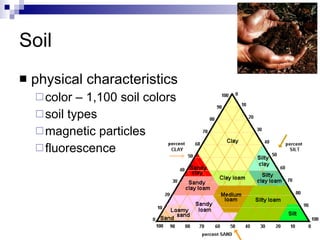
Soil analysis can link suspects to crime scenes by comparing soil on their clothing or vehicles to the soil at the crime scene. Physical characteristics like plant and animal materials or artificial debris are examined microscopically. Chemical characteristics like pH levels and minerals are also analyzed. To determine if soil samples have a common origin, analysts consider multiple comparable features and how frequently they occur. Proper training in geology is important since there are over 2,200 minerals that can be present in soil.