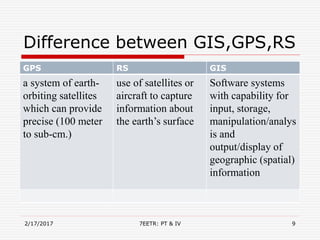
The document discusses Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and presents information on:
- The history and definition of GIS and how it allows users to integrate and analyze spatial data layers.
- Types of GIS software including desktop GIS like QGIS, web-based GIS, and geobrowsers like Google Earth.
- Features of GIS like handling large datasets, data integration and unique analysis methods.
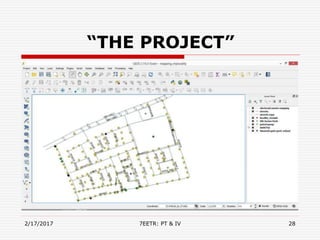
- An example project mapping electrical assets in India using tools like QGIS, Google Earth, and the MAPinr app.