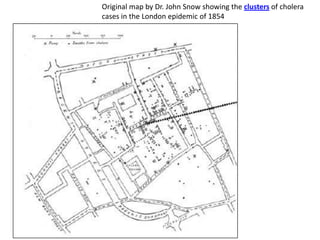
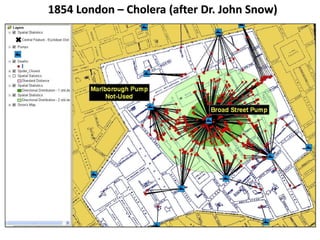
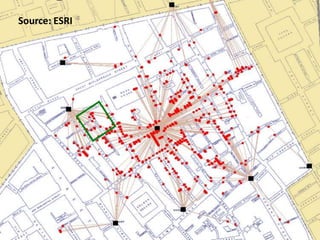
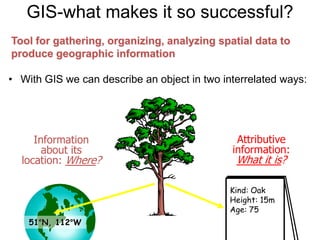
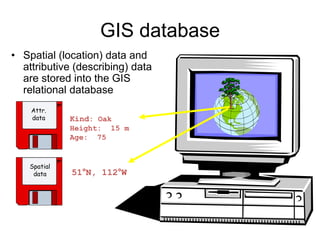
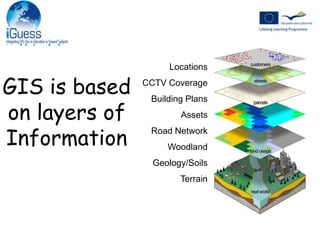
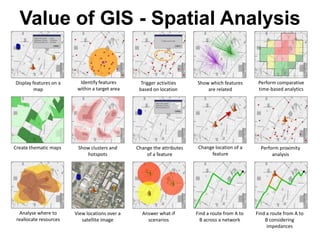
Geographical Information Systems (GIS) are tools that gather, organize, and analyze spatial data, linking digital maps with data about locations. The document highlights the applications of GIS in various fields such as healthcare, engineering, and urban planning, showcasing its role in solving problems like the 1854 cholera epidemic. By using layers of information, GIS allows for spatial analysis, resource allocation, and the creation of thematic maps.