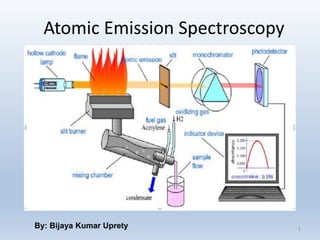
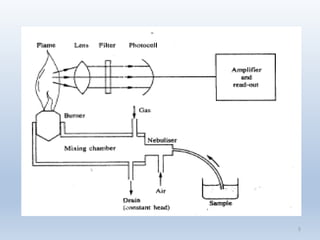
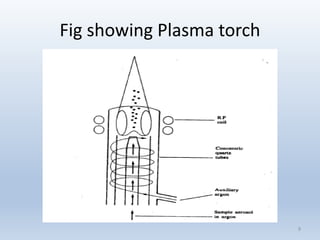
The document discusses atomic emission spectroscopy (AES) and two specific techniques: flame photometry and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES). Flame photometry uses a low temperature flame to atomize samples and determine the presence and concentration of sodium, potassium, lithium, and calcium. ICP-AES uses a plasma torch to produce excited atoms and ions from samples. The plasma is much hotter than a flame and allows for more complete atomization and a wider dynamic range of analysis.