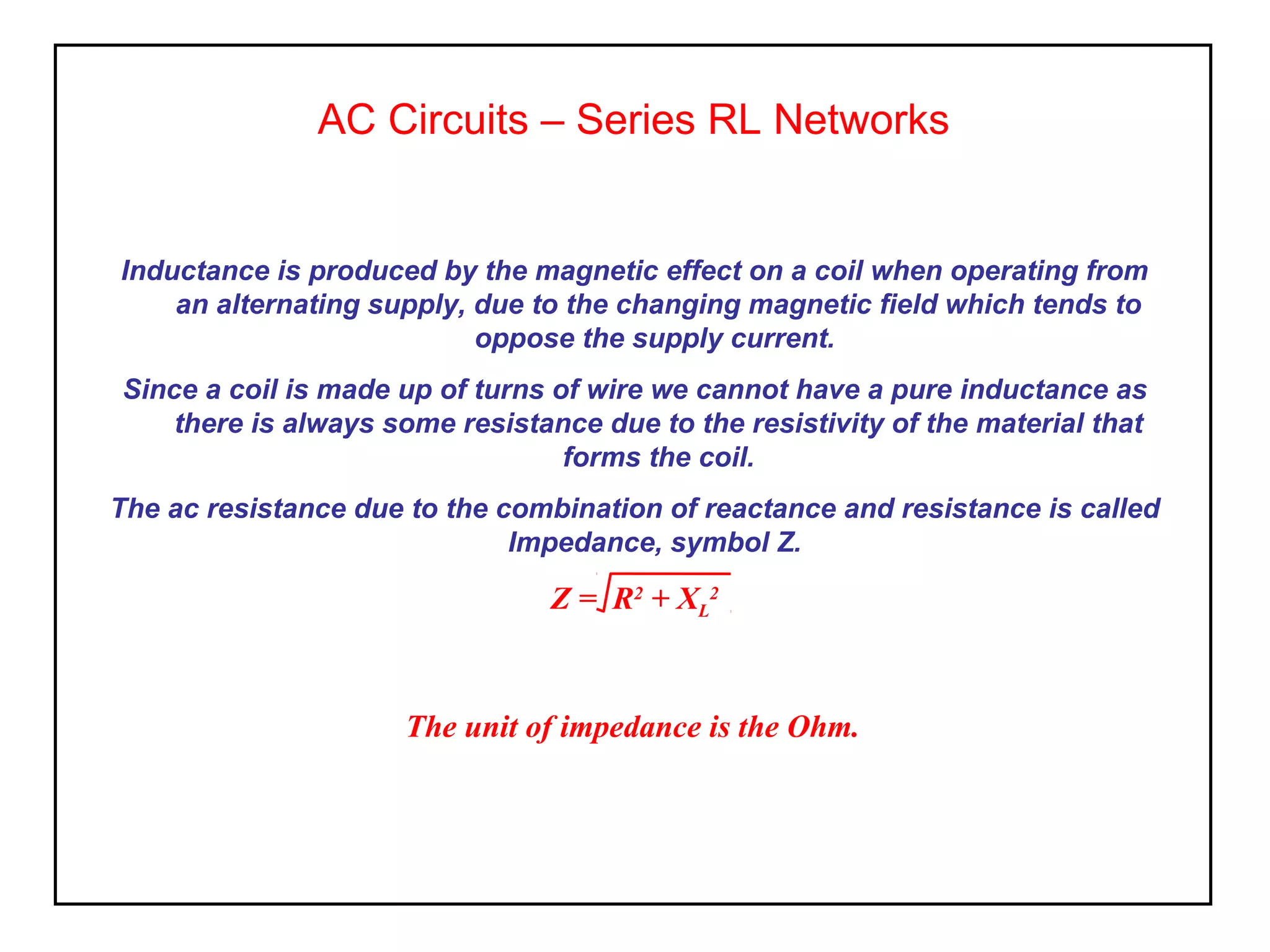
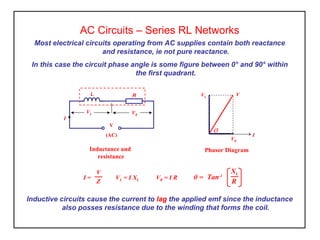
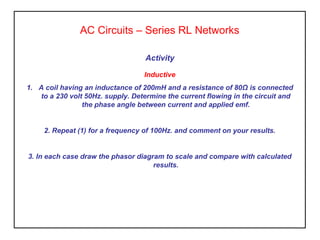
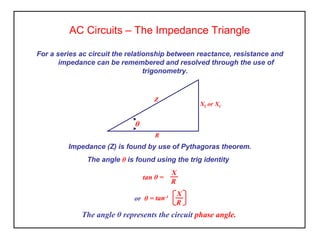
Inductance is produced in a coil by a changing magnetic field from an alternating current supply, which opposes the supply current. In an AC circuit containing both resistance and inductance, the impedance Z is equal to the square root of resistance R squared plus reactance XL squared. The current lags the applied voltage by an angle θ between 0 and 90 degrees, as calculated by the tangent of θ being equal to XL over R.