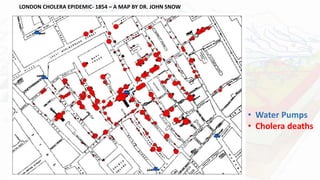
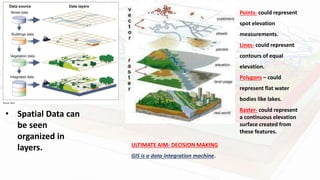
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are computer systems for capturing, storing, analyzing and displaying spatial data. GIS allows users to visualize, question, interpret patterns in spatial data and relationships. A key example is John Snow's 1854 map of the London cholera epidemic, which linked outbreaks to specific water pumps. GIS integrates data from various sources and stores it in layers that can be analyzed and overlaid, such as points, lines, polygons and rasters. Applications of GIS in plant taxonomy include identifying suitable locations for crop expansion by comparing climatic and soil data, mapping and monitoring plant species distributions for conservation efforts, and designing on-farm conservation sites.