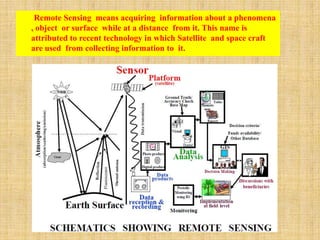
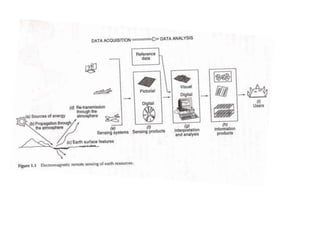
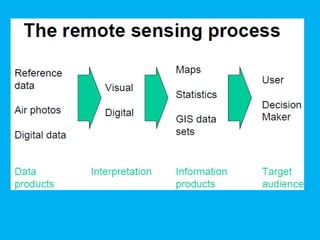
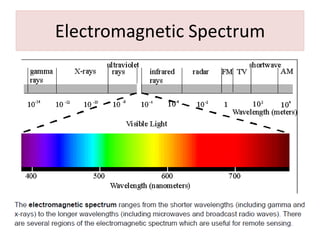
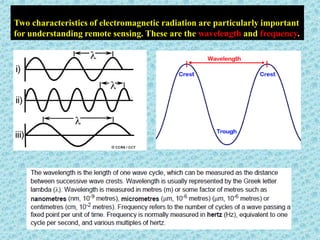
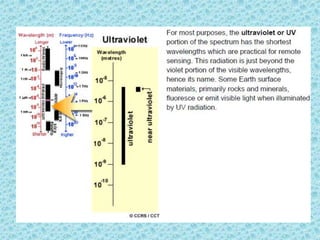
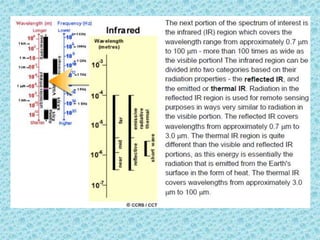
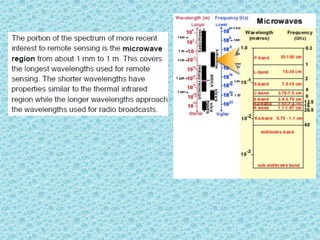
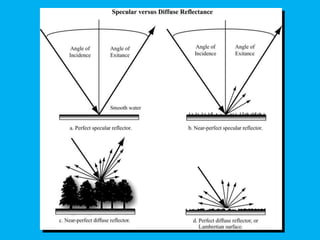
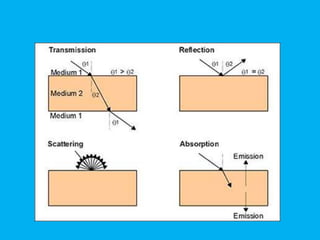
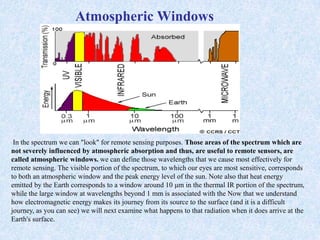
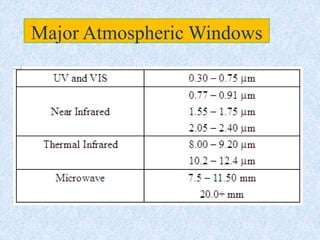
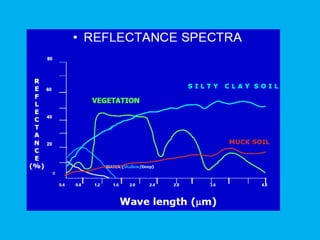
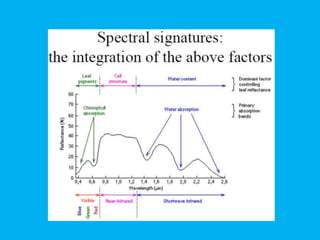
This document provides an overview of the basics of remote sensing. It defines remote sensing as acquiring information about an object without direct contact. It discusses key components of the remote sensing process including data acquisition, the electromagnetic spectrum, atmospheric interactions, spectral signatures, and satellite platforms and orbits. Remote sensing draws from many areas and plays an important role in monitoring the Earth through satellite imagery.