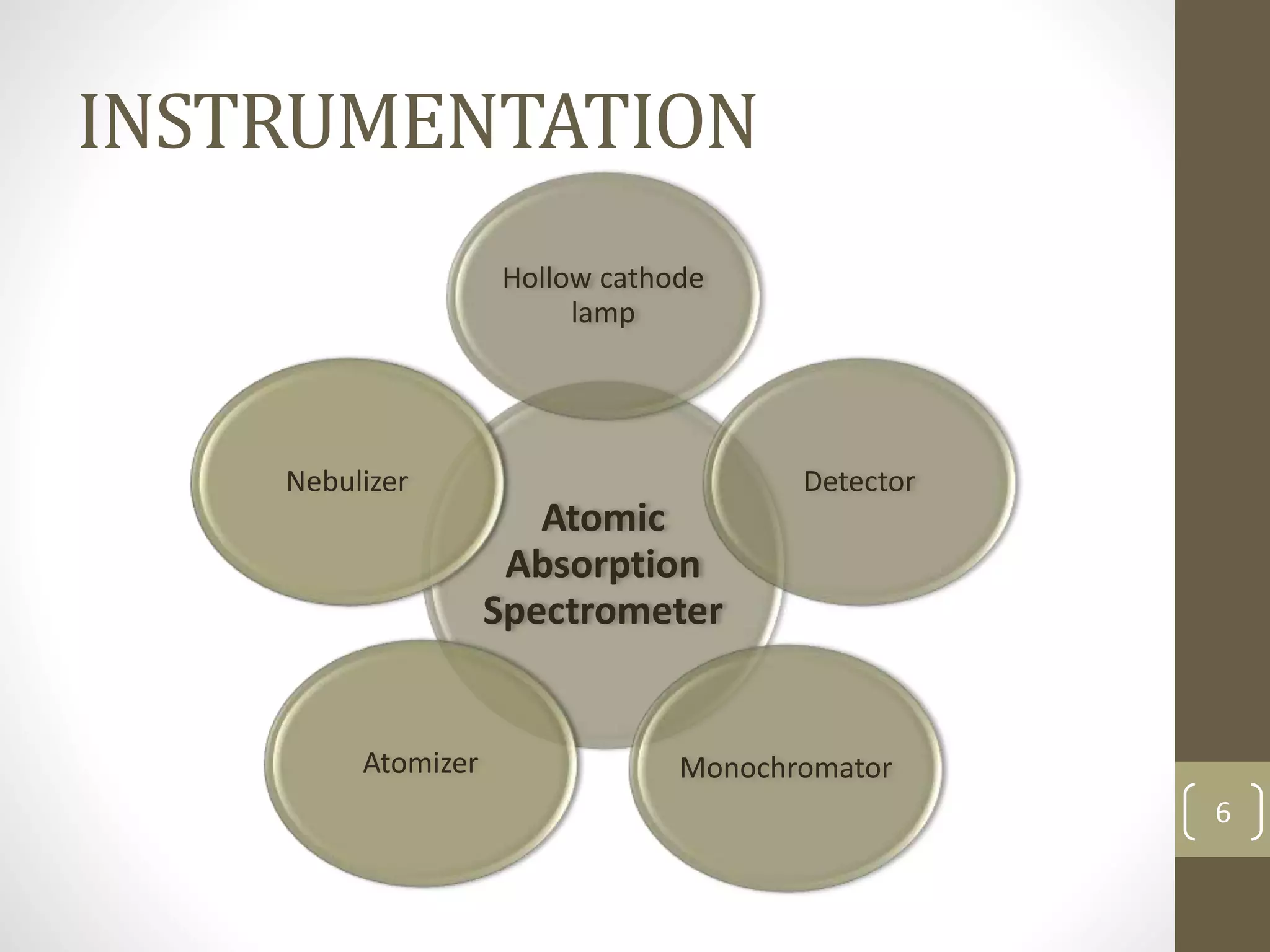
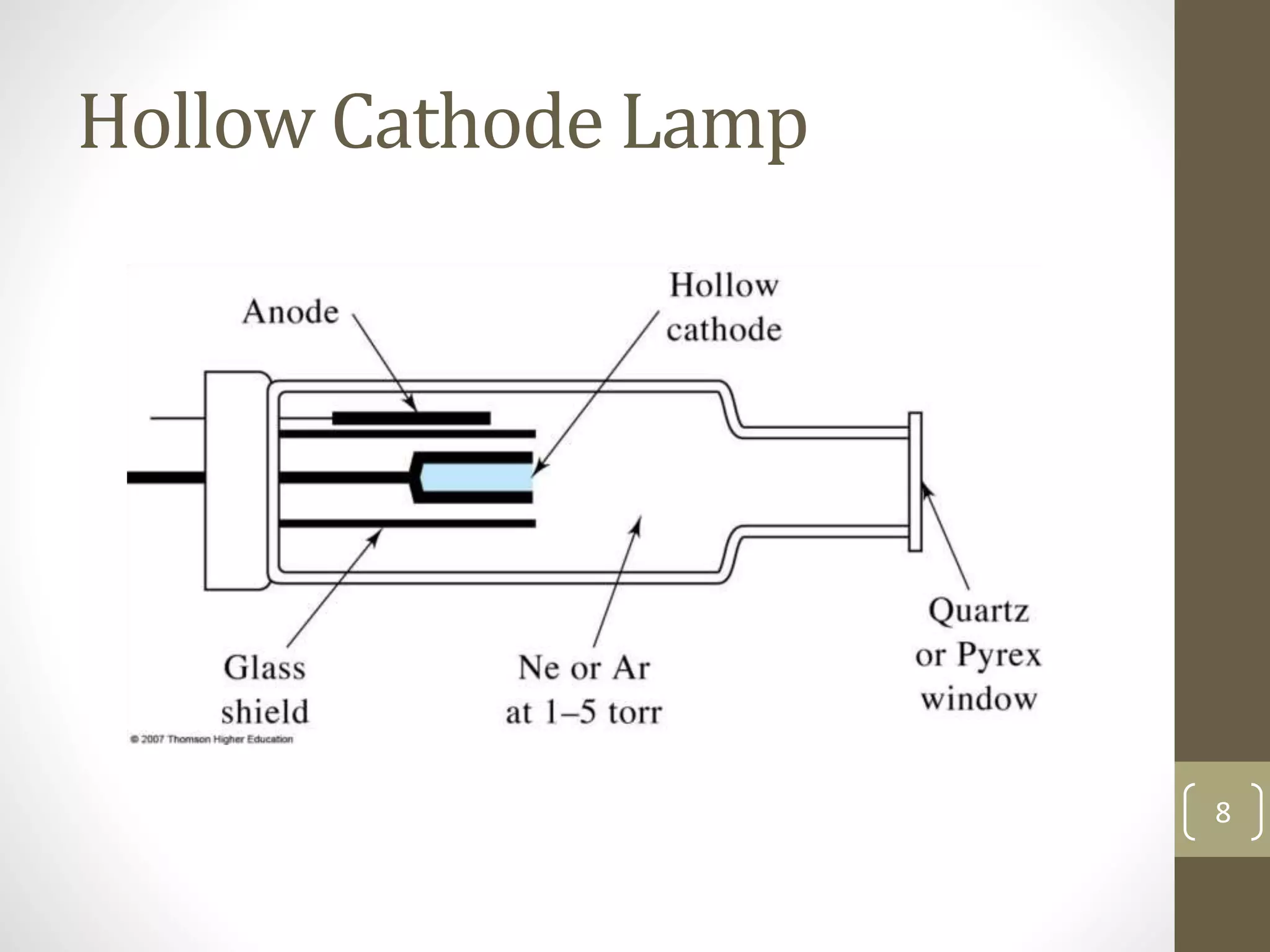
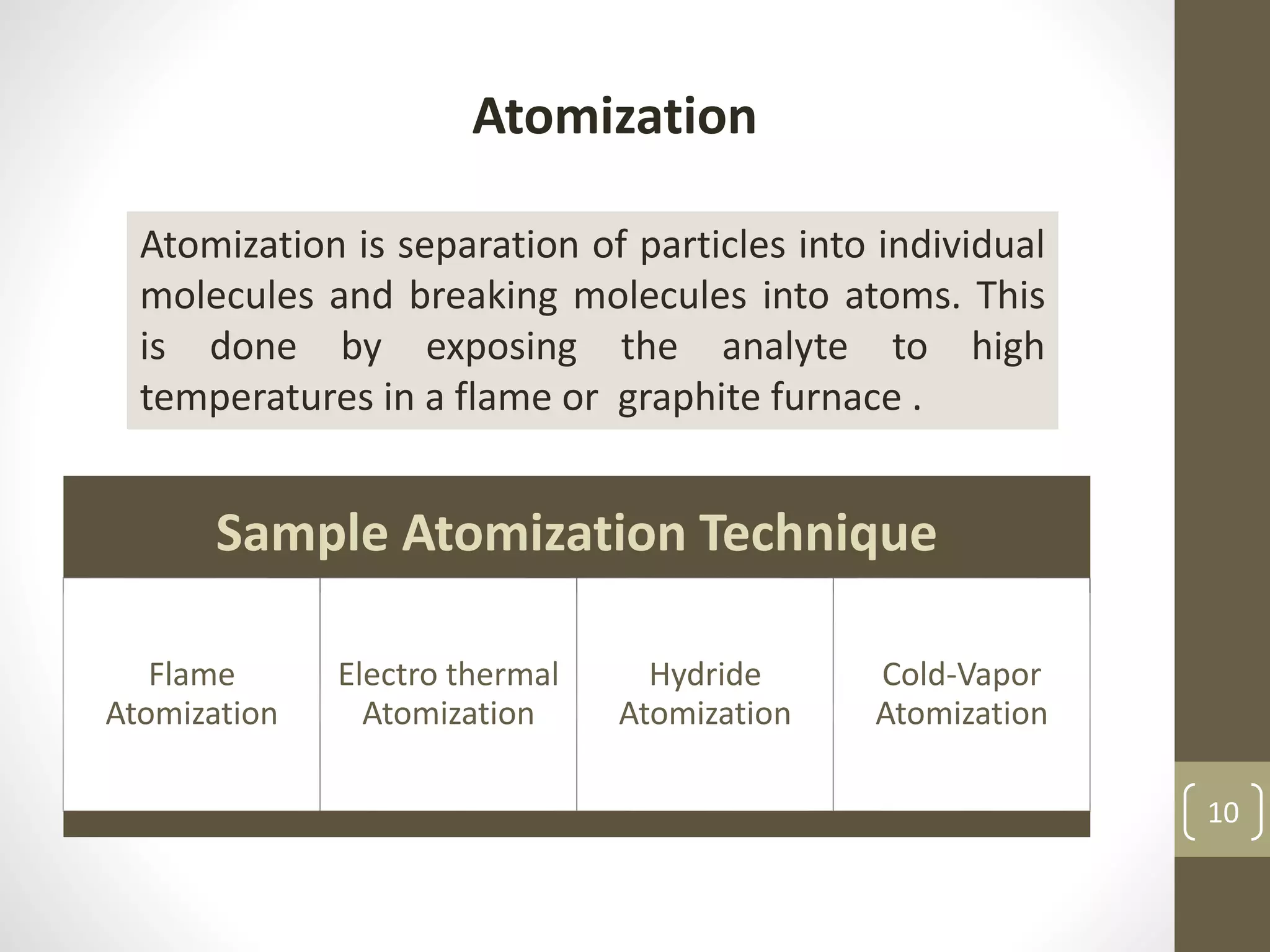
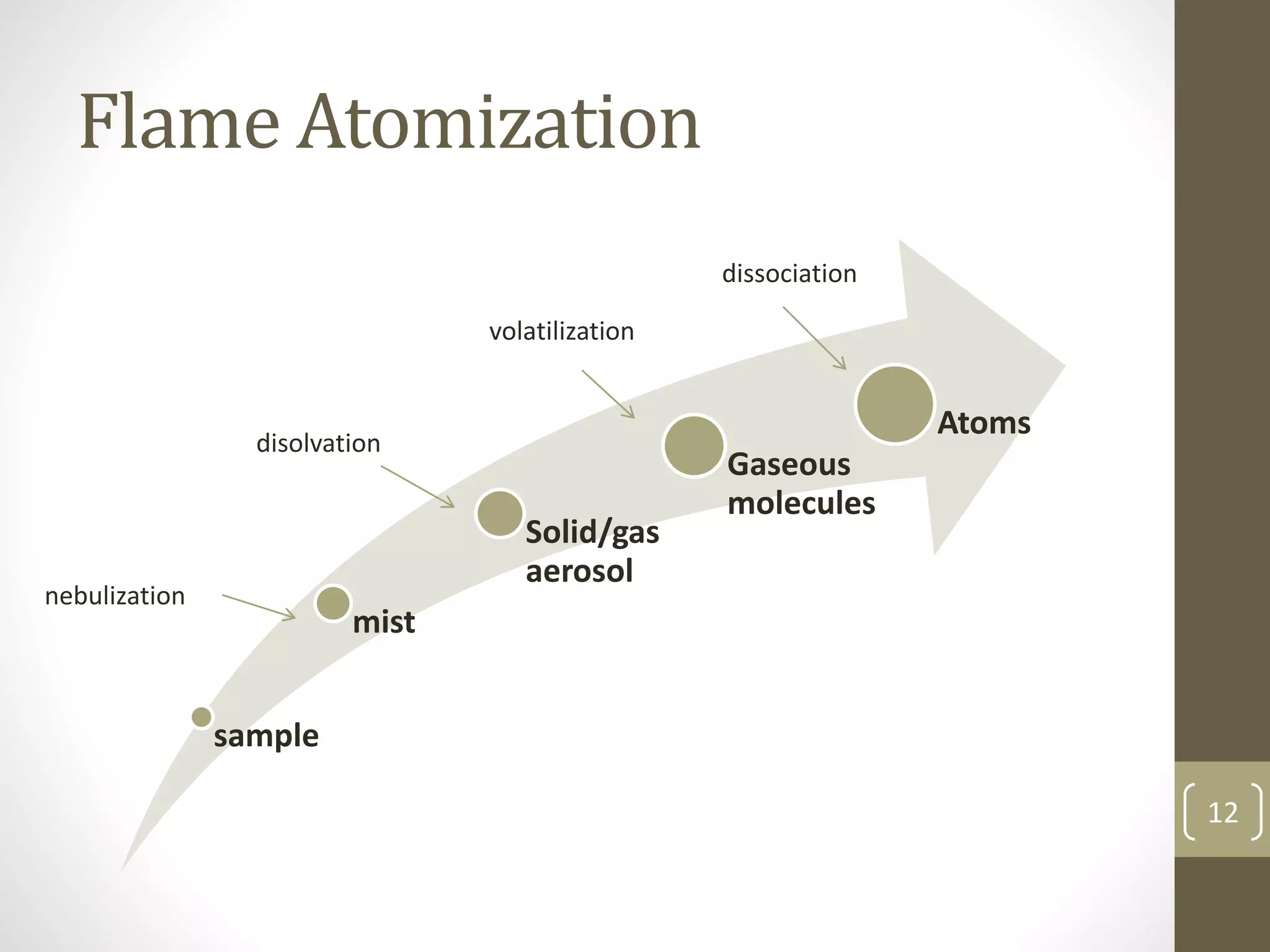
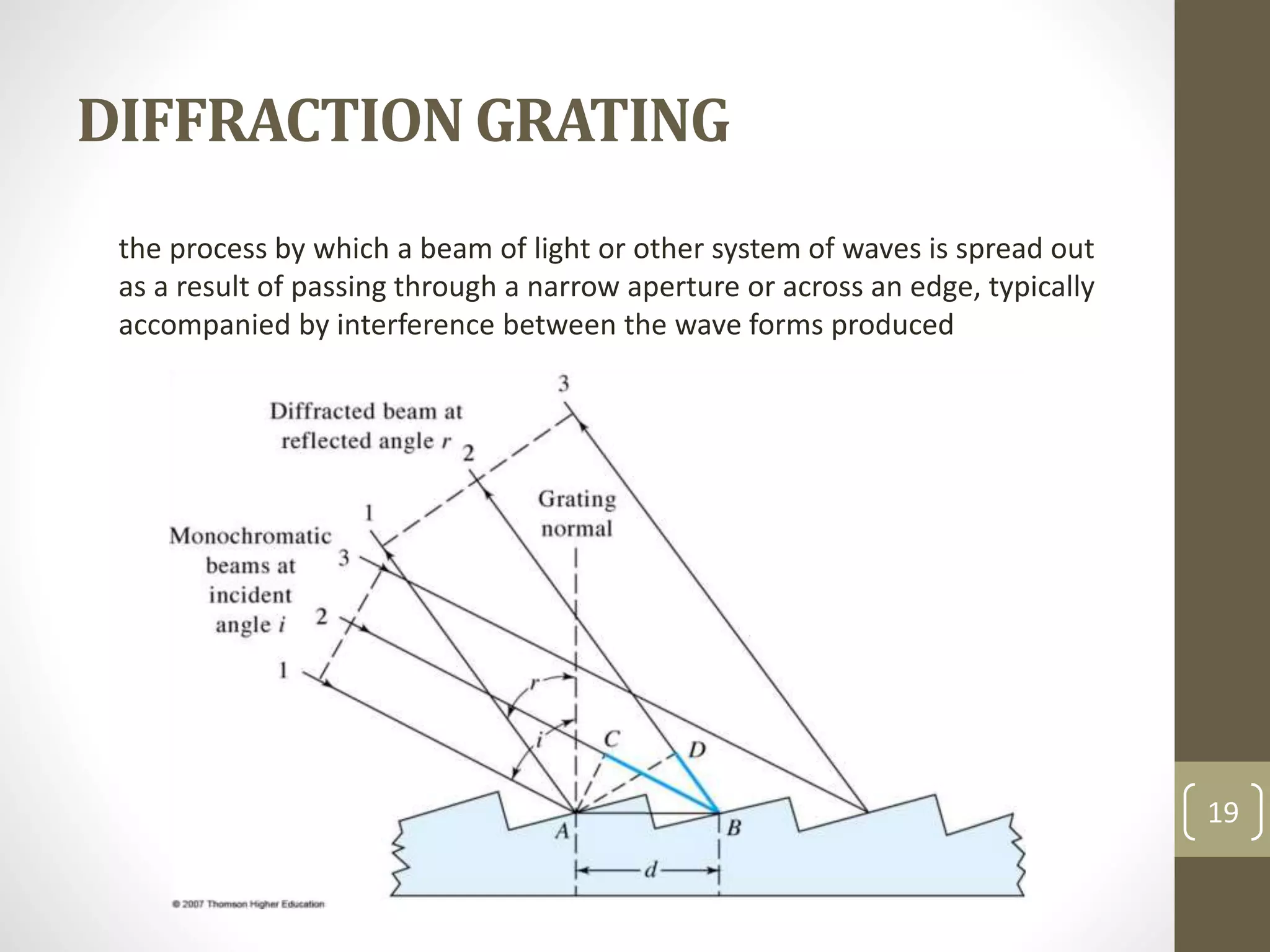
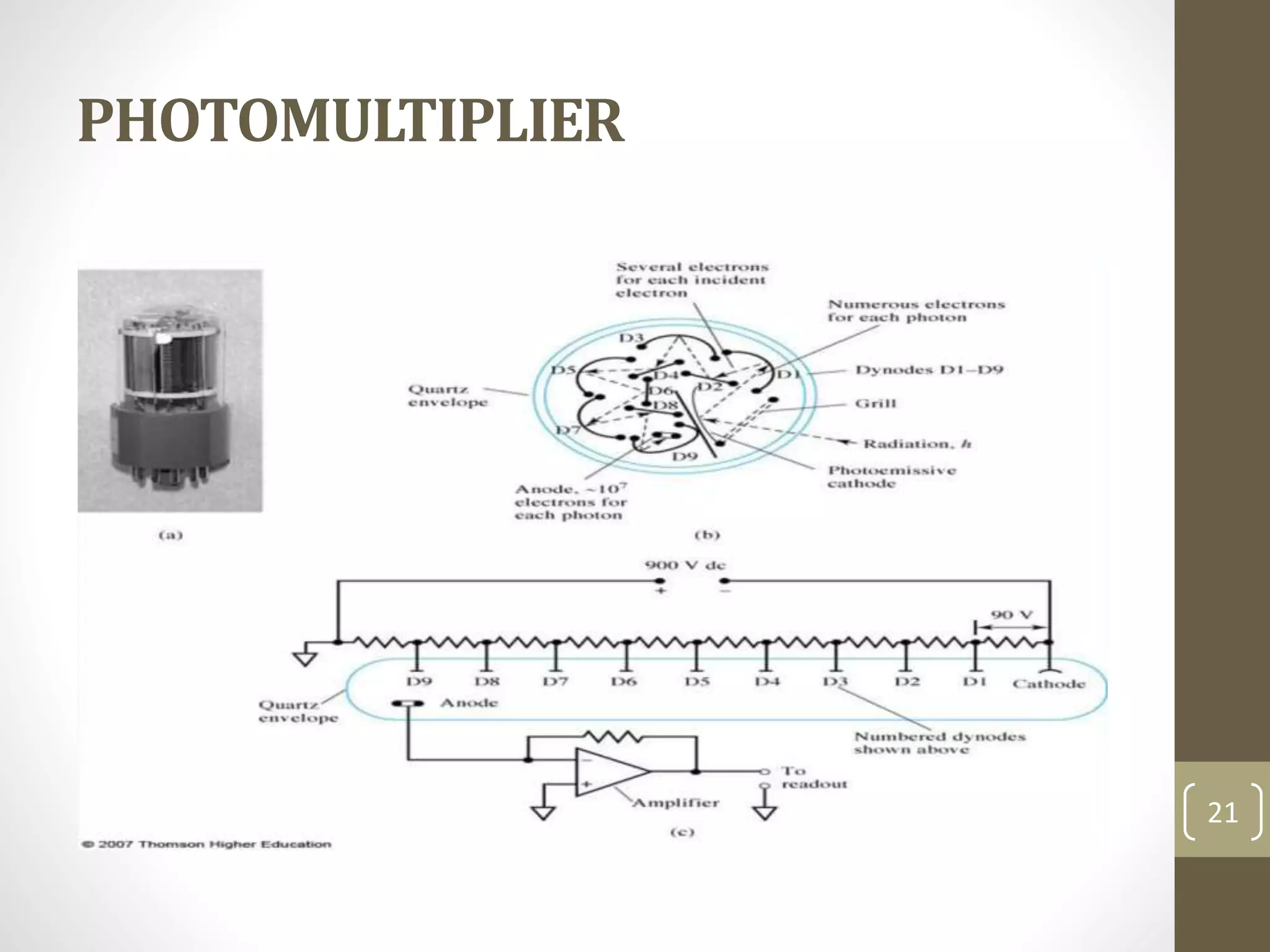
Atomic absorption spectroscopy is a quantitative analytical technique used to determine the concentration of metals and some nonmetals in solutions and samples. It works by vaporizing the sample into free atoms, then measuring the absorption of light from a hollow cathode lamp at a specific wavelength for the target element. The amount of light absorbed is directly proportional to the concentration of the element in the original sample. It can analyze over 62 elements with high sensitivity and reliability. Common applications include detecting metals in environmental and biological samples as well as determining impurities in alloys.