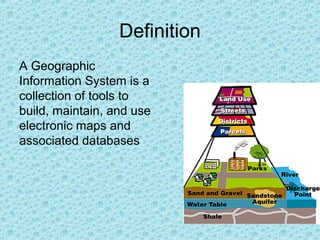
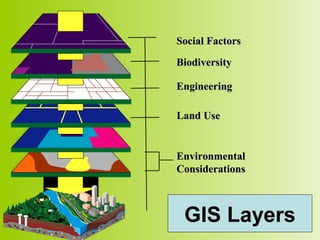
Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer system for capturing, storing, querying, analyzing, and displaying geospatial data. A GIS combines spatial data, like location coordinates, with attribute data that describes features. Some key components of a GIS include GIS software, computer hardware, data, users, and infrastructure. GIS allows users to explore data in both conventional and geographic ways, enabling holistic and location-based analysis. Typical applications of GIS include environmental assessments, land use mapping, health care analysis, natural resource management, urban planning, and more.