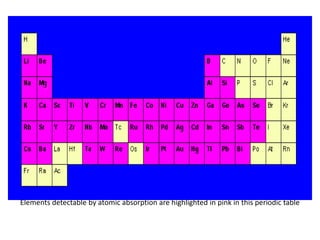
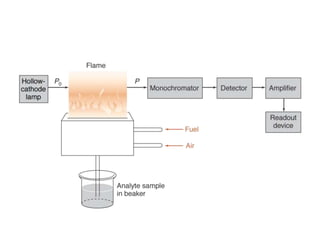
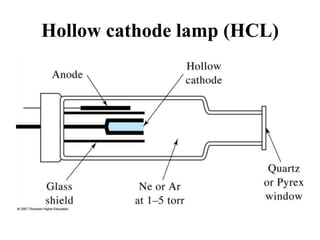
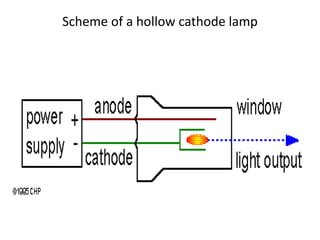
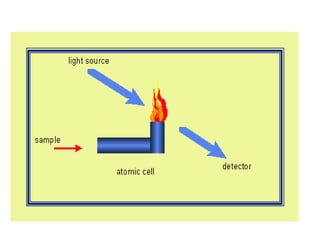
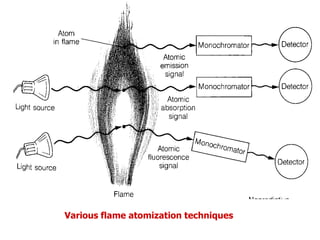
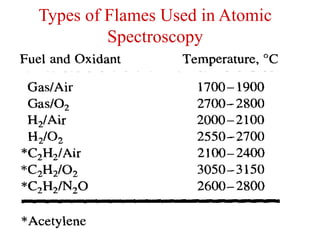
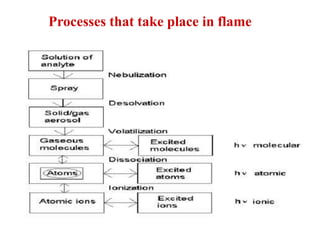
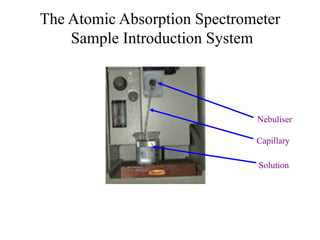
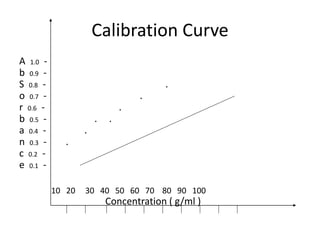
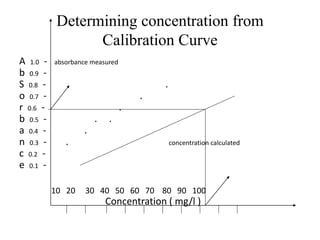
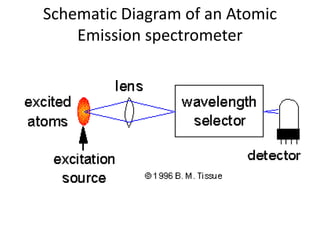
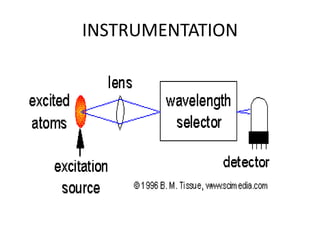
Atomic absorption spectroscopy is an analytical technique that measures the concentration of elements by using the absorption of light by ground state atoms. It works by vaporizing samples using a flame or furnace and passing light from a hollow cathode lamp of the element of interest through the vapor. The amount of light absorbed is measured and the concentration is determined using a calibration curve. Atomic emission spectroscopy similarly uses high temperatures to excite sample atoms, which then emit light of element-specific wavelengths that is measured to determine concentration. Both techniques use similar instrumentation including a light source, atomizer, monochromator, and detector.