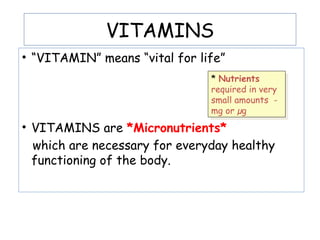
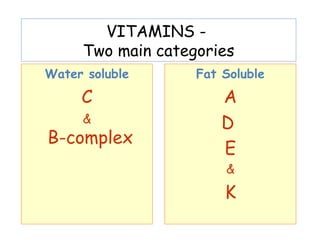
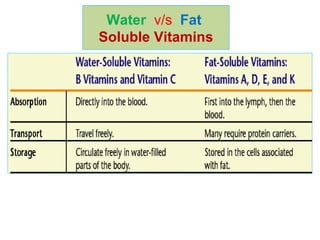
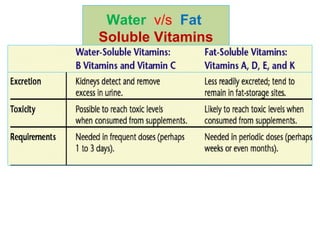
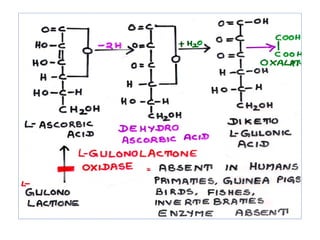
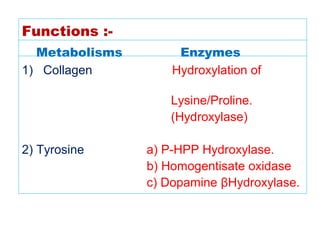
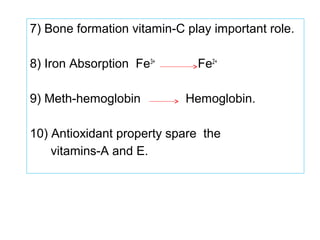
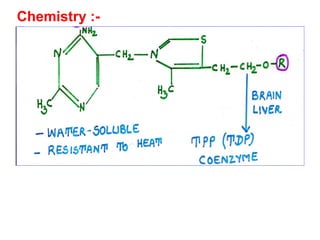
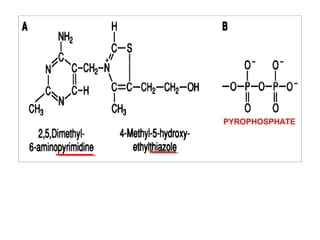
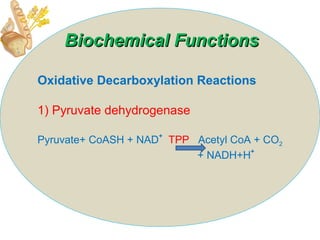
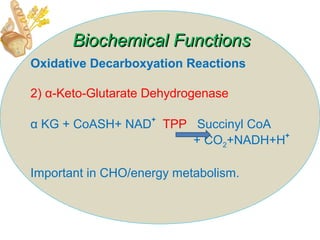
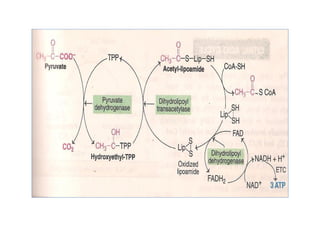
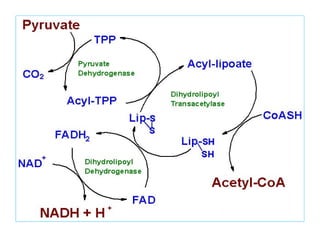
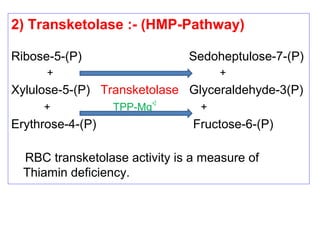
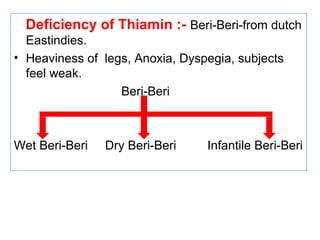
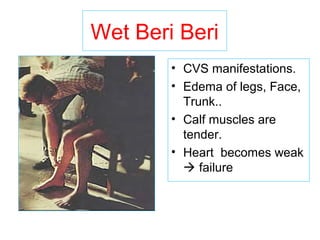
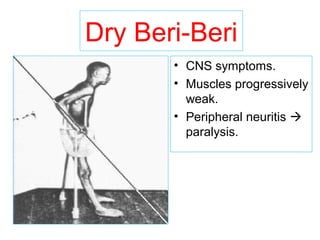
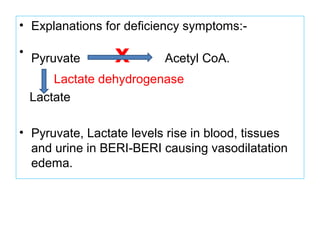
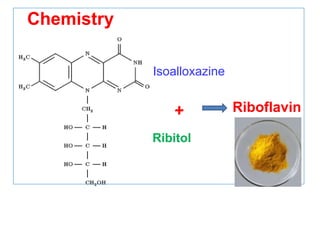
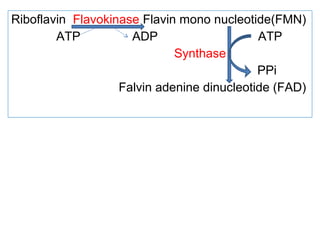
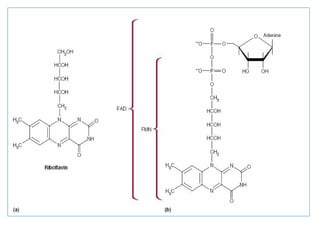
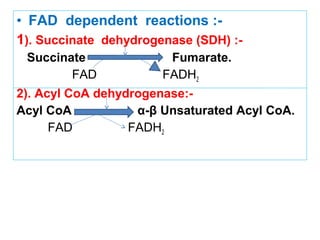
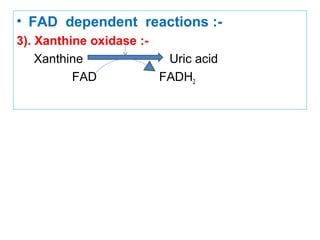
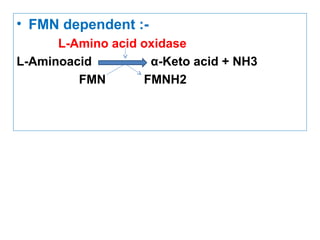
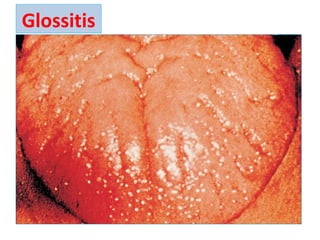
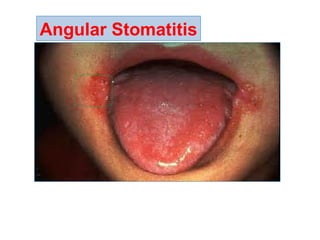
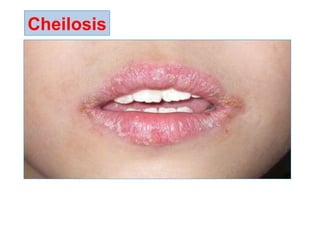
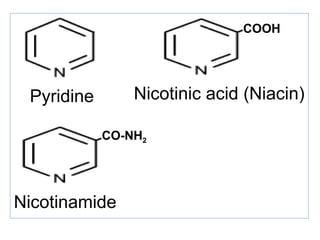
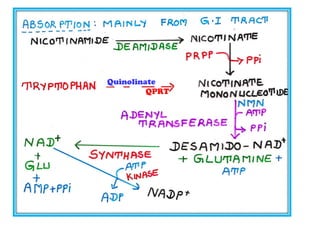
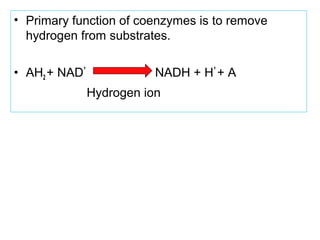
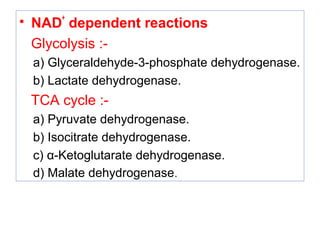
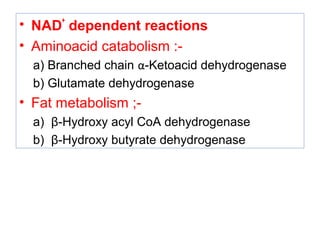
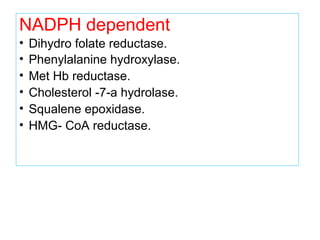
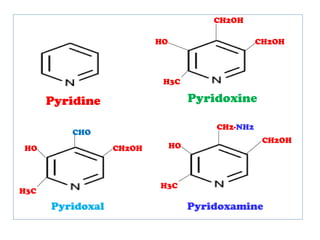
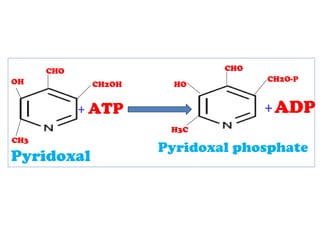
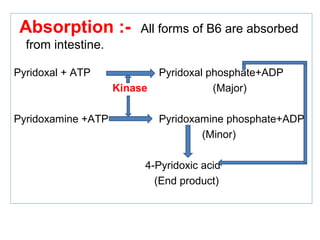
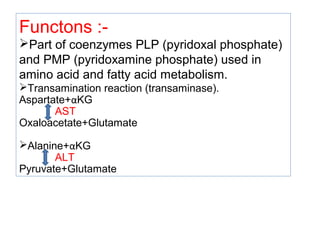
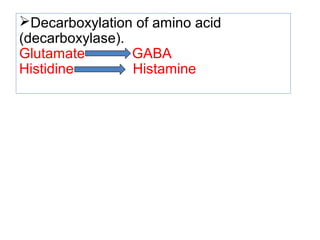
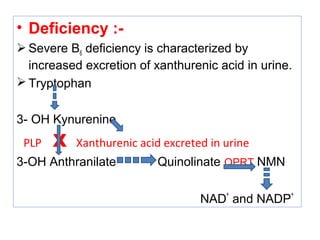
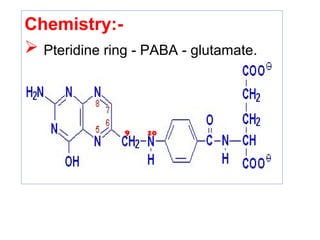
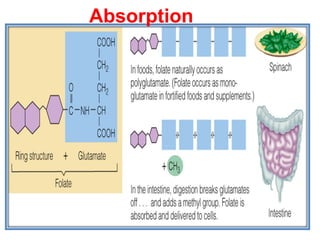
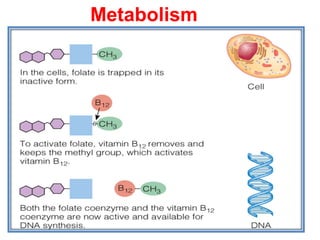
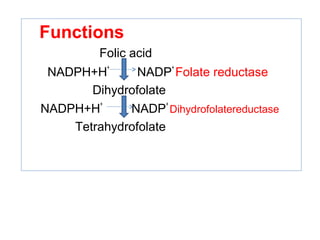
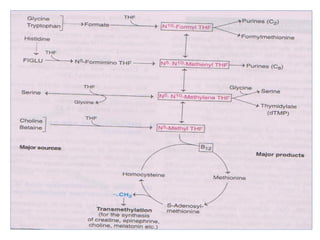
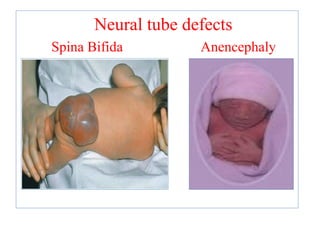
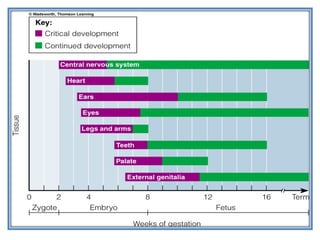
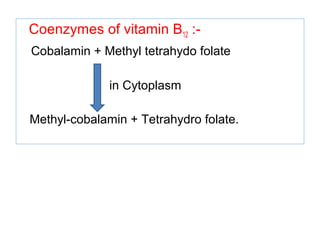
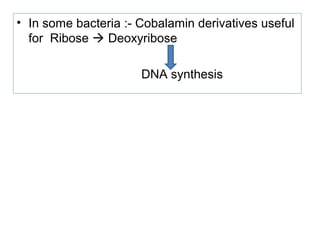
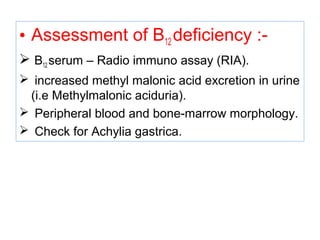
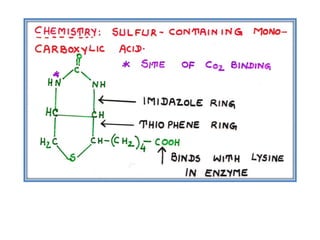
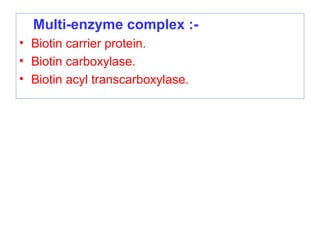
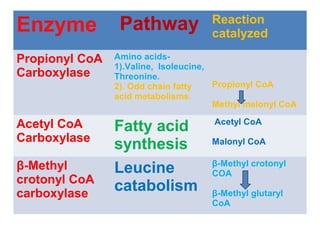
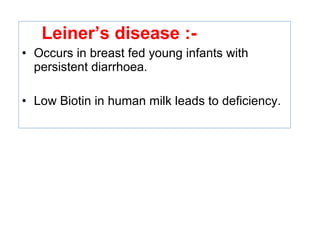
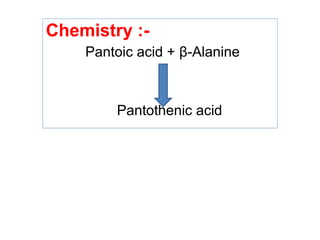
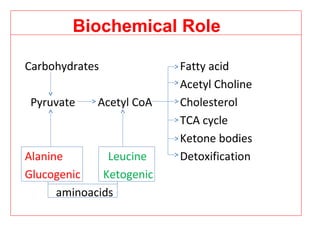
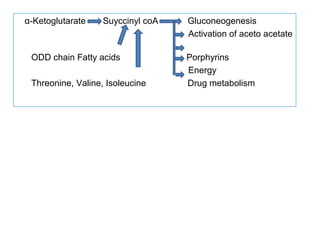
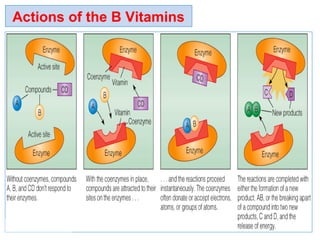
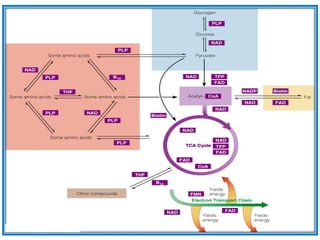
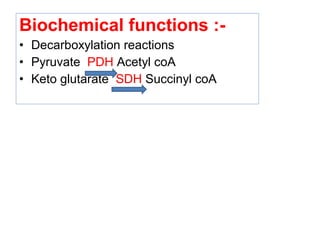
The document provides an in-depth overview of water-soluble vitamins, specifically focusing on vitamins C and B-complex. It details their chemistry, functions, sources, deficiency symptoms, and recommended dietary allowances (RDA). Key vitamins covered include ascorbic acid (vitamin C), thiamin (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), and pyridoxine (B6), among others.