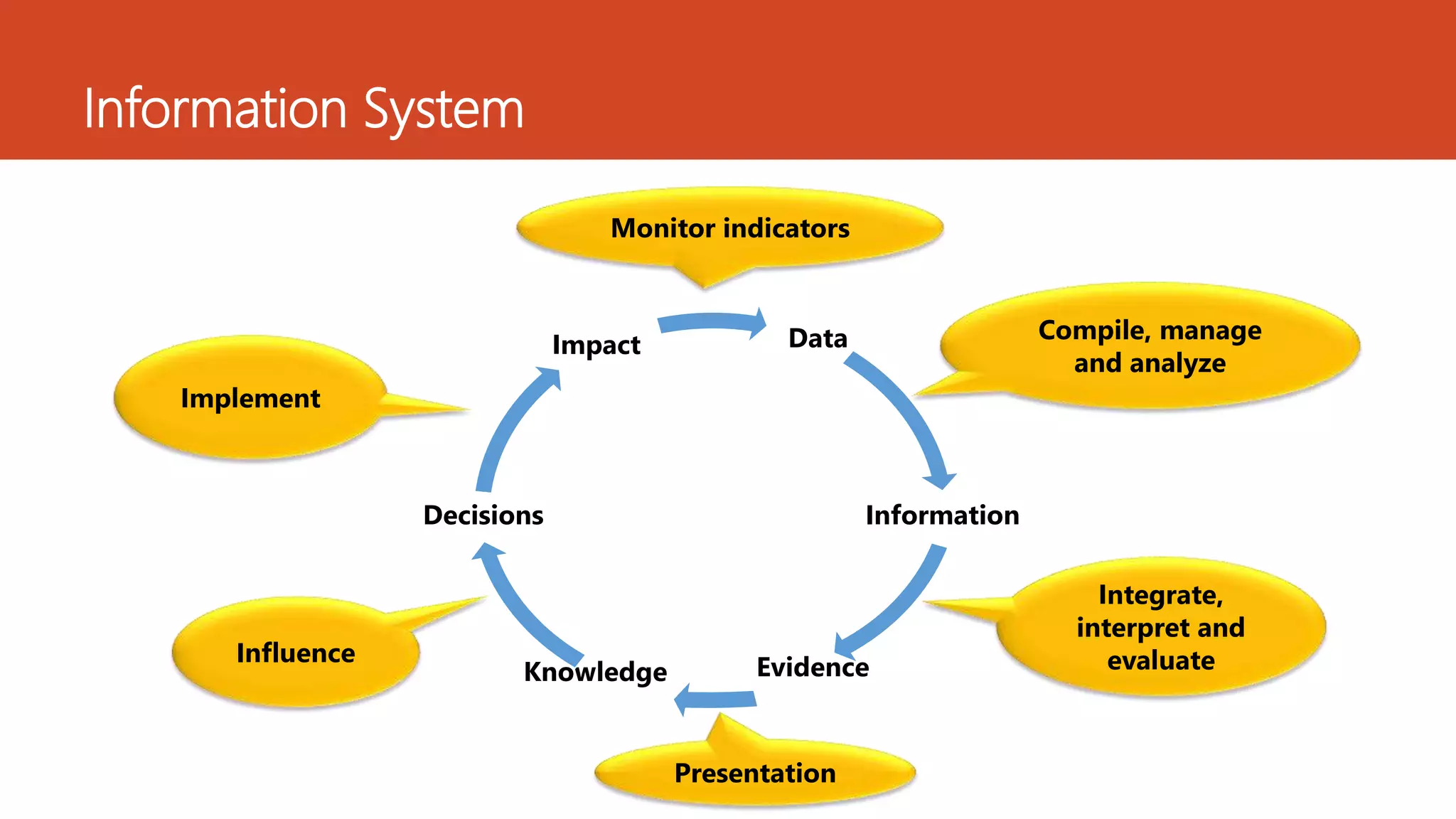
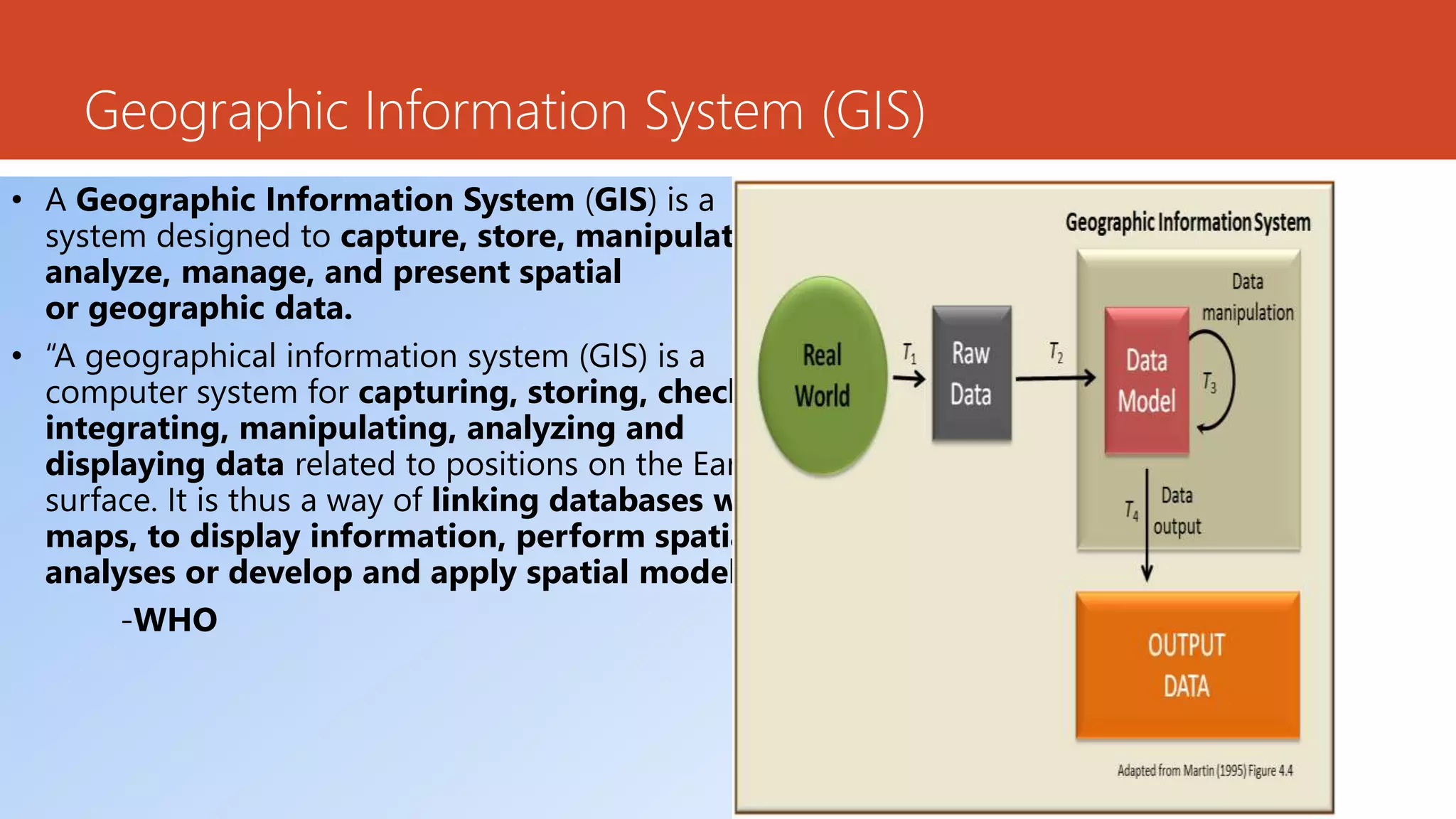
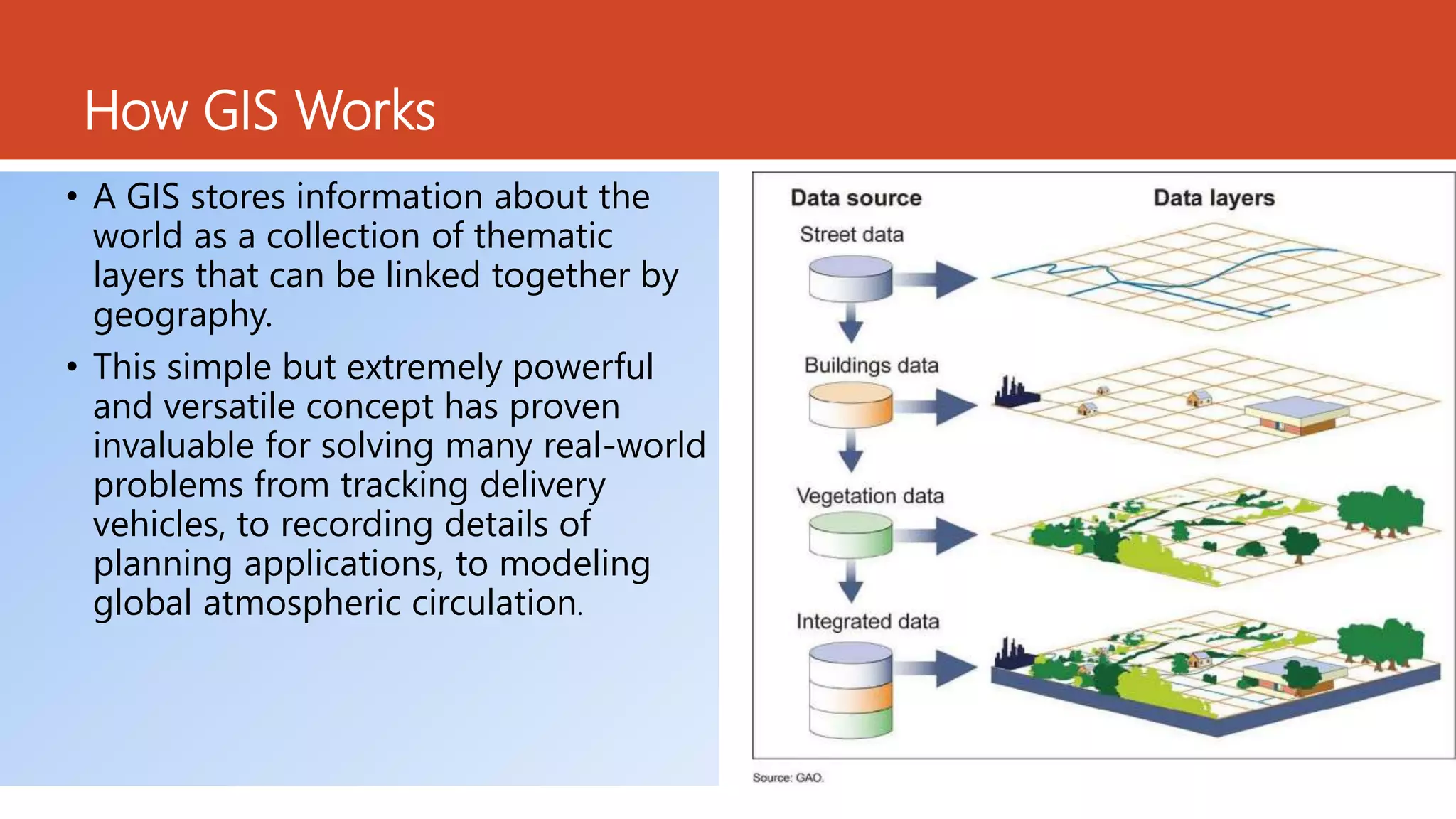
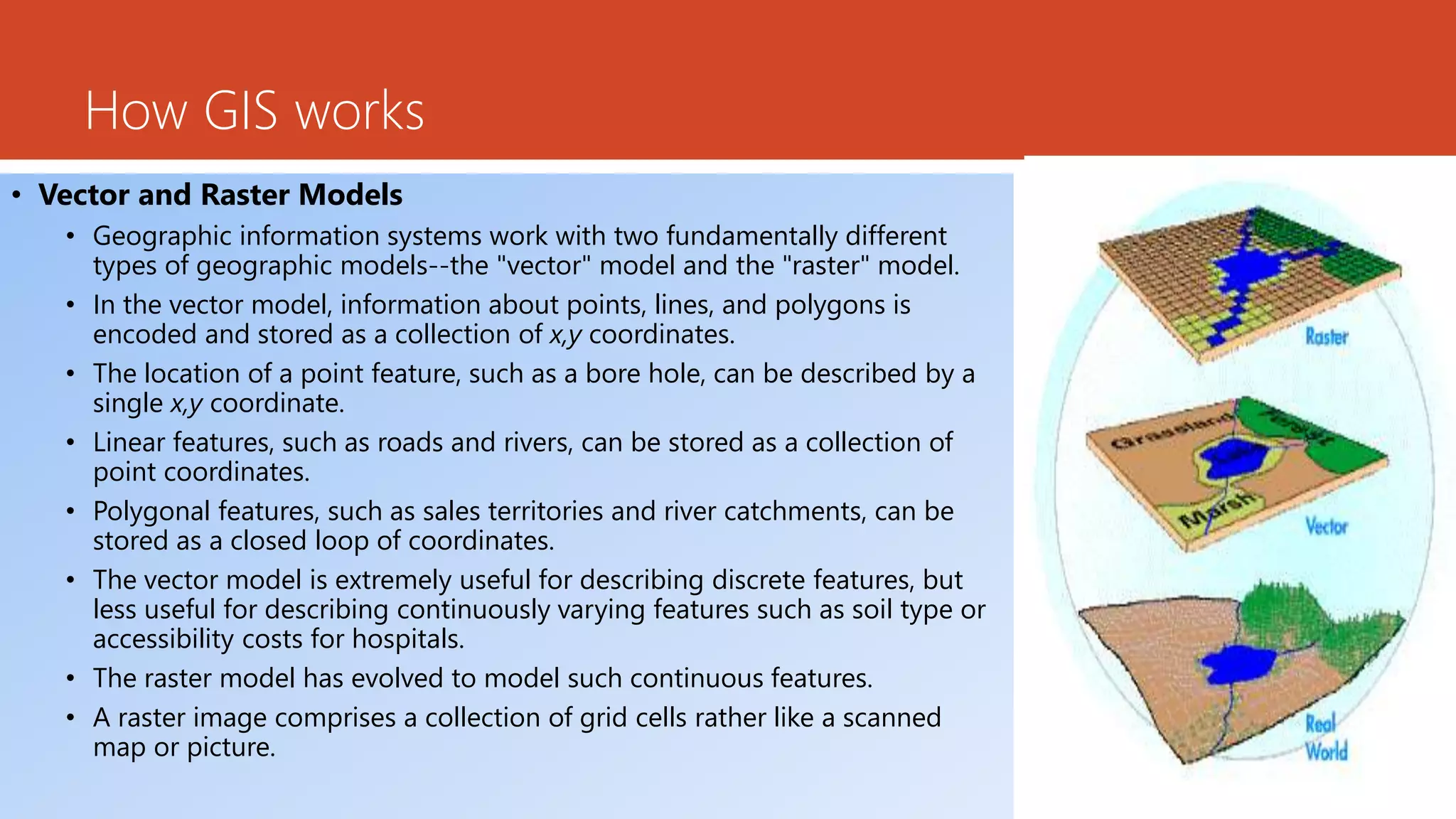
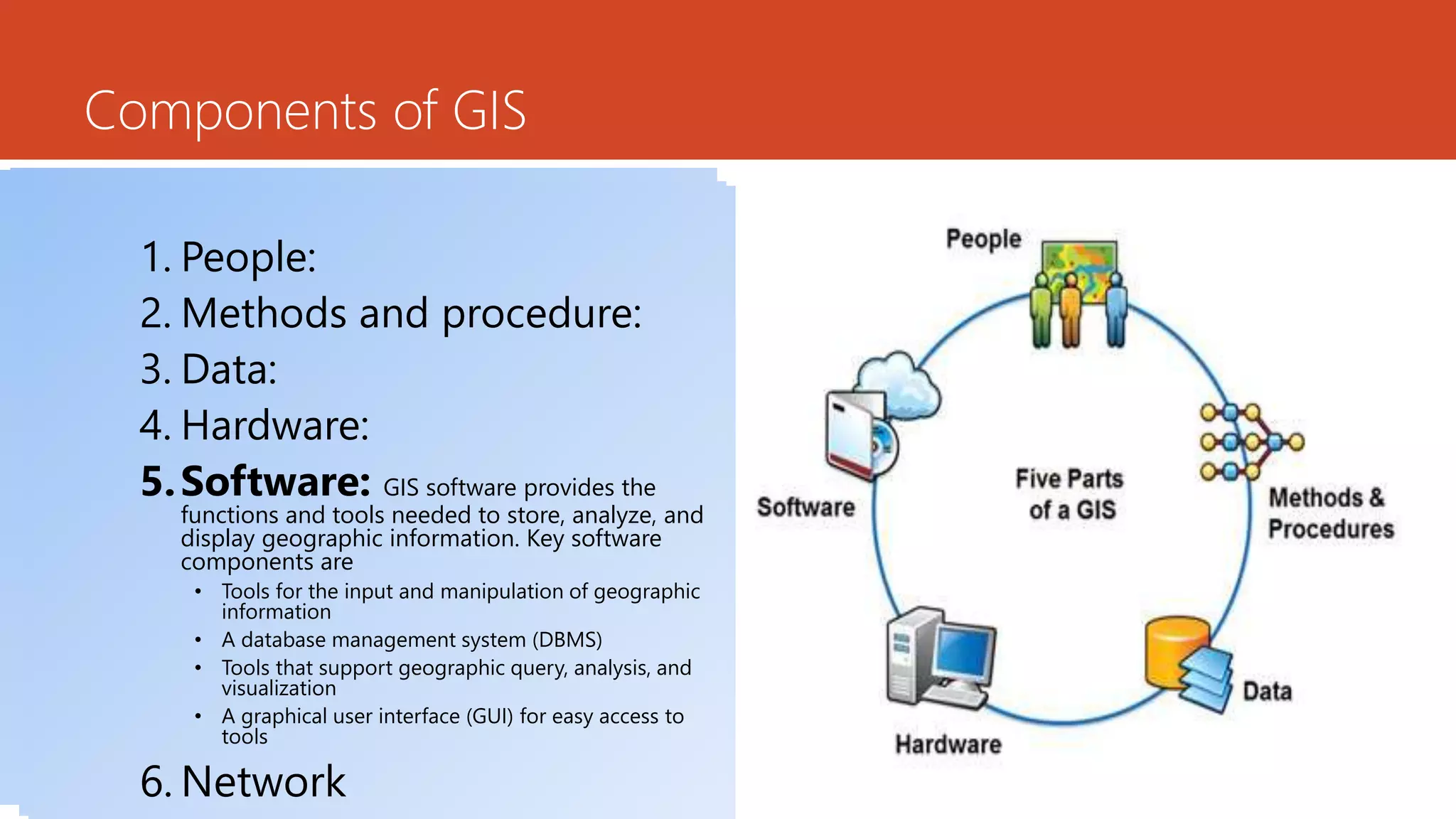
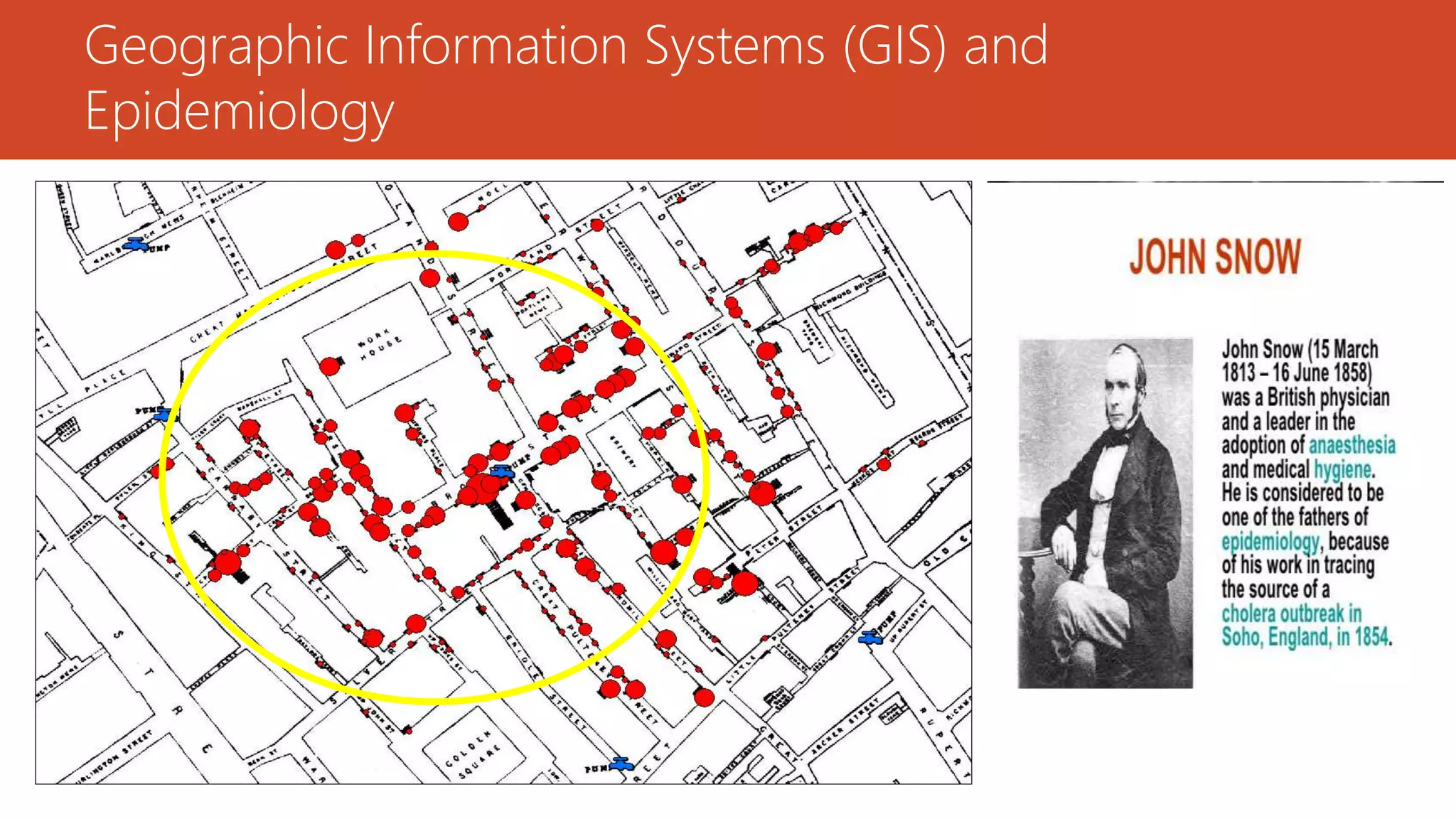
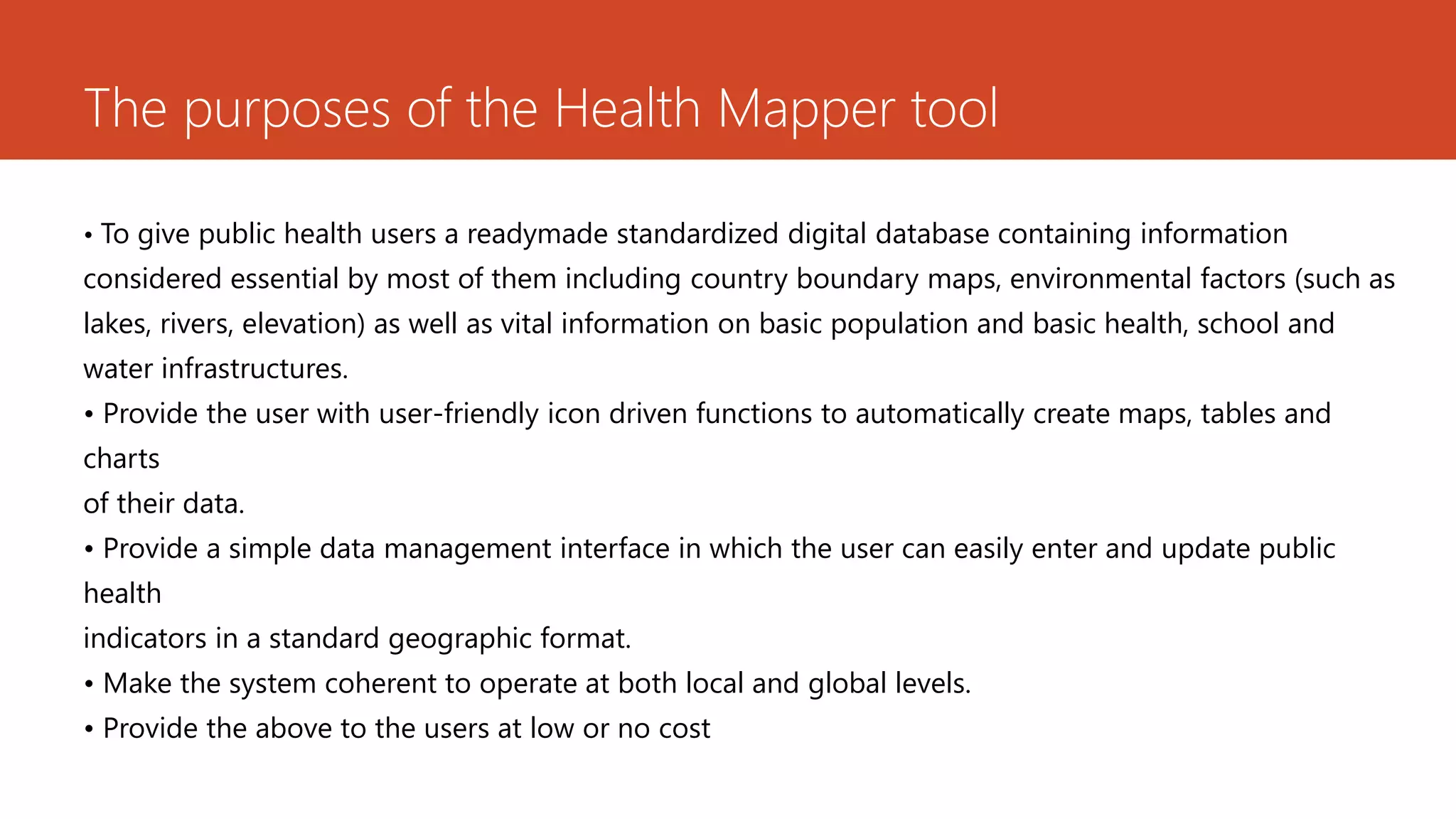
The document discusses the integration of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) with epidemiology, highlighting how GIS can transform raw data into valuable information for health decision-making and disease analysis. It outlines the essential components of GIS, its applications in public health such as disease surveillance, risk analysis, and health access planning, and provides examples of its use in monitoring various diseases. Additionally, the document describes tools like the Health Mapper and the Global Health Atlas developed by WHO to enhance public health initiatives through mapping and data visualization.