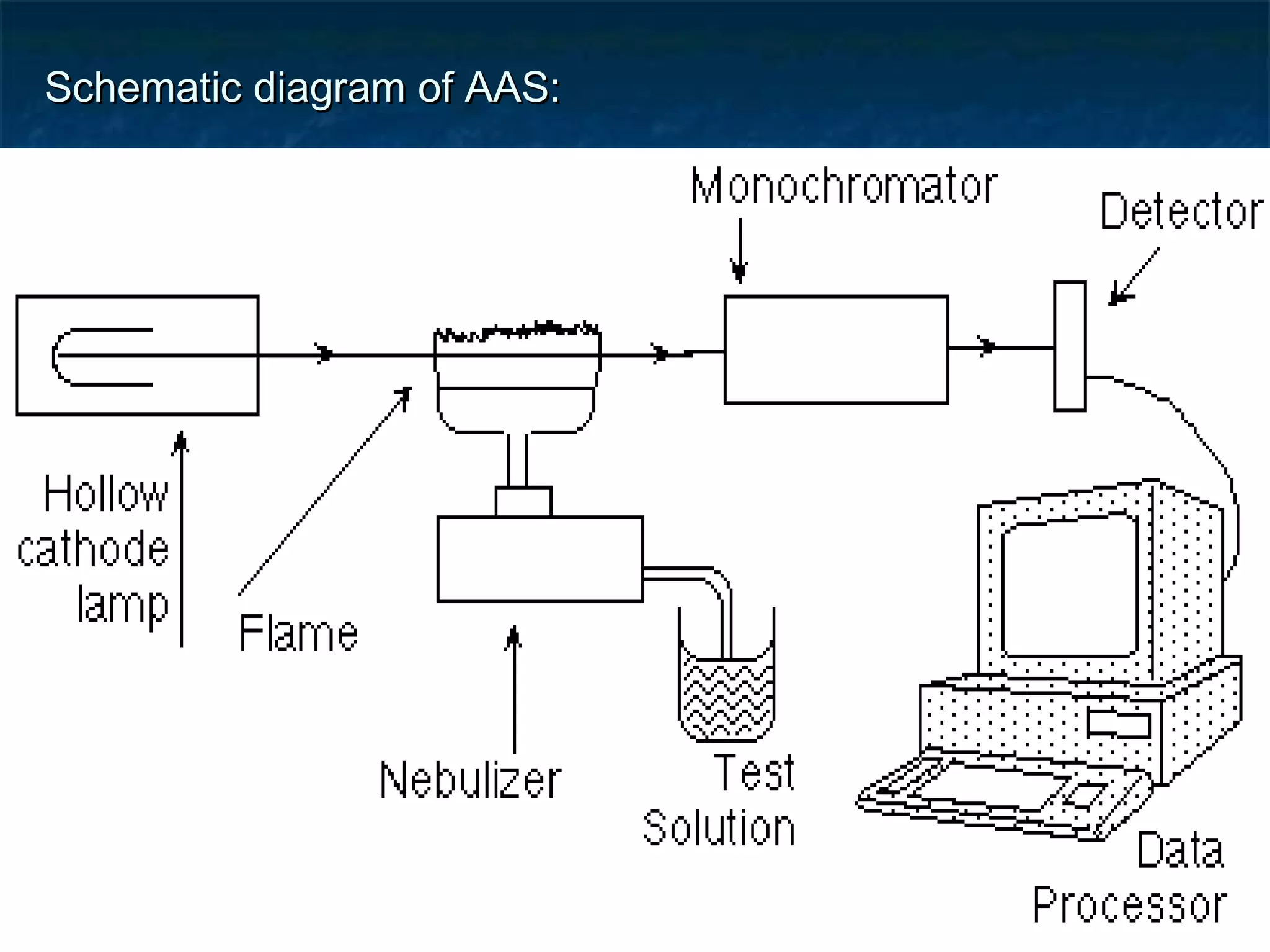
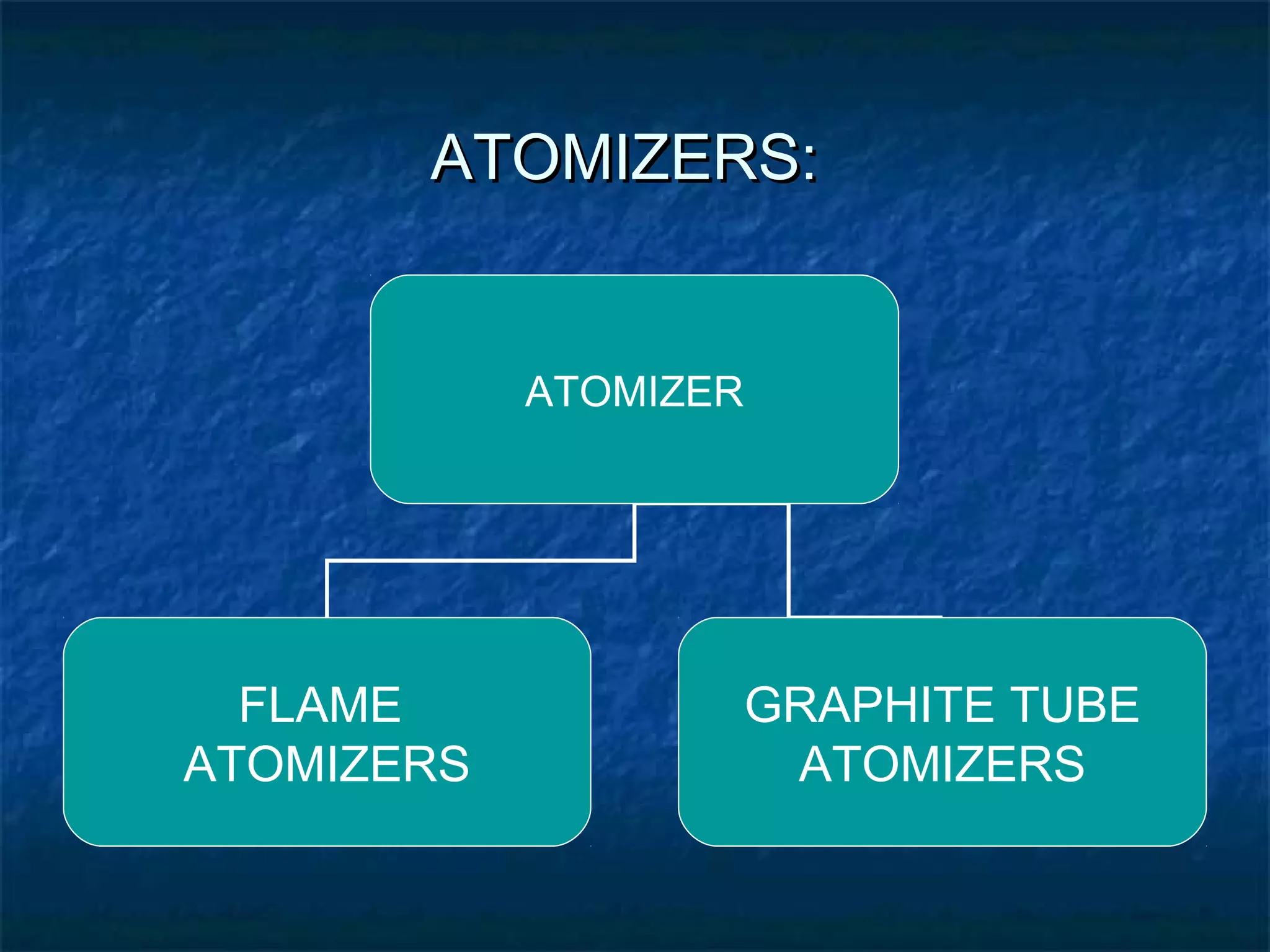
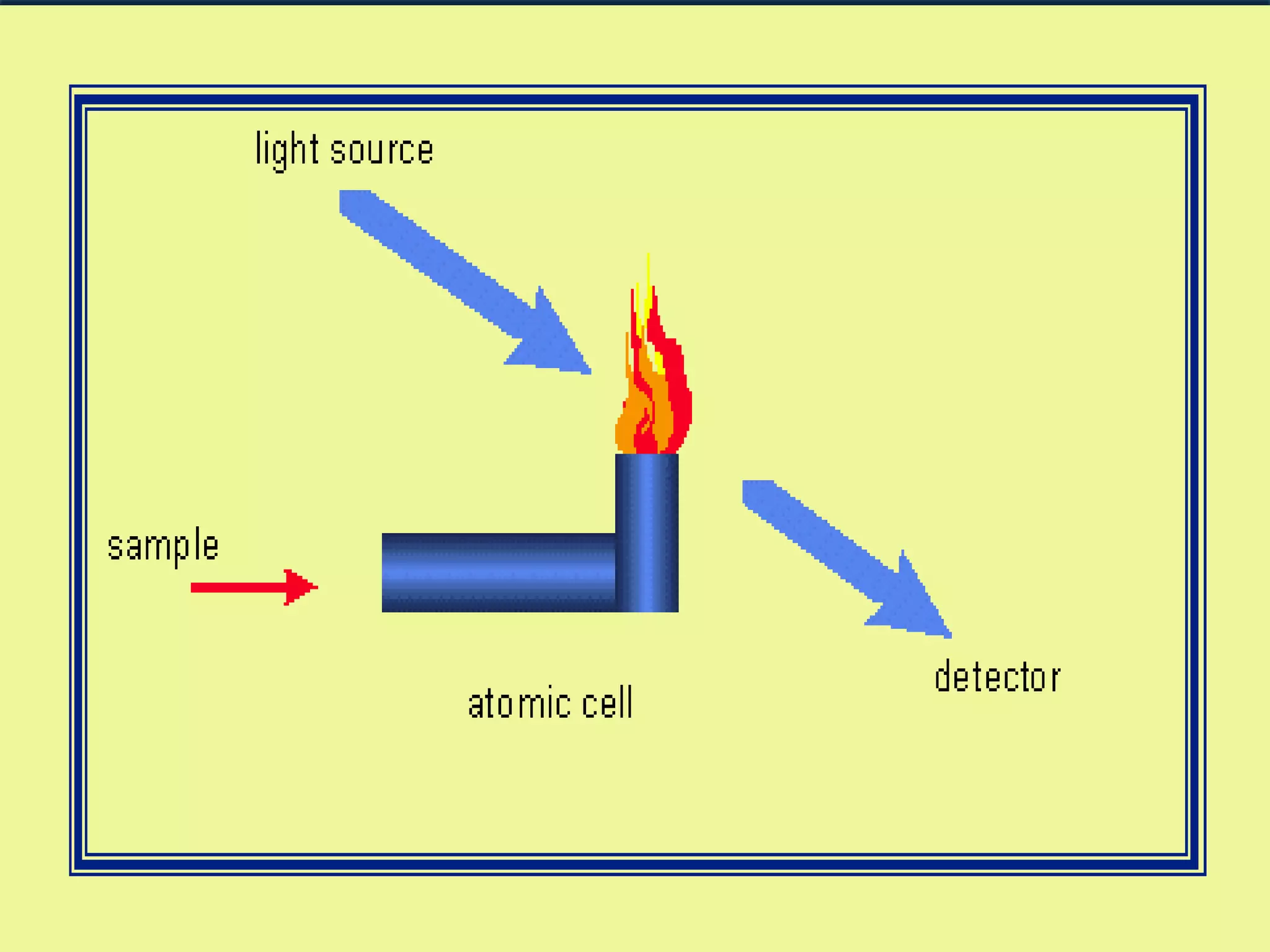
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy uses the principle that free atoms generated from a sample can absorb radiation at specific frequencies, allowing the technique to quantify the concentration of various metals and metalloids present. The sample is atomized using a flame or graphite furnace and exposed to light from a hollow cathode lamp, with absorption measured to generate calibration curves and determine unknown concentrations. AAS is a common analytical technique used across various fields like environmental analysis, food testing, and pharmaceutical applications.