Atomic absorption spectroscopy is a common technique for detecting metals in samples. It works by atomizing the sample and measuring the absorption of light at specific wavelengths by the atomic vapor. The concentration of metals in the sample can then be determined from a calibration curve. Key components of atomic absorption spectroscopy systems include a hollow cathode lamp radiation source, a nebulizer to create an aerosol of the sample, an atomizer such as a flame or graphite furnace to vaporize the sample, a monochromator to select the desired wavelength, and a detector to measure light absorption. Atomic absorption spectroscopy has various applications including environmental analysis, food and water quality testing, clinical analysis, and more.






















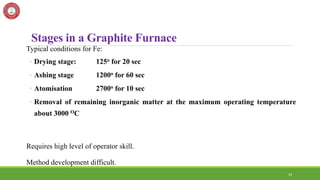









![33
CONCLUSION
One of the most important technique in quantitative analysis
It is based on the absorption of radiation
Measurements could be done at very sensitivity levels
It’s widely used method
The preparation of the sample is usually simple and rapid
Advantages
High sensitivity [10--10 g (flame), 10-14 g (non-flame)]
Good accuracy (Relative error 0.1 ~ 0.5 % )
High selectivity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atomicabsorptionspectroscopyfinal-231010213722-c3669f0b/85/Atomic-Absorption-Spectroscopy-Final-pptx-33-320.jpg)

