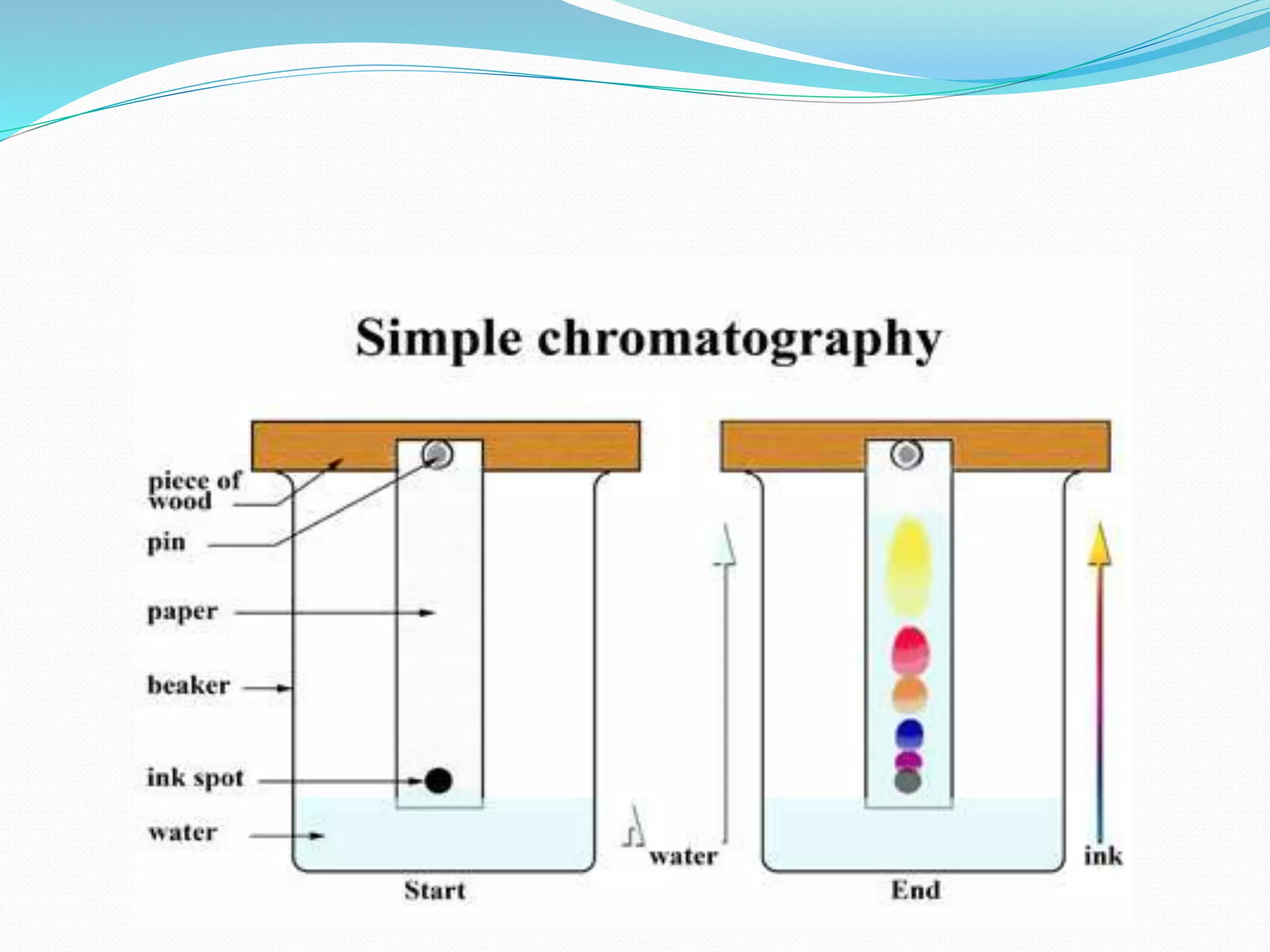
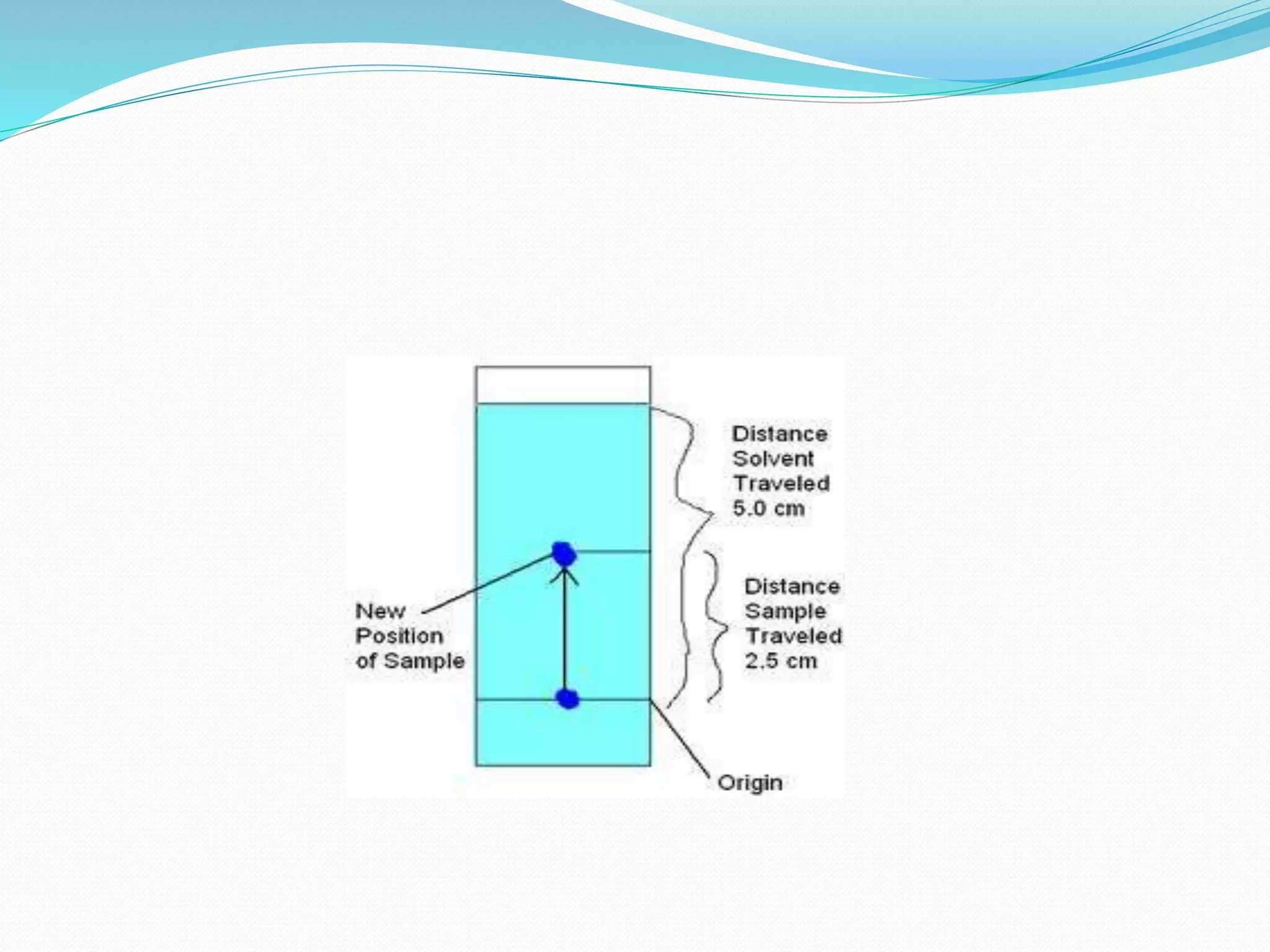
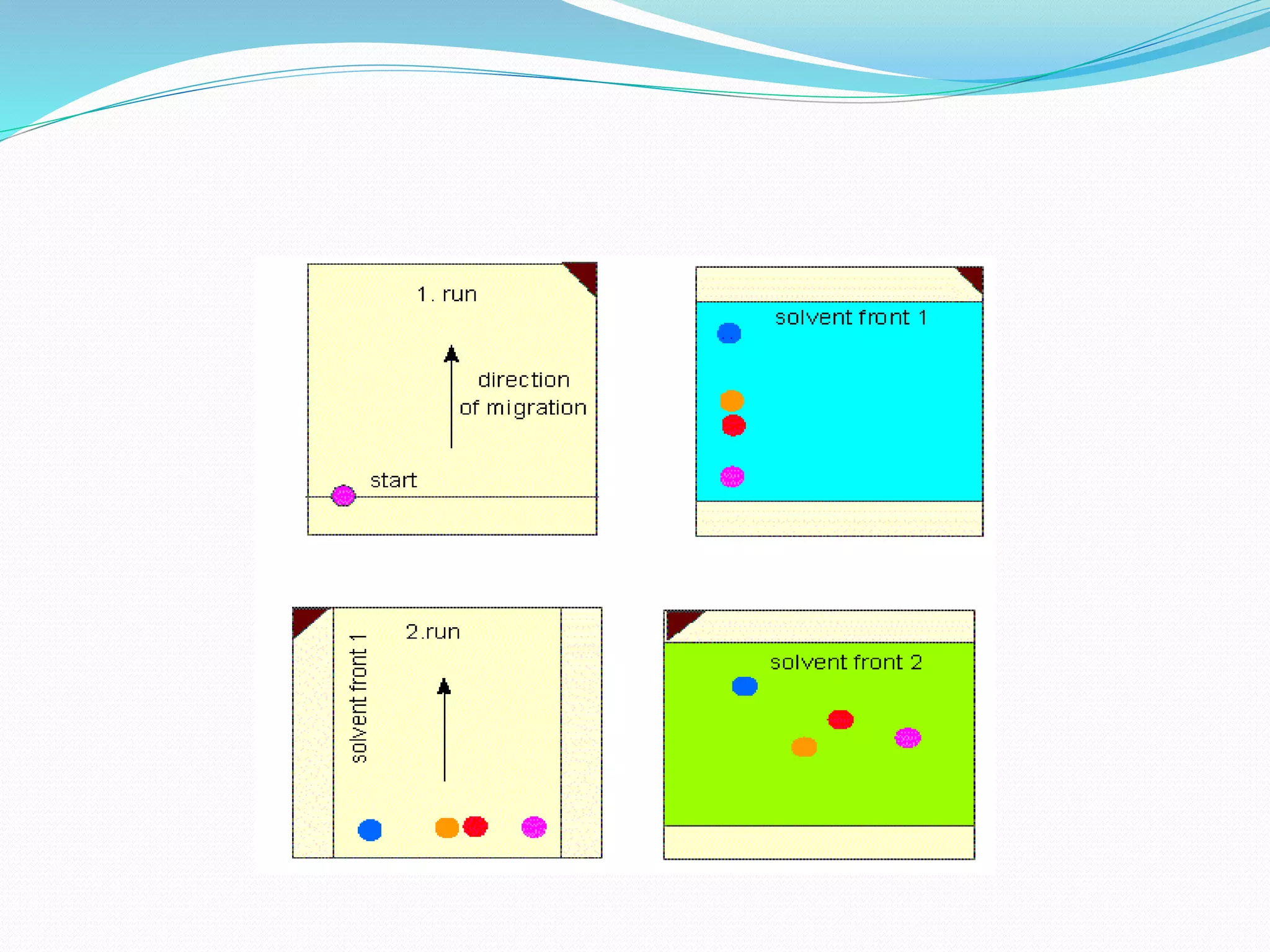
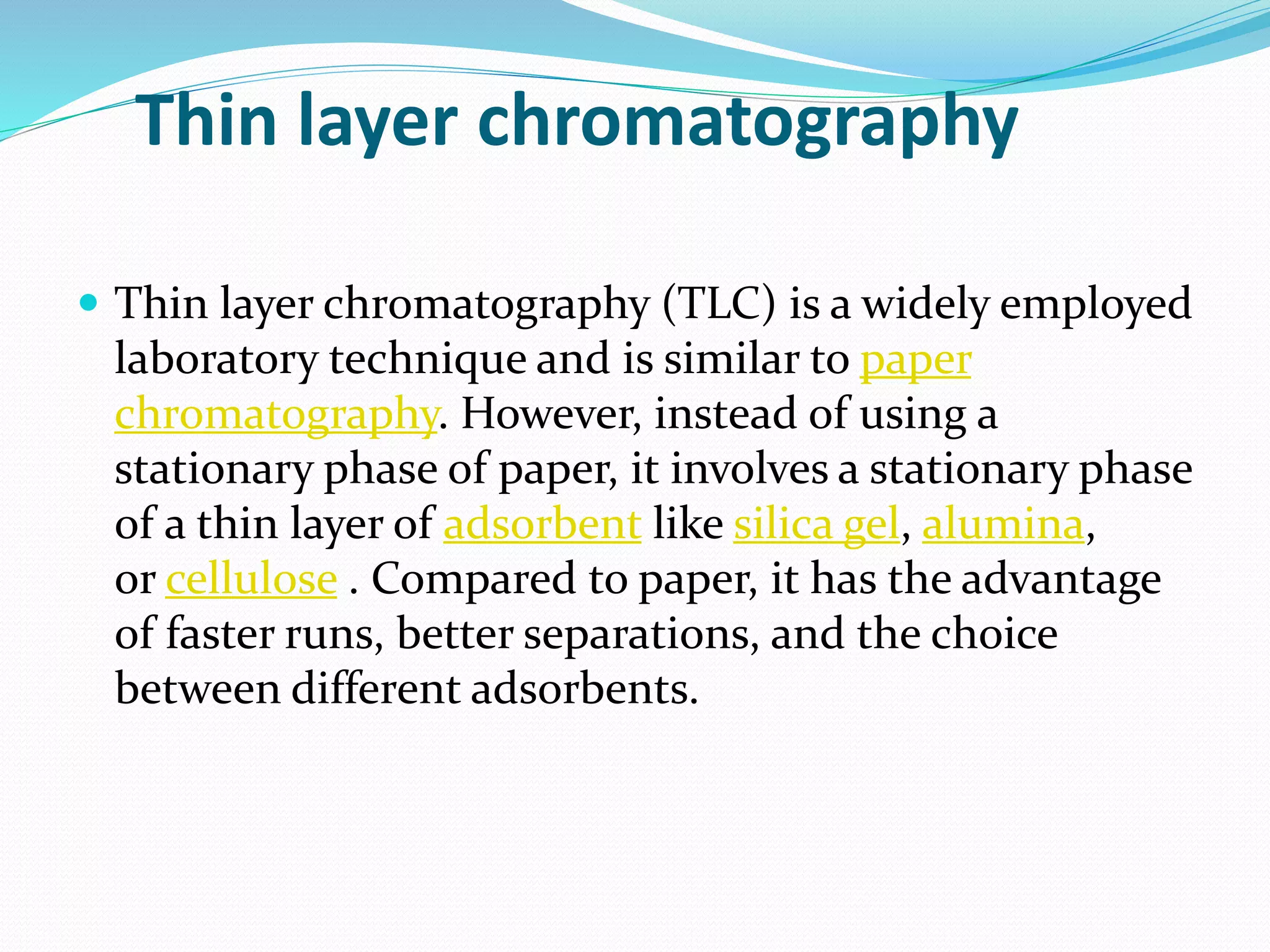
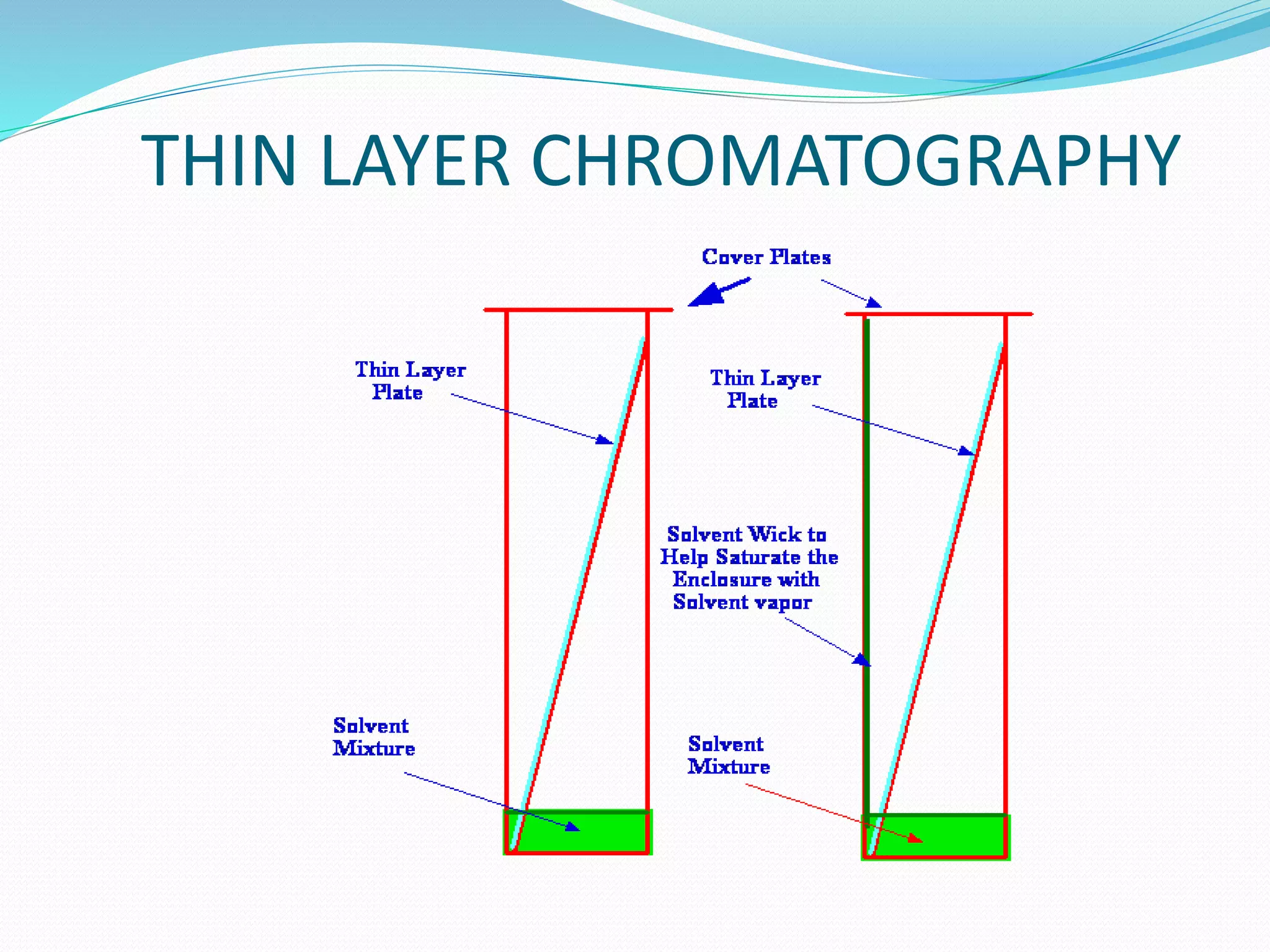
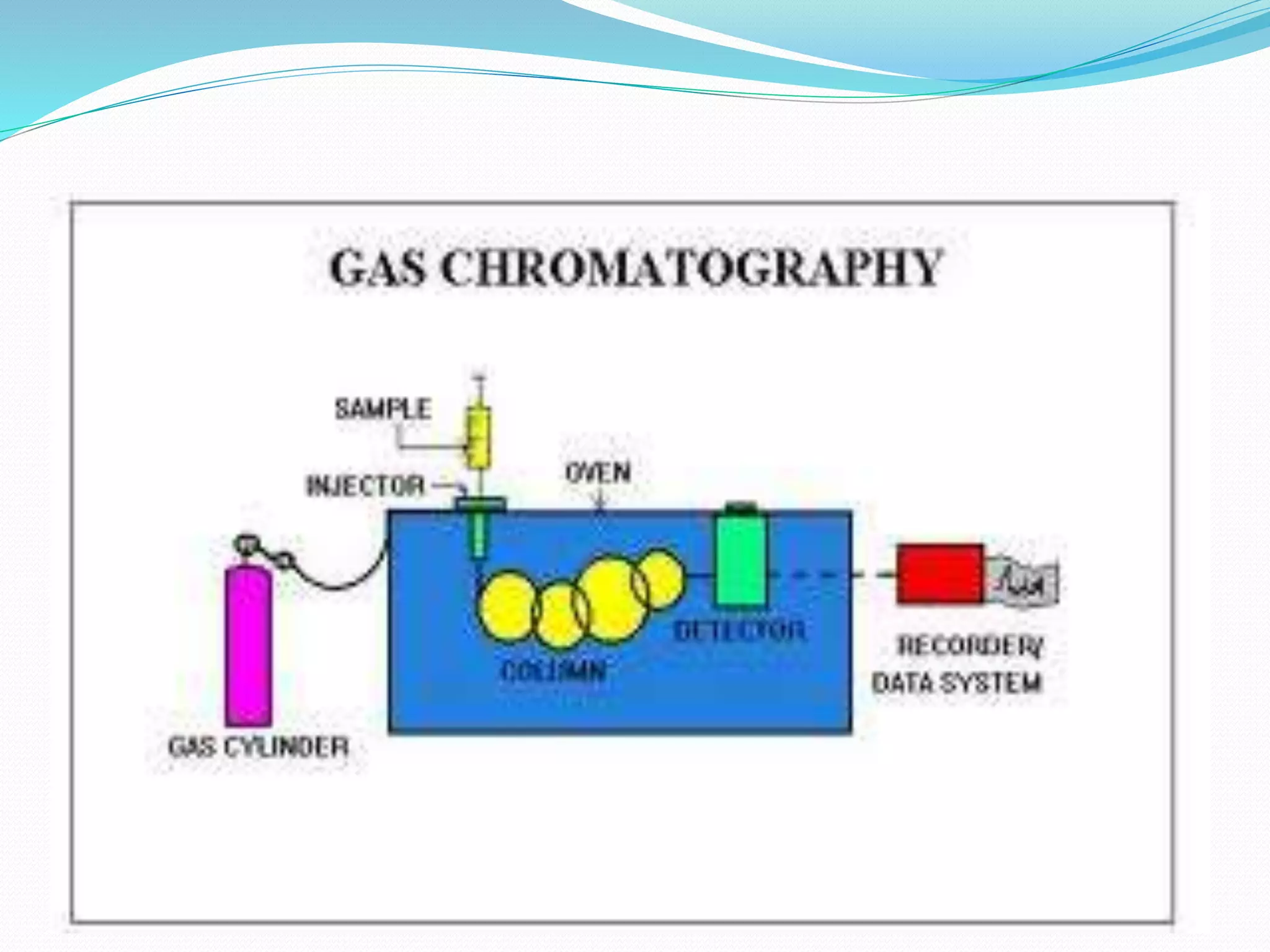
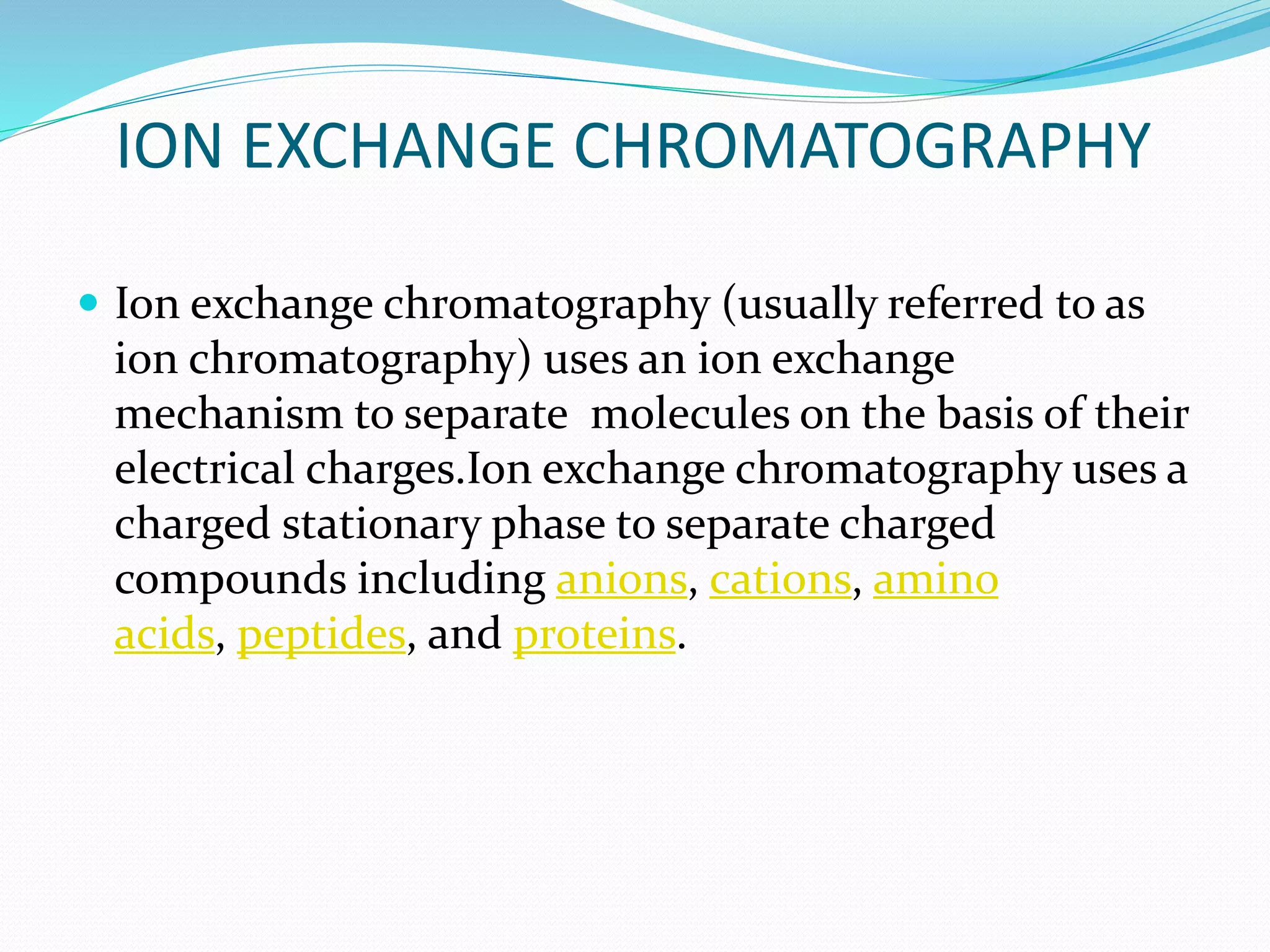
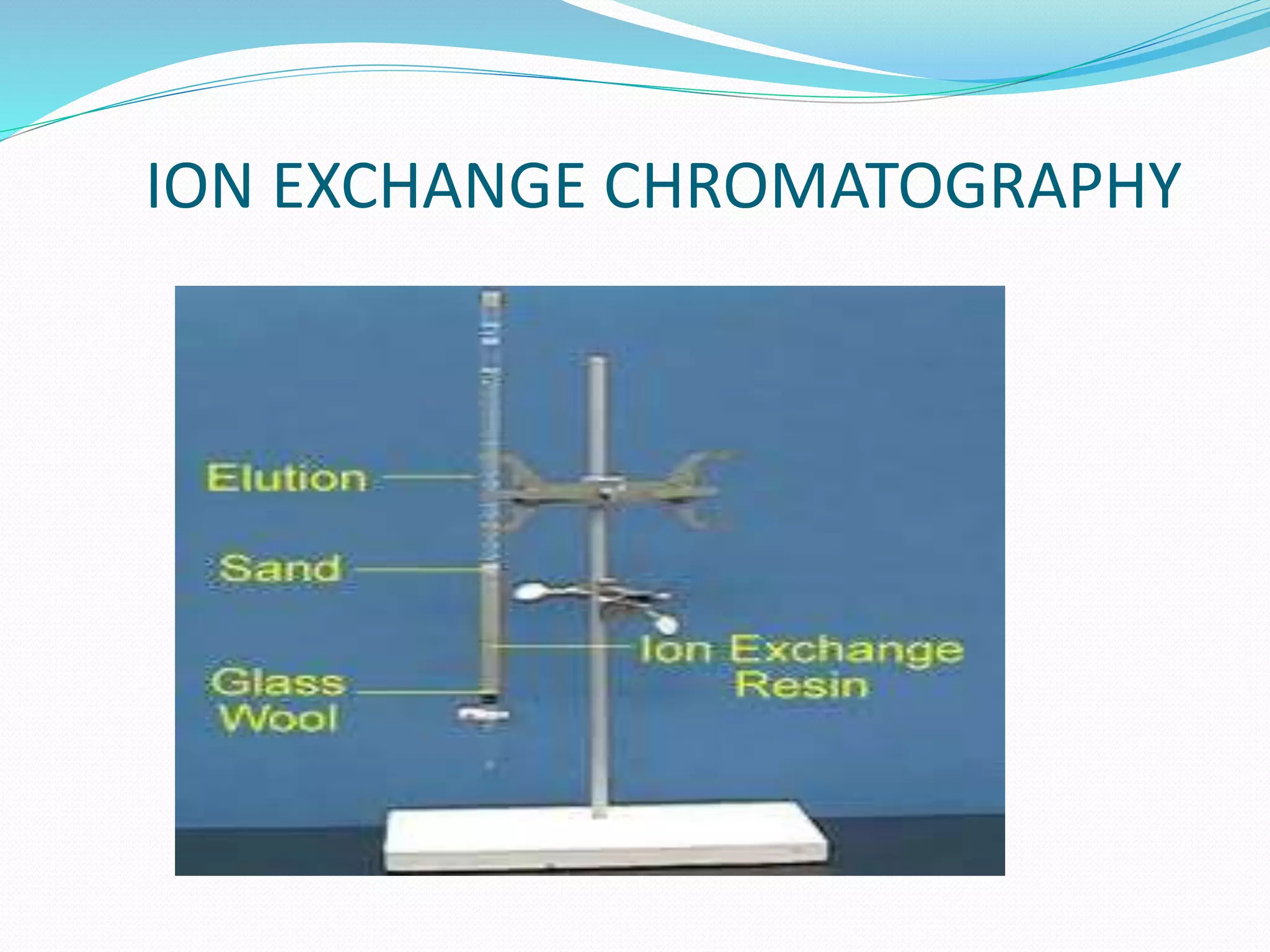
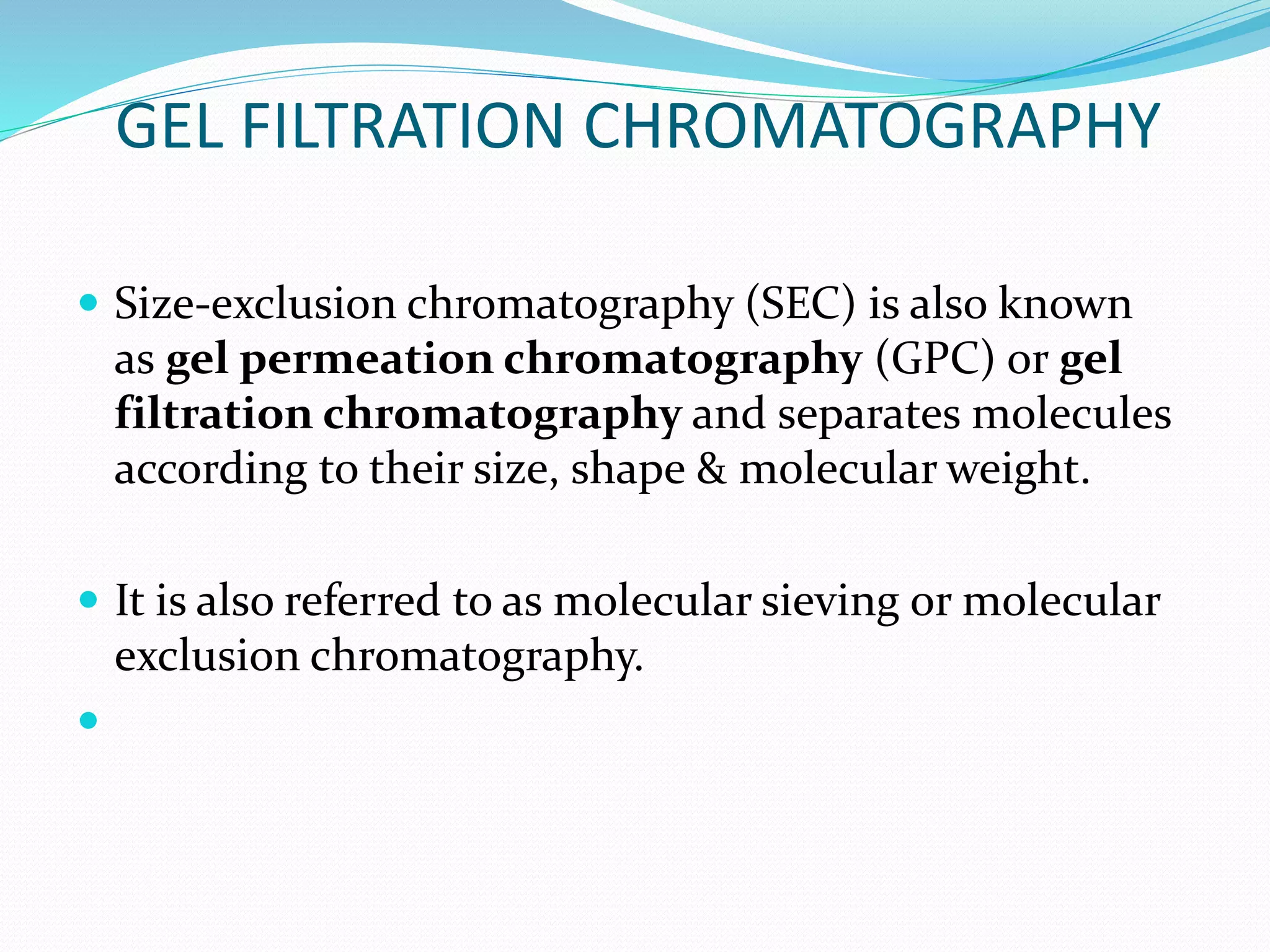
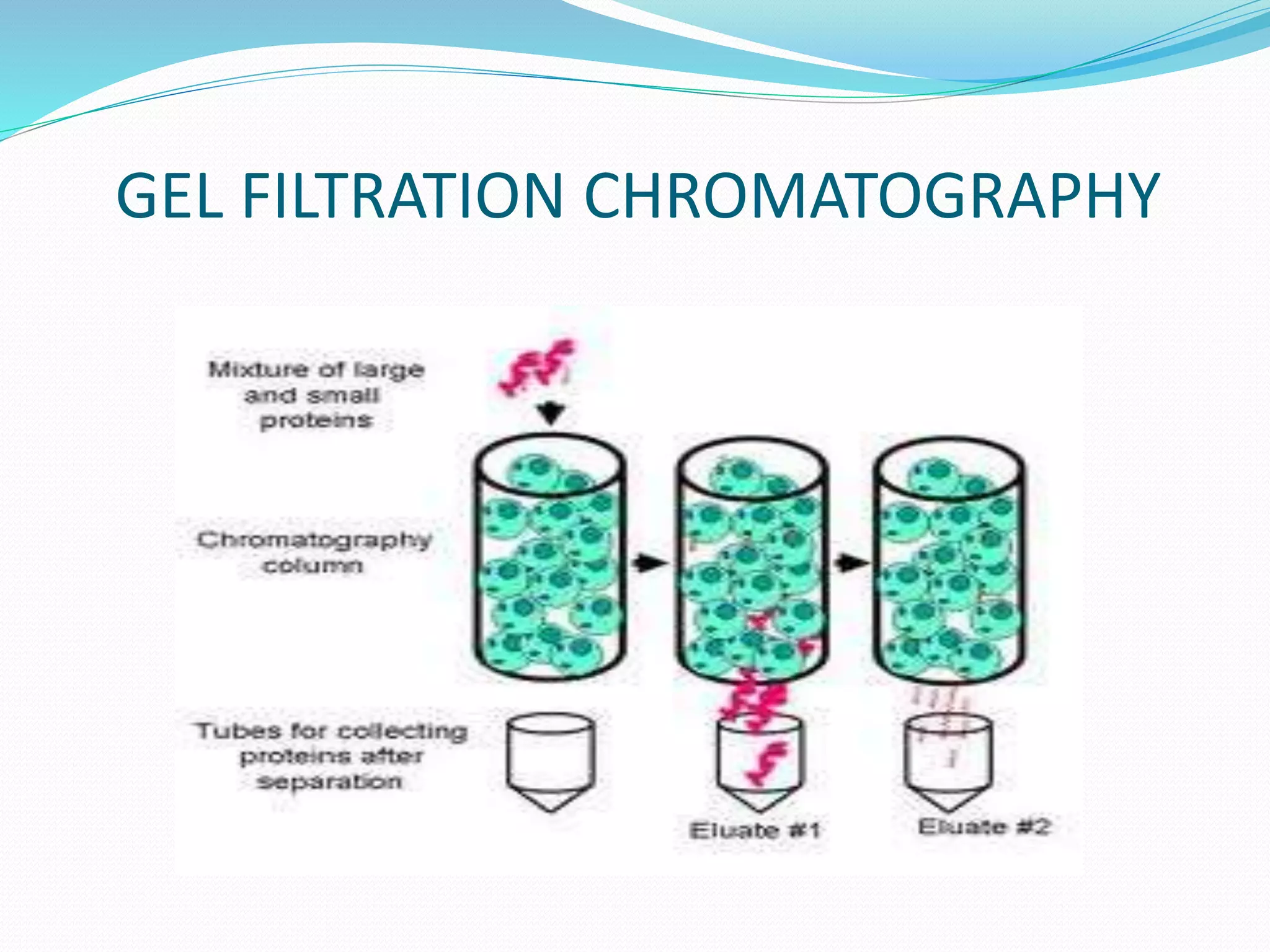
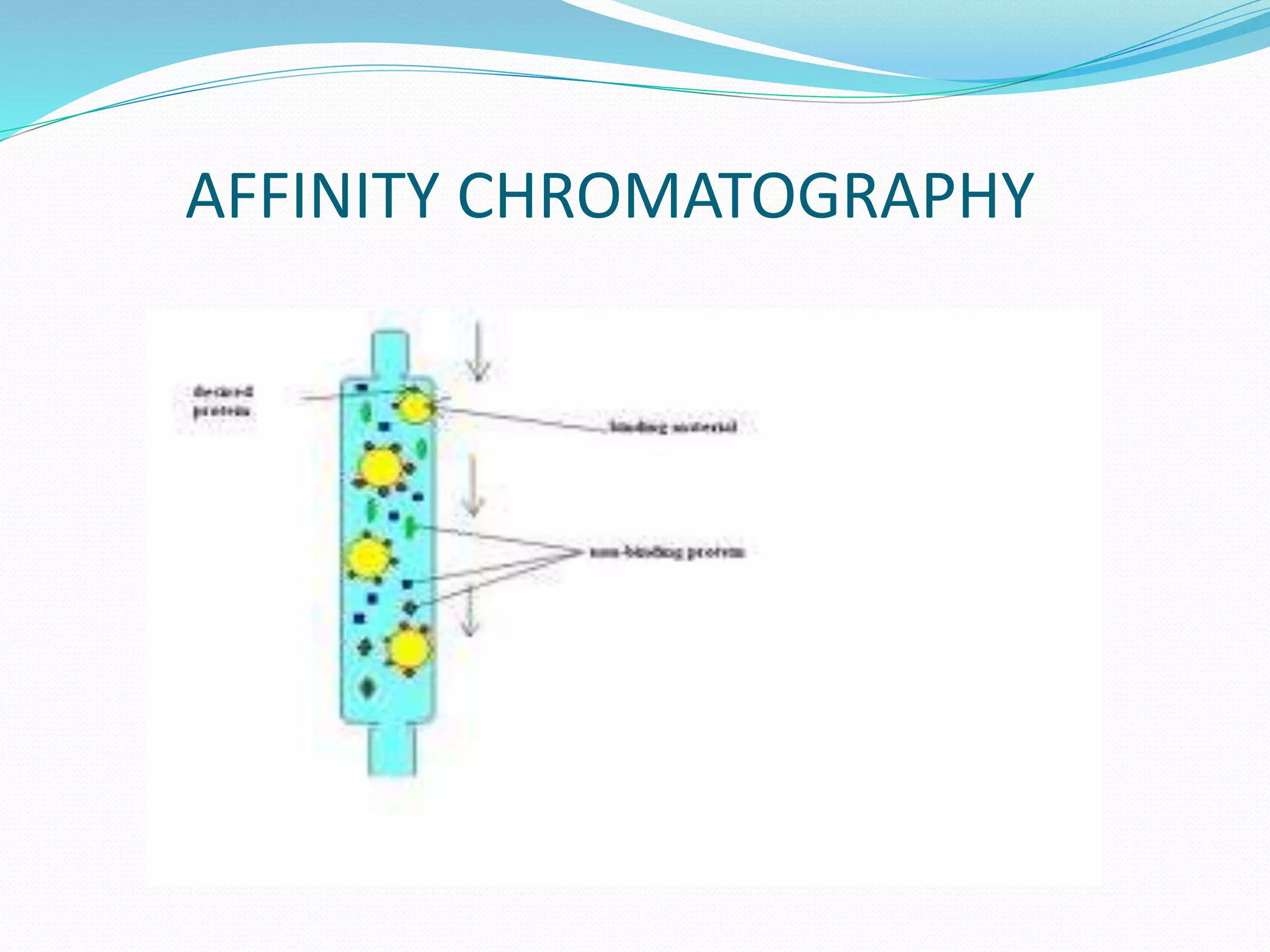
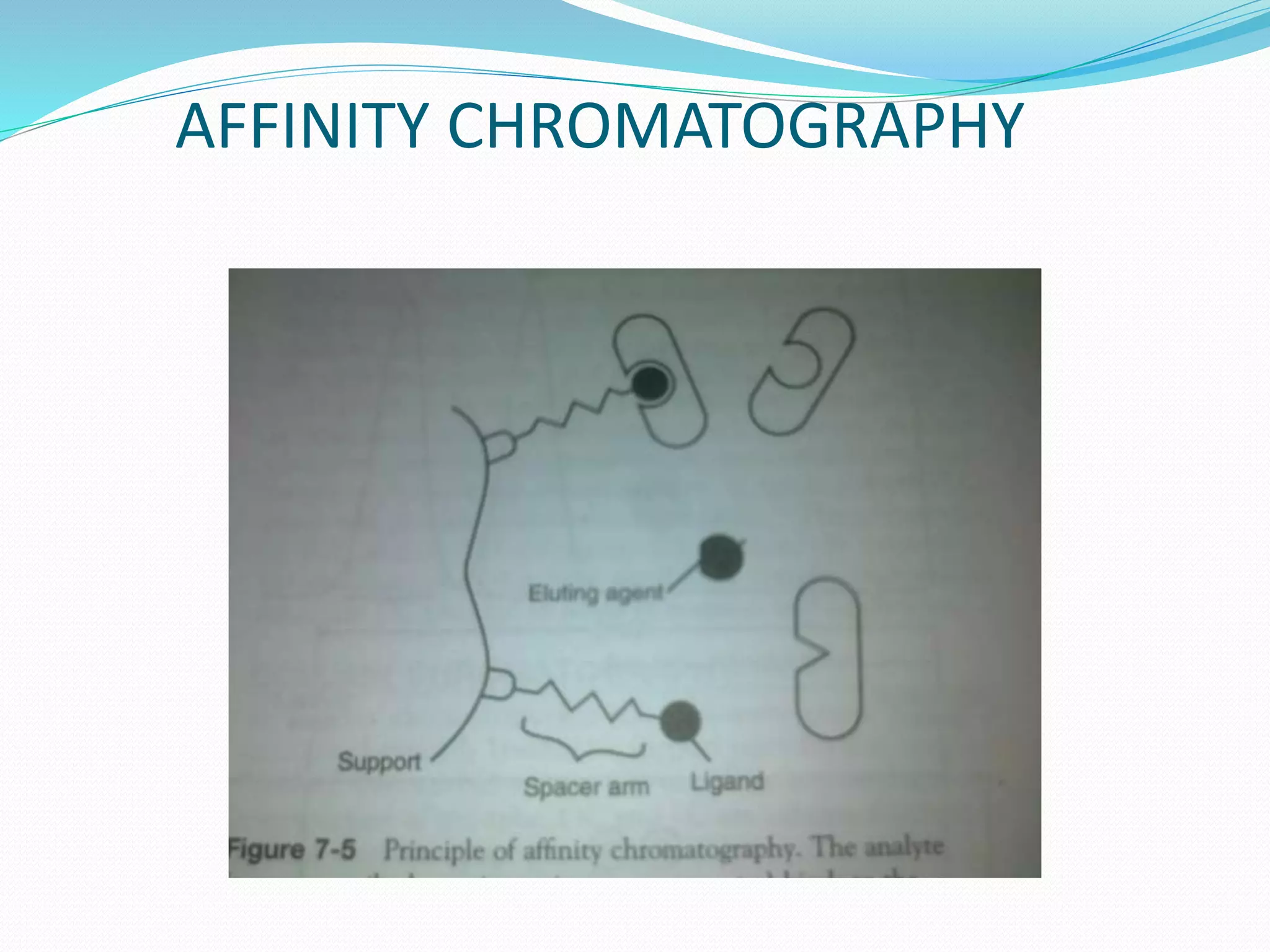
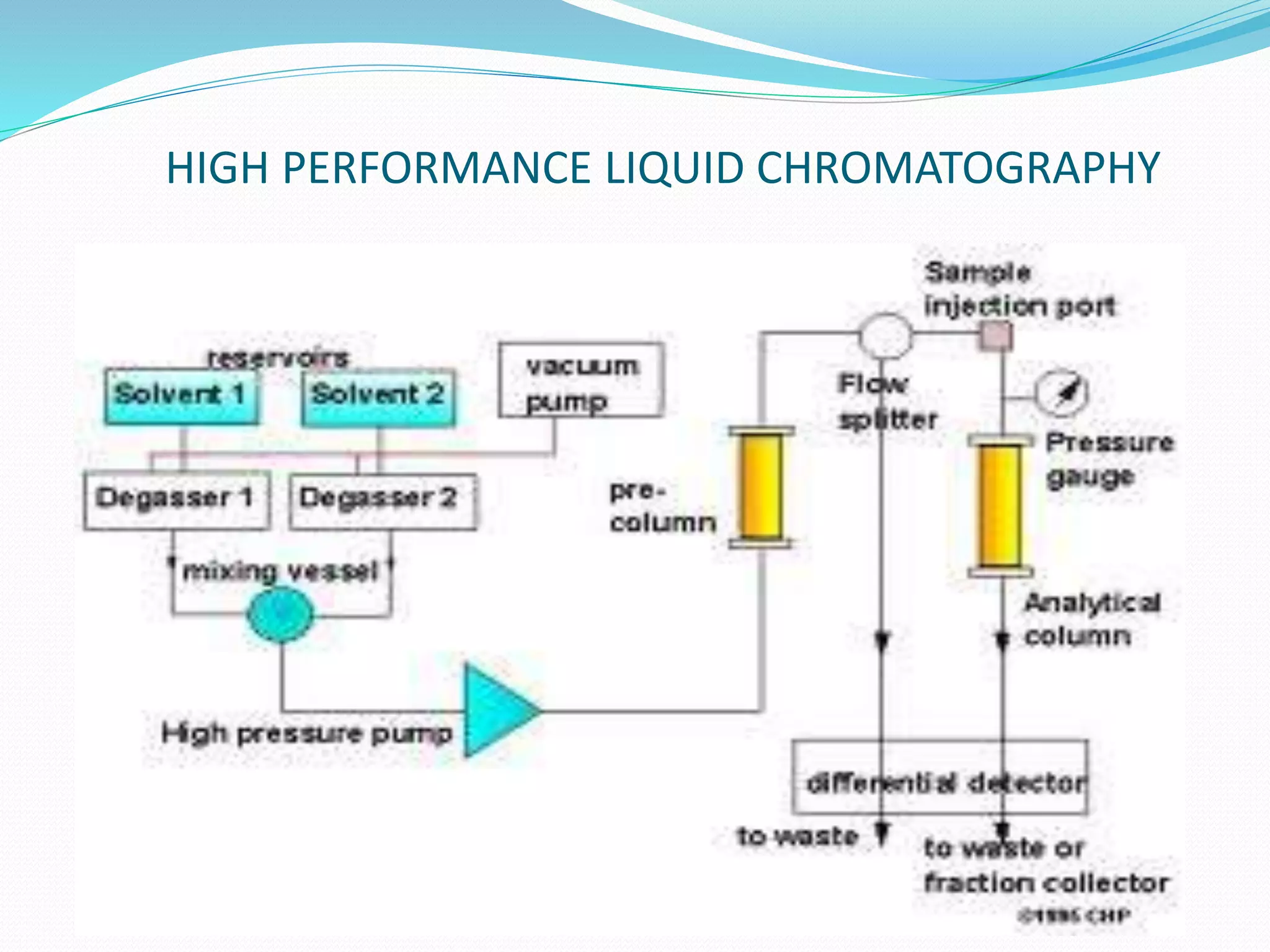
Chromatography is a technique used to separate mixtures based on how their components interact with both a mobile and stationary phase. It was first developed in 1900 by Russian scientist Mikhail Tsvet to separate plant pigments. There are several types of chromatography that differ based on the phases used, including paper chromatography, thin layer chromatography, gas chromatography, ion exchange chromatography, gel filtration chromatography, and affinity chromatography. High performance liquid chromatography is a modern technique that uses small particle sizes and high pressure to improve separation efficiency.