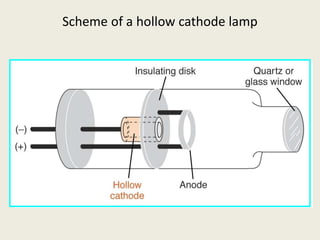
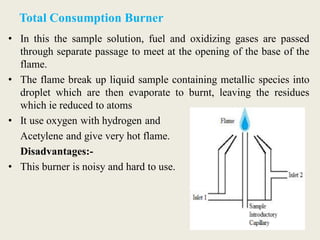
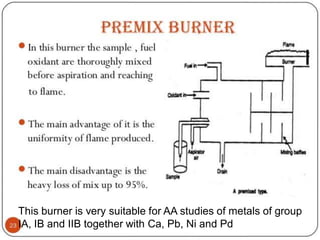
Atomic absorption spectroscopy and atomic emission spectroscopy are analytical techniques used to determine the concentration of metallic elements in solutions by measuring the absorption or emission of light from ground state and excited state atoms. Both techniques involve atomizing the sample using a flame or graphite furnace and using a light source and monochromator to detect specific elemental absorption or emission spectra, with the main difference being that atomic absorption relies on light absorption by ground state atoms while atomic emission detects light emitted from excited atoms. These techniques are commonly used for trace metal analysis in applications such as environmental monitoring, clinical analysis, and pharmaceutical and food analysis.